What Is The Molar Mass Of Kcl
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
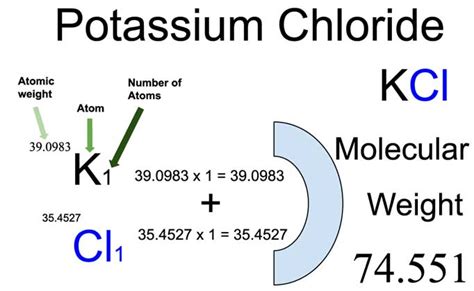
Table of Contents
What is the Molar Mass of KCl? A Deep Dive into Potassium Chloride
Potassium chloride (KCl), a ubiquitous inorganic salt, finds applications in various fields, from medicine to agriculture. Understanding its molar mass is crucial for numerous calculations in chemistry, particularly stoichiometry and solution preparation. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of KCl's molar mass, its calculation, and its relevance in diverse scientific and practical contexts.
Understanding Molar Mass
Before delving into the specifics of KCl, let's establish a foundational understanding of molar mass. Molar mass is defined as the mass of one mole of a substance. A mole, a fundamental unit in chemistry, represents Avogadro's number (approximately 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup>) of particles – atoms, molecules, ions, or other specified entities. Essentially, the molar mass tells us the mass of 6.022 x 10<sup>23</sup> particles of a given substance. Its unit is typically grams per mole (g/mol).
The molar mass of an element is numerically equivalent to its atomic weight (or standard atomic weight) as found on the periodic table. For compounds, the molar mass is the sum of the molar masses of all the atoms in its chemical formula.
Calculating the Molar Mass of KCl
Potassium chloride (KCl) is an ionic compound composed of potassium (K) and chlorine (Cl) ions. To calculate its molar mass, we need the molar masses of potassium and chlorine. These are readily available from the periodic table:
- Potassium (K): Approximately 39.10 g/mol
- Chlorine (Cl): Approximately 35.45 g/mol
The chemical formula for potassium chloride is KCl, indicating one potassium ion and one chlorine ion per formula unit. Therefore, the molar mass of KCl is calculated as follows:
Molar Mass (KCl) = Molar Mass (K) + Molar Mass (Cl)
Molar Mass (KCl) = 39.10 g/mol + 35.45 g/mol = 74.55 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of potassium chloride (KCl) is approximately 74.55 grams per mole.
The Significance of Molar Mass in Calculations
The molar mass of KCl is a cornerstone for various chemical calculations, including:
1. Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry involves the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. Knowing the molar mass of KCl allows us to convert between mass and moles, a critical step in many stoichiometric problems. For instance, if we want to determine the number of moles of KCl in a given mass, we can use the following formula:
Moles (KCl) = Mass (KCl) / Molar Mass (KCl)
Conversely, if we know the number of moles and need to determine the mass, we can rearrange the formula:
Mass (KCl) = Moles (KCl) x Molar Mass (KCl)
2. Solution Preparation
Molar mass is essential in preparing solutions of a specific concentration, particularly molarity (moles of solute per liter of solution). For example, to prepare a 1.0 M solution of KCl, we need to know the molar mass to determine the mass of KCl required to dissolve in one liter of solvent.
3. Titration Calculations
In titrations, where we determine the concentration of an unknown solution using a solution of known concentration, molar mass plays a critical role. It's used in calculating the moles of the analyte (the substance being analyzed) and the titrant (the solution of known concentration) involved in the reaction.
Applications of Potassium Chloride
The widespread use of potassium chloride stems from its unique properties and chemical reactivity. Here are some key applications:
1. Medicine
Potassium chloride is a crucial electrolyte that plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle function. It's used in various medications, including:
- Electrolyte replacement: KCl supplements are used to treat or prevent potassium deficiency (hypokalemia), a condition that can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and heart problems.
- Intravenous fluids: KCl is added to intravenous (IV) fluids to replenish electrolytes lost due to illness, surgery, or dehydration.
- Potassium supplements: KCl is available as an over-the-counter supplement for individuals who need to increase their potassium intake.
- Lethal injections: In some jurisdictions, potassium chloride is used in lethal injections as part of a three-drug cocktail.
2. Agriculture
Potassium is an essential macronutrient for plant growth, promoting strong stems, increased yield, and disease resistance. KCl is a common source of potassium fertilizer, contributing to optimal plant development.
3. Food Industry
KCl is used as a salt substitute in processed foods, providing a similar salty taste without the sodium content. This helps reduce sodium intake, promoting cardiovascular health.
4. Industrial Applications
KCl finds diverse uses in various industries:
- Electroplating: KCl is used as an electrolyte in electroplating processes, facilitating the deposition of metals onto surfaces.
- Metallurgy: KCl is utilized in the production of certain metals and alloys.
- Scientific Research: KCl is used in various scientific experiments and research due to its well-defined properties and reactivity.
Safety Precautions
While potassium chloride is generally safe in controlled environments and appropriate dosages, it is crucial to be aware of its potential hazards. High levels of potassium can lead to hyperkalemia, a potentially fatal condition. Always follow instructions and safety guidelines when using potassium chloride in any context, including medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications.
Conclusion
The molar mass of potassium chloride (KCl), approximately 74.55 g/mol, is a fundamental parameter in numerous chemical calculations. This value is crucial for stoichiometric problems, solution preparation, titration calculations, and understanding the quantitative relationships in reactions involving KCl. Its diverse applications in medicine, agriculture, the food industry, and various industrial processes highlight its significant role in various fields. Understanding its molar mass and its applications are integral to success in various scientific and practical endeavors. However, it's vital to exercise caution in handling KCl due to its potential health risks associated with high concentrations. Always adhere to appropriate safety protocols and guidelines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Kinds Of Elements Form Covalent Bonds
Mar 29, 2025
-
Why Water Is Liquid At Room Temperature
Mar 29, 2025
-
Examples Of Combustion In Everyday Life
Mar 29, 2025
-
Graph Of X 2y Y 2
Mar 29, 2025
-
Why Is Density A Derived Unit
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Molar Mass Of Kcl . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
