Whats The Lcm Of 8 And 10
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
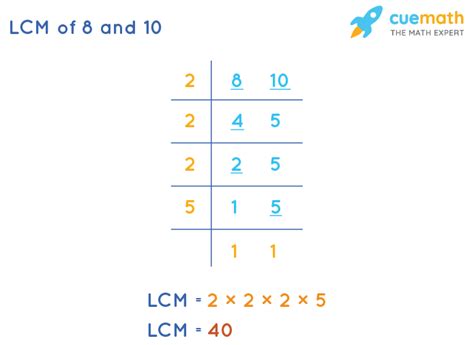
Table of Contents
- Whats The Lcm Of 8 And 10
- Table of Contents
- What's the LCM of 8 and 10? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
- Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
- Method 1: Listing Multiples
- Method 2: Prime Factorization
- Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
- Why is Understanding LCM Important?
- 1. Scheduling and Time Management:
- 2. Fraction Operations:
- 3. Music Theory:
- 4. Computer Science:
- 5. Engineering:
- Exploring Further: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
- Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Answer
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What's the LCM of 8 and 10? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and different methods for calculating it provides valuable insights into number theory and its applications. This article delves into the process of finding the LCM of 8 and 10, exploring various methods and their practical implications. We'll move beyond the simple answer and explore the broader context of LCMs, their uses in real-world problems, and how understanding them strengthens mathematical foundations.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 8 and 10, let's establish a solid understanding of what LCM actually means. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers in question as factors.
Think of it like this: imagine you have two gears with different numbers of teeth (8 and 10 in our case). The LCM represents the smallest number of rotations needed for both gears to return to their starting position simultaneously. This analogy highlights the practical applications of LCMs in various fields, from engineering and scheduling to music and computer science.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method to find the LCM is by listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. This is particularly useful for smaller numbers.
Let's list the multiples of 8 and 10:
Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 96...
Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple is 40. Therefore, the LCM of 8 and 10 is 40.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more efficient and systematic method, especially for larger numbers, involves using prime factorization. This method breaks down each number into its prime factors – the smallest prime numbers that multiply together to give the original number.
- Prime factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
To find the LCM using prime factorization, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization and multiply them together:
The prime factors are 2 and 5. The highest power of 2 is 2³ (from the factorization of 8), and the highest power of 5 is 5¹ (from the factorization of 10).
Therefore, LCM(8, 10) = 2³ x 5 = 8 x 5 = 40
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. We can use the following formula to calculate the LCM:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
First, let's find the GCD of 8 and 10. The factors of 8 are 1, 2, 4, and 8. The factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5, and 10. The greatest common factor is 2.
Now, we can apply the formula:
LCM(8, 10) = (8 x 10) / GCD(8, 10) = (80) / 2 = 40
Why is Understanding LCM Important?
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. It plays a crucial role in various fields, including:
1. Scheduling and Time Management:
Imagine you need to schedule two events that occur at different intervals. The LCM helps determine when both events will coincide again. For example, if one event happens every 8 days and another every 10 days, they will both occur on the same day again in 40 days (the LCM of 8 and 10).
2. Fraction Operations:
Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions relies on finding the LCM of the denominators. For instance, adding 1/8 and 1/10 requires finding the LCM of 8 and 10 (which is 40), converting the fractions to have a common denominator, and then adding the numerators.
3. Music Theory:
In music, LCM helps determine the least common multiple of the note values, which is used in rhythmic calculations. Understanding LCM is therefore essential for music composition and analysis.
4. Computer Science:
LCMs play a role in several algorithms and data structures used in computer programming, particularly in areas like scheduling and synchronization of processes.
5. Engineering:
In engineering applications, particularly those involving gears and rotating machinery, the LCM helps to determine the synchronization of different components. This ensures smooth and efficient operation of the system.
Exploring Further: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
While we focused on the LCM of two numbers (8 and 10), the concept extends to finding the LCM of three or more numbers. The methods remain similar, but the complexity increases slightly. You can extend the prime factorization method by considering all prime factors from all the numbers involved, and the GCD method can be extended using iterative approaches to find the GCD of multiple numbers.
Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Answer
The LCM of 8 and 10 is 40. However, this article goes beyond simply providing the answer. It delves into the underlying principles, exploring multiple methods for calculating the LCM and demonstrating its relevance in various contexts. Mastering the concept of LCM is not just about solving arithmetic problems; it's about developing a deeper understanding of number theory and its broad applications in diverse fields. By understanding the different methods and their practical implications, you gain a powerful tool for tackling more complex mathematical problems and real-world scenarios. Remember to practice using different methods to solidify your understanding and choose the most efficient method based on the numbers involved.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
6 Is What Percent Of 15
Mar 15, 2025
-
Enough Of A Monoprotic Acid Is Dissolved In Water
Mar 15, 2025
-
One Degree Celsius Is How Many Fahrenheit
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 40 As A Fraction
Mar 15, 2025
-
5 9 As A Decimal And Percent
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Whats The Lcm Of 8 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
