One Degree Celsius Is How Many Fahrenheit
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
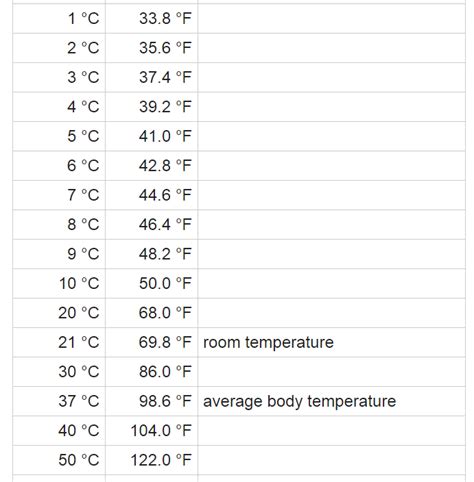
Table of Contents
One Degree Celsius is How Many Fahrenheit? A Deep Dive into Temperature Conversions
Understanding the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial for anyone working with temperature data, traveling internationally, or simply wanting to grasp fundamental scientific concepts. While the simple answer to "one degree Celsius is how many Fahrenheit?" is straightforward, a deeper understanding of the underlying conversion formulas and their historical context adds significant value. This article will delve into the intricacies of Celsius-Fahrenheit conversion, providing a comprehensive explanation suitable for both beginners and those seeking a more advanced understanding.
The Simple Answer and the Underlying Formula
The quick answer is that one degree Celsius is equal to 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit. This is a fundamental aspect of the conversion formula, which is far more than a simple multiplication. The complete formula reveals the nuanced relationship between the two scales:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Where:
- °F represents degrees Fahrenheit
- °C represents degrees Celsius
This formula highlights more than just a scaling factor; it also incorporates a significant offset (+32). This offset is critical because the two scales define their zero points differently. 0°C represents the freezing point of water, while 0°F is significantly colder.
Understanding the Different Scales: A Historical Perspective
To fully appreciate the conversion, let's briefly examine the origins of each scale:
Celsius (formerly Centigrade)
The Celsius scale, named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius, is a metric-based system that defines 0°C as the freezing point of water and 100°C as the boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure. Its simplicity and logical structure based on the properties of water make it the preferred system in most of the world and in scientific applications.
Fahrenheit
The Fahrenheit scale, developed by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, uses a different reference point. 0°F was originally defined as the temperature of a brine solution of ice, water, and ammonium chloride. The boiling point of water at standard atmospheric pressure is 212°F. While widely used in the United States, it's less common globally due to its less intuitive definition.
Why the 9/5 Factor and the 32 Offset?
The 9/5 factor in the conversion formula stems from the difference in the size of degrees between the two scales. The 100-degree range between the freezing and boiling points of water in Celsius is equivalent to a 180-degree range in Fahrenheit (212°F - 32°F = 180°F). This 100:180 ratio simplifies to 5:9 or 9/5. Therefore, a change of 5°C corresponds to a change of 9°F.
The +32 offset compensates for the difference in the zero points of the two scales. Since 0°C is equivalent to 32°F, we must add 32 to the scaled Celsius temperature to get the equivalent Fahrenheit temperature.
More Examples: Illustrating the Conversion
Let's explore a few more examples to solidify your understanding of the conversion:
-
Converting 20°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (20°C × 9/5) + 32 = 68°F
-
Converting 100°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (100°C × 9/5) + 32 = 212°F (the boiling point of water)
-
Converting 0°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (0°C × 9/5) + 32 = 32°F (the freezing point of water)
-
Converting -40°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (-40°C × 9/5) + 32 = -40°F (a unique point where both scales have the same value)
-
Converting 25°C (a pleasant room temperature) to Fahrenheit:
°F = (25°C × 9/5) + 32 = 77°F
The Reverse Conversion: Fahrenheit to Celsius
It's equally important to know how to convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius. The formula is the inverse of the previous one:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let’s look at a few examples:
-
Converting 68°F to Celsius:
°C = (68°F - 32) × 5/9 = 20°C
-
Converting 212°F to Celsius:
°C = (212°F - 32) × 5/9 = 100°C
-
Converting 32°F to Celsius:
°C = (32°F - 32) × 5/9 = 0°C
-
Converting -40°F to Celsius:
°C = (-40°F - 32) × 5/9 = -40°C
Beyond the Basics: Practical Applications and Considerations
The ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit extends beyond simple calculations. It's vital in various fields:
-
Meteorology: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit, requiring accurate conversion for international communication and data analysis.
-
Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either scale, demanding accurate conversion to ensure consistent results.
-
Medicine: Body temperature is frequently measured in both scales, demanding accurate conversion for proper diagnosis and treatment.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: Many industrial processes are temperature-sensitive, and converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential for maintaining accurate control and safety.
-
Scientific Research: Converting temperature measurements is a common practice in scientific experiments, especially when working with international collaborations or referencing literature using different measurement systems.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
While the conversion formulas are straightforward, several common mistakes should be avoided:
-
Order of Operations: Always perform multiplication or division before addition or subtraction, adhering to the standard order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS).
-
Fractional Values: Ensure that you correctly calculate the fractional values (9/5 and 5/9). Using a calculator can minimize errors.
-
Incorrect Formula: Double-check the formula being used to avoid confusion and incorrect results.
-
Units: Always include the degree symbol (°), and clearly state whether you're dealing with Celsius or Fahrenheit to avoid ambiguity.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversions
Understanding how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a practical and valuable skill. While the initial conversion might seem simple – one degree Celsius is 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit – the underlying formulas reveal a deeper understanding of the historical development and nuanced relationship between these two temperature scales. Mastering the conversion formulas and avoiding common errors will allow for accurate calculations and confident interpretation of temperature data in various contexts. The ability to seamlessly move between these systems is a testament to a robust grasp of fundamental scientific principles and practical numerical skills. Therefore, understanding the nuances of temperature conversion isn’t just about numbers; it's about grasping the fundamental building blocks of scientific measurement.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 3 2
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Derivative Of Ln 1 X
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Type Of Molecule Is Shown Below
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Find The Domain Of F O G
Mar 17, 2025
-
Amino Acids Are The Monomers For
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One Degree Celsius Is How Many Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
