Whats The Lcm Of 7 And 4
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
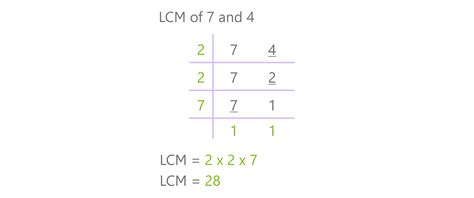
Table of Contents
- Whats The Lcm Of 7 And 4
- Table of Contents
- What's the LCM of 7 and 4? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
- Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
- Methods for Calculating LCM
- 1. Listing Multiples Method
- 2. Prime Factorization Method
- 3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
- The Significance of LCM in Real-World Applications
- Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
- Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What's the LCM of 7 and 4? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it is crucial for a strong foundation in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "What's the LCM of 7 and 4?" but also explore the broader significance of LCMs and equip you with multiple strategies to solve similar problems efficiently.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we delve into the specifics of finding the LCM of 7 and 4, let's solidify our understanding of what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and so on. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The least common multiple is 6.
Methods for Calculating LCM
Several methods exist to determine the LCM of two or more numbers. We'll explore three common and effective techniques:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
Let's find the LCM of 7 and 4 using this method:
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56...
Notice that 28 and 56 appear in both lists. However, 28 is the smallest common multiple. Therefore, the LCM of 7 and 4 is 28.
This method is effective for small numbers but can become tedious and time-consuming for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method leverages the prime factorization of each number. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
Here's how to find the LCM of 7 and 4 using prime factorization:
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 7 = 7 (7 is a prime number)
- 4 = 2 x 2 = 2²
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The prime factors are 2 and 7.
- The highest power of 2 is 2².
- The highest power of 7 is 7.
-
Multiply the highest powers of all prime factors together:
- LCM(7, 4) = 2² x 7 = 4 x 7 = 28
This method is more efficient than the listing multiples method, especially for larger numbers, as it avoids the need for extensive listing.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. The LCM and GCD are related by the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
Let's find the LCM of 7 and 4 using this method:
-
Find the GCD of 7 and 4:
- The factors of 7 are 1 and 7.
- The factors of 4 are 1, 2, and 4.
- The greatest common factor is 1. Therefore, GCD(7, 4) = 1.
-
Apply the formula:
- LCM(7, 4) = (7 x 4) / 1 = 28
This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers, as finding the GCD can often be easier than directly finding the LCM. Algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm can efficiently compute the GCD.
The Significance of LCM in Real-World Applications
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. It has practical applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine you have two events that occur at regular intervals. One event happens every 7 days, and another happens every 4 days. The LCM helps determine when both events will coincide again. In this case, the LCM of 7 and 4 (28) indicates that both events will occur simultaneously every 28 days.
-
Fractions: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial for determining the least common denominator (LCD), which simplifies the addition/subtraction process.
-
Engineering and Construction: LCM is essential in projects involving repetitive patterns or cycles, ensuring synchronization and efficient resource allocation.
-
Music: Musical intervals and harmonies often rely on LCM calculations to determine the frequencies and timing of notes.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method remains particularly efficient:
Example: Find the LCM of 6, 8, and 12.
-
Prime Factorization:
- 6 = 2 x 3
- 8 = 2³
- 12 = 2² x 3
-
Highest Powers:
- Highest power of 2 is 2³
- Highest power of 3 is 3
-
Multiplication:
- LCM(6, 8, 12) = 2³ x 3 = 8 x 3 = 24
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Understanding and mastering LCM calculations is fundamental to various mathematical applications and real-world scenarios. Whether you use the listing multiples, prime factorization, or GCD method, the key is to choose the approach most suitable for the numbers involved. Remember that the prime factorization method offers the most efficient and generalizable solution for a wide range of problems. With practice and a solid grasp of these techniques, you'll confidently tackle any LCM challenge that comes your way. The answer to "What's the LCM of 7 and 4?" is definitively 28, and this guide has provided you with the tools and understanding to solve many more such problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor For 12 And 18
Mar 25, 2025
-
Solve P 2l 2w For L
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Stronger Acid
Mar 25, 2025
-
How To Find Radius From Arc Length
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Unit Of Measurement For Potential Energy
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Whats The Lcm Of 7 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
