What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 26 And 39
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
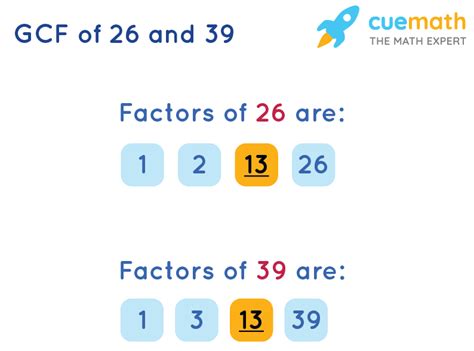
Table of Contents
What is the Greatest Common Factor of 26 and 39? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts unlocks a deeper appreciation for number theory and its applications in various fields. This article delves into the methods of determining the GCF of 26 and 39, exploring different approaches, and expanding on the significance of GCF in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The greatest common factor, also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that can perfectly divide both numbers. Understanding GCF is crucial in simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and even in advanced mathematical concepts.
Why is finding the GCF important?
The applications of finding the GCF extend far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Here are some key reasons why it's important:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The GCF is used to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. By dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF, we obtain an equivalent fraction that is easier to understand and work with.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: GCF plays a significant role in factoring algebraic expressions. Finding the GCF of the terms in an expression allows us to simplify and solve equations more efficiently.
-
Real-world Applications: GCF has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Geometry: Calculating the dimensions of shapes or finding the largest possible square that can tile a given rectangle.
- Computer Science: Used in algorithms for data compression and cryptography.
- Music Theory: Determining common rhythmic patterns.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 26 and 39
Several methods can be used to determine the GCF of 26 and 39. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Factors Method
This method involves listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the largest common factor.
Factors of 26: 1, 2, 13, 26 Factors of 39: 1, 3, 13, 39
Comparing the two lists, we can see that the common factors are 1 and 13. The greatest common factor is 13.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. The GCF is then found by multiplying the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
- Prime factorization of 26: 2 x 13
- Prime factorization of 39: 3 x 13
The only common prime factor is 13. Therefore, the GCF of 26 and 39 is 13.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF of two numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, which is the GCF.
- Divide the larger number (39) by the smaller number (26): 39 ÷ 26 = 1 with a remainder of 13.
- Replace the larger number with the remainder: The new pair of numbers is 26 and 13.
- Repeat the process: 26 ÷ 13 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- The GCF is the last non-zero remainder: The last non-zero remainder is 13. Therefore, the GCF of 26 and 39 is 13.
The Euclidean algorithm is particularly useful for finding the GCF of larger numbers, as it's significantly faster than the other methods.
Exploring the Concept of Coprimality
Two numbers are considered coprime (or relatively prime) if their greatest common factor is 1. While 26 and 39 are not coprime (their GCF is 13), understanding coprimality is essential in number theory. Many mathematical theorems and concepts rely on the properties of coprime numbers.
For example, if two numbers are coprime, their least common multiple (LCM) is simply their product. The LCM is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both numbers. This relationship between GCF and LCM is fundamental in various mathematical applications.
Applications of GCF in Real-World Scenarios
Beyond the theoretical realm, the GCF has practical applications in several areas:
-
Recipe Scaling: Imagine you're baking a cake and want to adjust the recipe to make a smaller or larger batch. Finding the GCF of the ingredient quantities can help you proportionally reduce or increase the recipe while maintaining the correct ratios.
-
Tiling and Pattern Design: In tiling or pattern design, understanding the GCF helps determine the size of the largest square tile that can perfectly fit a rectangular area without leaving gaps or overlaps.
-
Resource Allocation: In project management or resource allocation, the GCF can be used to find the most efficient way to divide resources among different teams or tasks, ensuring fair distribution and optimal utilization.
-
Data Compression: In computer science, the GCF is used in algorithms for data compression. By identifying common factors in data streams, compression techniques can reduce storage space and transmission time.
Advanced Concepts Related to GCF
The concept of GCF extends to more complex mathematical ideas:
-
Modular Arithmetic: GCF plays a crucial role in modular arithmetic, which is used in cryptography and other areas of computer science.
-
Diophantine Equations: GCF is essential in solving Diophantine equations, which are algebraic equations where only integer solutions are considered.
-
Abstract Algebra: The concept of GCF generalizes to abstract algebra, where it's studied in the context of rings and ideals.
Conclusion: The Significance of Finding the GCF
Finding the greatest common factor of 26 and 39, as demonstrated through various methods, is not just a basic arithmetic exercise. It highlights the fundamental concepts of number theory and unveils its broad applications across multiple fields. Understanding GCF is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and tackling more advanced mathematical problems. Its practical applications range from baking to computer science, showcasing the importance of this seemingly simple concept in various aspects of life. Mastering the calculation of GCF equips you with a valuable tool for solving problems and understanding the intricate world of numbers. The seemingly simple question, "What is the greatest common factor of 26 and 39?" opens the door to a rich and fascinating exploration of mathematical principles and their real-world relevance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 50 As A Fraction
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Protons Are In The Element Gold
Mar 17, 2025
-
Is Boiling Water Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 2
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 65 In A Fraction
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 26 And 39 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
