What Role Do Plants Play In The Carbon Cycle
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
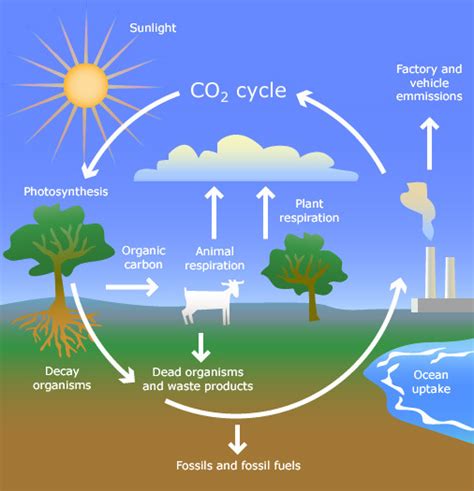
Table of Contents
What Role Do Plants Play in the Carbon Cycle?
Plants are fundamental to the carbon cycle, acting as crucial intermediaries between the atmosphere and the Earth's biosphere. Their role is multifaceted, influencing both the uptake and release of carbon dioxide (CO2), a primary greenhouse gas, significantly impacting global climate patterns. Understanding the intricate ways plants interact with carbon is essential to comprehending climate change and developing effective mitigation strategies.
The Carbon Cycle: A Brief Overview
Before diving into the plant's role, let's briefly review the carbon cycle itself. It's a biogeochemical cycle describing the continuous movement of carbon atoms through various reservoirs on Earth:
- Atmosphere: The largest active reservoir, containing CO2, methane (CH4), and other carbon-containing gases.
- Oceans: A massive carbon sink, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere through physical and biological processes.
- Land Biosphere: This includes all living organisms on land, with plants playing the dominant role in carbon storage and cycling.
- Lithosphere (Rocks and Soil): A long-term carbon store, with carbon locked up in sedimentary rocks, fossil fuels, and soil organic matter.
The carbon cycle involves complex interactions between these reservoirs, driven by various processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly altered the natural balance of the carbon cycle, leading to increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations and contributing to climate change.
Plants as Carbon Sinks: The Power of Photosynthesis
Plants are primary producers, meaning they form the base of most food chains. Their most significant contribution to the carbon cycle is through photosynthesis, a process that converts atmospheric CO2 into organic carbon compounds. This process can be summarized as follows:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation shows that plants utilize sunlight, water (H₂O), and CO2 to produce glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), a simple sugar, and oxygen (O₂). Glucose serves as the building block for all plant tissues, effectively sequestering carbon from the atmosphere. This carbon is stored in various forms within the plant:
- Biomass: The total mass of living organic material, including leaves, stems, roots, and fruits. Forests, grasslands, and other plant communities act as massive carbon sinks, storing vast amounts of carbon in their biomass.
- Soil Organic Matter (SOM): When plants die and decompose, a portion of their carbon is released back into the atmosphere. However, a significant fraction is incorporated into the soil as SOM, a complex mixture of organic compounds that enriches the soil and stores carbon for extended periods. Healthy soil with high SOM content acts as a crucial carbon reservoir.
- Roots: Plant roots play a vital role in carbon sequestration, not only by storing carbon within their own tissues but also by stimulating microbial activity in the soil, which further enhances carbon storage. Mycorrhizal fungi, which form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, are particularly important in this process.
Factors Affecting Photosynthetic Carbon Uptake
Several factors influence the rate of photosynthetic carbon uptake by plants:
- Light intensity: Photosynthesis is light-dependent, with higher light intensity generally leading to increased carbon uptake, up to a certain saturation point.
- CO2 concentration: Increased atmospheric CO2 levels can initially stimulate photosynthesis, but this effect can be limited by other factors such as nutrient availability and water stress.
- Temperature: Temperature influences enzyme activity in photosynthetic processes, with optimal temperature ranges varying among different plant species. Extreme temperatures can inhibit photosynthesis.
- Water availability: Water is essential for photosynthesis, and water stress can significantly reduce carbon uptake.
