What Is The Number Of Valence Electrons In Cadmium Cd
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
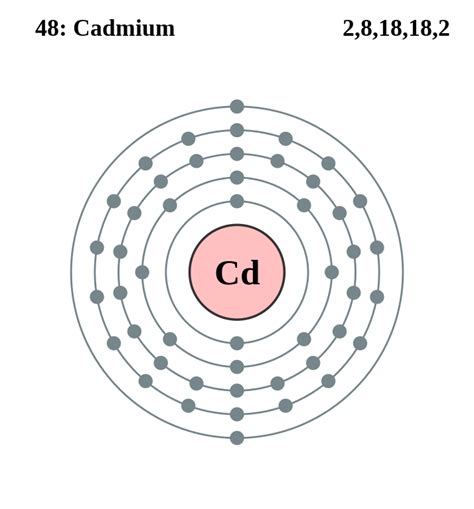
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Cadmium: Unveiling the Number of Valence Electrons
Cadmium (Cd), a fascinating element nestled in the periodic table, holds a unique position in the world of chemistry and materials science. Understanding its electronic structure, specifically the number of valence electrons, is key to comprehending its properties and behavior. This comprehensive article will explore everything you need to know about cadmium's valence electrons, delving into its electronic configuration, its chemical reactivity, its applications, and its environmental impact.
What are Valence Electrons?
Before diving into cadmium specifically, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (or energy level) of an atom. These electrons are crucial because they determine an element's chemical properties and its ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms. They are the primary players in chemical reactions, dictating how an atom will interact with its environment. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses directly influences its reactivity, its bonding capabilities (whether it forms ionic, covalent, or metallic bonds), and its oxidation states.
Cadmium's Position in the Periodic Table
Cadmium (Cd) is a transition metal located in Group 12, period 5 of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 48, indicating it has 48 protons and, in its neutral state, 48 electrons. Understanding its placement is crucial because the periodic table is organized based on electron configuration, providing clues about electron arrangement. The group number (12) provides a strong hint about its valence electron count. However, transition metals often exhibit some complexity in their valence electron behavior.
Determining Cadmium's Electronic Configuration
To accurately determine the number of valence electrons in cadmium, we need to understand its electronic configuration. This describes how electrons are distributed among the different energy levels and subshells within the atom. The electronic configuration of cadmium is: [Kr] 4d<sup>10</sup> 5s<sup>2</sup>.
Let's break this down:
- [Kr]: This represents the electron configuration of krypton (a noble gas), which is a shorthand notation for the filled inner electron shells (1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 3d¹⁰ 4s² 4p⁶). These inner electrons are considered core electrons and are generally not involved in chemical bonding.
- 4d<sup>10</sup>: This signifies ten electrons in the 4d subshell. While these electrons are part of the outermost electron shell, they behave differently than valence electrons in main group elements.
- 5s<sup>2</sup>: This indicates two electrons in the 5s subshell. These two electrons are the valence electrons of cadmium.
Why only two valence electrons? The nuances of transition metals
Unlike main group elements where valence electrons are readily identified by their position in the periodic table, transition metals like cadmium exhibit more complex behavior. While the 4d electrons are in the outermost shell, they are relatively less involved in typical chemical bonding compared to the 5s electrons. The 4d electrons are more strongly attracted to the nucleus, thus participating less in chemical reactions. Consequently, it's the two 5s electrons that primarily determine cadmium's chemical reactivity and bonding behavior. This explains why cadmium often exhibits a +2 oxidation state, losing these two valence electrons to form ions.
Chemical Reactivity and Bonding in Cadmium
The presence of only two valence electrons significantly influences cadmium's chemical reactivity. Cadmium is relatively unreactive compared to some other metals, exhibiting a moderate tendency to lose electrons and form ionic bonds. It readily forms compounds in the +2 oxidation state, demonstrating a stable +2 ion (Cd²⁺). The 4d electrons remain largely unaffected during these processes.
Cadmium's chemical reactivity and bonding also contribute to its various applications:
- Batteries: Cadmium is used in nickel-cadmium (NiCd) rechargeable batteries. The electrochemical reactions in these batteries involve the reversible oxidation and reduction of cadmium.
- Pigments: Cadmium compounds, such as cadmium sulfide (CdS) and cadmium selenide (CdSe), are used as vibrant yellow, orange, and red pigments in paints and plastics. The color arises from the electronic transitions within the cadmium-containing compounds.
- Metal alloys: Cadmium is added to other metals to form alloys with specific properties. For example, it is used in low-melting-point alloys and bearings, where it contributes to increased strength and corrosion resistance.
- Nuclear reactors: Cadmium's ability to absorb neutrons makes it useful as a control rod material in nuclear reactors, helping to regulate the rate of nuclear fission.
Environmental Concerns and Cadmium Toxicity
Despite its useful applications, cadmium poses significant environmental and health concerns. Cadmium is a toxic heavy metal, and its environmental persistence and bioaccumulation pose risks. Exposure to cadmium through inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact can lead to various health problems, including kidney damage, bone disease, and lung cancer. The widespread use of cadmium in the past has led to its presence in soil and water, necessitating careful management and remediation efforts.
Conclusion: Understanding Cadmium's Valence Electrons is Key
Cadmium's two valence electrons are not merely a numerical fact; they are the foundation upon which its chemical properties, reactivity, and applications rest. Understanding these valence electrons, the electronic configuration, and the subtleties of its behavior as a transition metal provides a complete picture of cadmium’s role in both technological advancements and environmental concerns. From its use in rechargeable batteries to its role as a toxic heavy metal, the behaviour determined by these two electrons has profound implications in our world. The information discussed here highlights the importance of understanding atomic structure and its impact on the properties and behavior of elements, particularly those with complex electronic configurations like transition metals. Future research and development will continue to utilize and mitigate the impacts of cadmium, necessitating ongoing efforts in safe handling and sustainable material management.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Empirical Formula Of Magnesium Oxide
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Are Two Subatomic Particles Found In The Nucleus
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 17 Yards
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Does The T Stand For In Trna
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Degrees Celsius Is 70 Fahrenheit
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Number Of Valence Electrons In Cadmium Cd . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
