What Order Does A Dog Belong To
listenit
Mar 29, 2025 · 5 min read
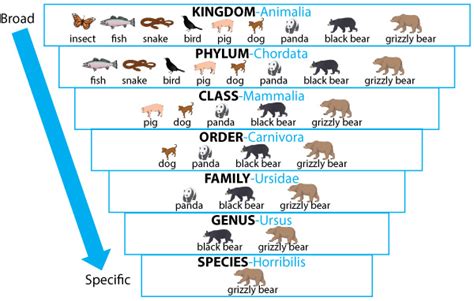
Table of Contents
What Order Does a Dog Belong To? A Deep Dive into Canine Classification
Dogs, our beloved canine companions, hold a special place in our hearts and homes. But beyond their endearing personalities and unwavering loyalty lies a fascinating scientific classification that places them within a specific branch of the animal kingdom. Understanding the order to which dogs belong provides invaluable insight into their evolutionary history, biological characteristics, and their place within the broader context of life on Earth. This article will delve deep into the taxonomic classification of dogs, exploring the intricacies of their order, family, genus, and species, and highlighting the key features that define them.
The Order Carnivora: A Family of Predators
Dogs belong to the order Carnivora. This order encompasses a vast and diverse group of mammals characterized by their predatory adaptations and, in most cases, a diet heavily reliant on meat. The name itself, "Carnivora," meaning "meat-eaters," accurately reflects this defining characteristic. However, it's important to note that while many carnivorans are obligate carnivores (meaning they must consume meat to survive), many others, including domestic dogs, are omnivores, meaning they can thrive on a diet that includes both meat and plant matter. This dietary flexibility is a testament to their adaptability and evolutionary success.
Key Characteristics of Carnivora
Members of the order Carnivora share several key anatomical and physiological traits that distinguish them from other mammalian orders:
- Sharp teeth: Carnivorans possess specialized teeth, including prominent canines for grasping and tearing prey, and sharp premolars and molars for shearing meat. These adaptations are crucial for efficiently processing a meat-based diet.
- Powerful jaws: Their jaw muscles are exceptionally strong, providing the force necessary to subdue and consume prey. The jaw's structure also allows for a wide range of jaw movements, essential for tearing and manipulating food.
- Claws: Most carnivorans have sharp, retractable claws, which aid in capturing and killing prey. The retractable nature of the claws helps protect them from wear and tear during locomotion.
- Keen senses: Carnivores typically possess highly developed senses of smell, hearing, and sight, which are vital for hunting and navigating their environment. Their olfactory capabilities are particularly impressive.
- Digestive system: Their digestive systems are adapted to efficiently process meat, with a relatively short intestinal tract compared to herbivores.
Suborders and Families Within Carnivora
The order Carnivora is further divided into two suborders: Caniformia (dog-like carnivores) and Feliformia (cat-like carnivores). Dogs belong to the suborder Caniformia, which includes a wide array of animals, such as wolves, foxes, bears, and weasels.
Within Caniformia, dogs belong to the family Canidae. This family is characterized by several defining features:
- Long snouts: Canids are easily recognizable by their elongated snouts, which house their powerful olfactory receptors.
- Digitigrade locomotion: They walk on their toes (digitigrade), which enables speed and agility.
- Excellent sense of smell: Their sense of smell is extraordinarily acute, far exceeding that of humans.
- Highly social behavior: Many canids live in packs, exhibiting complex social structures and cooperative hunting strategies.
The Family Canidae: A Closer Look at Dog-like Carnivores
The family Canidae encompasses a diverse group of animals, including wolves, foxes, jackals, and, of course, domestic dogs. They share several key characteristics that set them apart from other caniforms:
- Highly developed social structures: Many canids, especially wolves and dogs, live in complex social units with established hierarchies and cooperative behaviors. This social structure plays a vital role in hunting, raising young, and territorial defense.
- Vocalizations: Canids communicate using a wide range of vocalizations, including barks, howls, whines, and growls, each carrying specific meaning within their social groups.
- Scent marking: They utilize scent marking, often through urination and defecation, to establish territory and communicate with other individuals. This olfactory communication is crucial for social interactions and territorial boundaries.
- Adaptive foraging: Canids have evolved a diverse range of hunting and foraging strategies depending on their environment and prey availability. Some are pack hunters, while others are solitary scavengers.
The Genus Canis: Wolves, Coyotes, and Dogs
Within the Canidae family, dogs belong to the genus Canis. This genus includes several closely related species, including the gray wolf (Canis lupus), the coyote (Canis latrans), and the domestic dog (Canis familiaris). The close genetic relationship between these species is evident in their shared physical characteristics and behavioral traits.
The Gray Wolf (Canis lupus): The Ancestor
The gray wolf is widely accepted as the ancestor of the domestic dog. Genetic studies have shown a strong phylogenetic link between the two, demonstrating that dogs evolved from wolves thousands of years ago. This evolutionary history has had a profound impact on the physical and behavioral characteristics of dogs.
The Domestic Dog (Canis familiaris): A Product of Domestication
The domestic dog (Canis familiaris) is a subspecies of the gray wolf, the result of a long process of domestication that began thousands of years ago. The exact circumstances and timeline of domestication are still debated, but it's clear that humans and dogs have coexisted for millennia, forging a unique and enduring relationship. The domestication process led to significant changes in dogs' physical appearance and behavior, resulting in the incredible diversity of breeds we see today.
The Species Canis familiaris: The Amazing Diversity of Dogs
The species Canis familiaris encompasses the vast array of dog breeds we know and love. This remarkable diversity is a testament to the power of artificial selection, as humans have selectively bred dogs for specific traits, leading to the incredible range of sizes, shapes, coat colors, and temperaments we see in dogs today. From the tiny Chihuahua to the giant Great Dane, each breed exhibits unique characteristics resulting from centuries of human intervention.
Understanding Breed Variations
The remarkable diversity within Canis familiaris highlights the adaptability and genetic plasticity of this species. However, this diversity also comes with complexities, as certain breeds are predisposed to specific genetic health issues. Responsible breeding practices are essential to minimize the risk of these problems and maintain the health and well-being of dogs.
Conclusion: A Journey Through Canine Classification
Tracing the lineage of dogs from the order Carnivora down to the species Canis familiaris provides a fascinating insight into their evolutionary journey and biological characteristics. Understanding their place within the animal kingdom helps us appreciate the intricate relationships between different species and the processes that have shaped their evolution. The incredible diversity of dog breeds further underscores the remarkable adaptability of this species and its unique relationship with humans. By understanding their classification, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable creatures that share our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Adenine A Purine Or Pyrimidine
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Quadrilateral With Opposite Sides Parallel
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Are Elements In The Modern Periodic Table Arranged
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Type Of Rock Is Most Fossils Found In
Mar 31, 2025
-
Do Lone Pairs Count As Sigma Bonds
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Order Does A Dog Belong To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