- Nutrient availability: Nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus are crucial for plant growth and photosynthesis. Nutrient deficiencies can limit carbon uptake.
Plants and Carbon Release: Respiration and Decomposition
While plants are net carbon sinks, they also release carbon back into the atmosphere through respiration. This is the process by which plants break down glucose to release energy for growth and other metabolic processes. The equation for respiration is essentially the reverse of photosynthesis:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy
Respiration occurs continuously in all living plant tissues, releasing CO2 back into the atmosphere. The rate of respiration depends on several factors, including temperature, light intensity, and plant growth stage.
Another significant pathway for carbon release is decomposition. When plants die, their organic matter is broken down by decomposers, primarily bacteria and fungi. This decomposition process releases CO2 back into the atmosphere, completing the carbon cycle. The rate of decomposition depends on various factors, including temperature, moisture, and the type of plant material.
The Impact of Different Plant Types on Carbon Cycling
Different types of plants play varying roles in the carbon cycle:
- Forests: Forests are considered among the most significant carbon sinks, with trees storing large amounts of carbon in their biomass and soil. Old-growth forests, with their extensive root systems and large biomass, can sequester carbon for centuries.
- Grasslands: Grasslands also contribute significantly to carbon sequestration, particularly through the accumulation of SOM in their soils.
- Agricultural lands: Agricultural practices can impact carbon cycling significantly. Intensive agriculture can lead to soil degradation and reduced carbon storage, while sustainable agricultural practices can enhance carbon sequestration.
- Mangroves and Seagrasses: Coastal ecosystems like mangroves and seagrasses are highly productive and play a crucial role in blue carbon sequestration. They store significant amounts of carbon in their biomass and sediments.
Human Impact and Management of Plant-Based Carbon Sequestration
Human activities have dramatically altered the natural carbon cycle, leading to increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations. Deforestation, land-use change, and unsustainable agricultural practices have reduced the planet's capacity to sequester carbon. To mitigate climate change, it’s crucial to implement strategies that enhance plant-based carbon sequestration:
- Reforestation and Afforestation: Planting trees in deforested areas or establishing new forests can significantly increase carbon sequestration.
- Sustainable Forestry Management: Responsible forest management practices, such as selective logging and reduced-impact logging, can help maintain forest carbon stocks.
- Sustainable Agricultural Practices: Implementing practices like no-till farming, cover cropping, and agroforestry can enhance soil carbon storage and reduce emissions from agriculture.
- Protecting and Restoring Coastal Ecosystems: Conserving and restoring mangroves, seagrasses, and other coastal ecosystems can significantly enhance blue carbon sequestration.
- Carbon Farming: Carbon farming involves implementing agricultural practices that specifically aim to sequester carbon in soils and biomass. This includes practices like integrating trees into agricultural systems, and enhancing soil health.
Conclusion: Plants as Essential Players in Climate Change Mitigation
Plants play a critical role in regulating the Earth's carbon cycle, acting as both carbon sinks and sources. Their capacity to absorb CO2 through photosynthesis and store it in biomass and soil is crucial for mitigating climate change. However, human activities have significantly altered the natural balance, reducing the planet's capacity for carbon sequestration. Implementing sustainable land management practices, protecting existing ecosystems, and promoting reforestation are essential strategies for enhancing plant-based carbon sequestration and mitigating the effects of climate change. Further research and innovation are needed to understand the full potential of plants in combating climate change and building a more sustainable future. The intricate interplay between plants and the carbon cycle underscores the urgent need for global cooperation to protect and enhance our planet's natural carbon sinks. The future of our climate depends, in no small part, on the health and vitality of the plant kingdom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Calculate The Ph At Equivalence Point
Mar 25, 2025
-
Derivative Of 4 Square Root X
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is A Equivalent Fraction For 5 8
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Water Molecules In A Drop
Mar 25, 2025
-
Derivative Of 2 Square Root X
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Role Do Plants Play In The Carbon Cycle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
