What Is The Square Root Of 39
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
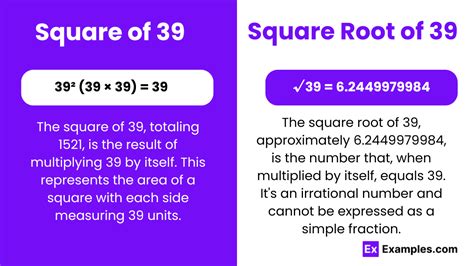
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 39? A Deep Dive into Calculation and Applications
The seemingly simple question, "What is the square root of 39?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of mathematics, encompassing fundamental concepts, calculation methods, and practical applications. While a simple calculator provides a decimal approximation, understanding the underlying principles and exploring different approaches enriches our mathematical understanding. This article delves into the intricacies of calculating the square root of 39, examining both approximate and precise methods, and highlighting its relevance in various fields.
Understanding Square Roots
Before we tackle the square root of 39 specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of square roots. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the original number. In simpler terms, it's the inverse operation of squaring a number. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 * 3 = 9.
This concept is crucial in many mathematical and scientific disciplines. It forms the basis of numerous calculations, from solving quadratic equations to calculating distances and areas in geometry.
Calculating the Square Root of 39: Methods and Approaches
Unlike perfect squares (like 9, 16, 25, etc.), 39 doesn't have a whole number as its square root. This means we'll need to employ methods to find an approximate or precise value.
1. Using a Calculator: The Quickest Approach
The simplest method is to use a calculator. Most calculators have a square root function (√). Simply input 39 and press the square root button. The calculator will give you an approximate decimal value, usually around 6.245. This is a practical approach for quick calculations, but it doesn't reveal the underlying mathematical process.
2. The Babylonian Method (or Heron's Method): An Iterative Approach
The Babylonian method is an iterative algorithm that progressively refines an initial guess to approach the square root. It's a powerful technique that demonstrates the iterative nature of numerical computation.
Here's how it works:
-
Make an initial guess: Start with a reasonable guess. For √39, let's guess 6.
-
Improve the guess: Divide the number (39) by your guess (6), then average the result with your guess: (6 + 39/6) / 2 = 6.25
-
Repeat: Use the improved guess (6.25) as your new guess and repeat step 2. (6.25 + 39/6.25) / 2 ≈ 6.24499
-
Iterate until desired accuracy: Continue this process until the difference between successive guesses is smaller than your desired level of accuracy. Each iteration brings you closer to the true value.
This method converges quickly towards the accurate square root. The more iterations you perform, the more precise the result becomes.
3. Using the Taylor Series Expansion: A Powerful Analytical Approach
For those familiar with calculus, the Taylor series provides a powerful analytical way to approximate the square root. The Taylor series expansion for √(1+x) around x=0 is:
√(1+x) ≈ 1 + x/2 - x²/8 + x³/16 - ...
To use this for √39, we need to rewrite 39 in a suitable form:
√39 = √(36 + 3) = 6√(1 + 3/36) = 6√(1 + 1/12)
Now, substitute x = 1/12 into the Taylor series:
√(1 + 1/12) ≈ 1 + (1/12)/2 - (1/12)²/8 + (1/12)³/16 - ...
This calculation, though more complex, provides a highly accurate approximation when enough terms of the series are included.
4. Numerical Methods: Sophisticated Algorithms
Advanced numerical methods, such as the Newton-Raphson method, are also used to approximate square roots. These methods use iterative processes, similar to the Babylonian method, but often converge faster and are more efficient for complex calculations. These methods are typically implemented in computer programs and software for high-precision calculations.
Applications of the Square Root of 39
The square root, while seemingly a fundamental mathematical operation, finds its way into numerous practical applications across various fields. The specific value of √39 might not be prominently featured in every application, but the concept of square roots is essential.
1. Geometry and Physics: Calculating Distances and Areas
In geometry, the square root is frequently used when calculating distances and areas. For example, the Pythagorean theorem (a² + b² = c²) uses squares and square roots to determine the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle. If the legs of a right triangle have lengths that, when squared and added together, result in 39, then the length of the hypotenuse would be √39.
In physics, the square root is used in various formulas, including calculations involving velocity, energy, and displacement. For instance, calculating the distance an object travels under constant acceleration involves square roots.
2. Engineering and Architecture: Designing Structures
Engineers and architects utilize square roots extensively in structural design. Calculations for load-bearing capacity, stress analysis, and determining the dimensions of structures often involve the use of the square root function. The stability and safety of buildings and other structures rely heavily on these calculations.
3. Data Analysis and Statistics: Standard Deviation and Error Calculations
In statistics, the square root plays a vital role in calculating the standard deviation, a crucial measure of data dispersion. The standard deviation quantifies the spread of data points around the mean, and its calculation inherently involves the square root. This is critical in understanding data variability and making informed decisions based on statistical analyses. Similar applications extend to error calculations in experimental physics and engineering.
4. Computer Graphics and Game Development: Transformations and Simulations
In computer graphics, manipulating images and 3D models often requires employing square roots in mathematical transformations. Calculating distances between points, rotating objects, and handling other geometric transformations relies on square root calculations. Game development heavily utilizes these concepts for realistic simulations and dynamic environments.
5. Financial Modeling and Investments: Calculating Risk and Return
Financial models often involve square roots in calculating risk measures, such as standard deviation of returns on investments. Understanding the variability of investment performance requires applying square roots to analyze data and assess risk. Sophisticated financial algorithms rely heavily on these concepts.
Conclusion: Beyond the Decimal Approximation
The seemingly simple question of finding the square root of 39 leads us on a journey through various mathematical concepts and their wide-ranging applications. While a calculator quickly provides the approximate decimal value, understanding the different calculation methods and their underlying principles is crucial for appreciating the power and versatility of mathematics. The square root function, far from being a mere mathematical curiosity, is a cornerstone of countless scientific, engineering, and technological advancements. The applications presented here represent only a fraction of the vast landscape where the concept of square roots plays a vital and indispensable role.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Common Factors Of 36 And 60
Mar 17, 2025
-
Draw The Product Of The Hydration Of 2 Butene
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lewis Acid And Base Vs Bronsted
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Are A Mole And A Dozen Similar
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 0 2
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Square Root Of 39 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
