How Many Protons Are In The Element Gold
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
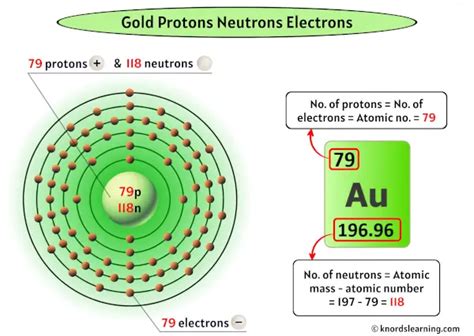
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Are in the Element Gold? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Gold. The word conjures images of shimmering treasures, ancient empires, and timeless elegance. But beyond its cultural significance and inherent beauty lies a fascinating world of atomic structure, a world governed by fundamental particles and their interactions. This article delves into the core of gold's atomic makeup, specifically answering the question: how many protons are in the element gold? We'll explore the concept of atomic number, isotopes, and the role of protons in defining an element's identity and properties.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Building Blocks of Matter
Before we pinpoint the number of protons in gold, it's crucial to understand the basic structure of an atom. Atoms are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. Each atom consists of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also located in the nucleus.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in shells or energy levels.
The nucleus, the atom's dense central core, contains both protons and neutrons. The electrons, much lighter than protons and neutrons, occupy the space surrounding the nucleus. The arrangement of these particles dictates an atom's properties and behavior.
Atomic Number: The Defining Characteristic of an Element
The atomic number of an element is a fundamental property that defines its identity. This number represents the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom of that element. It's a unique identifier; no two elements have the same atomic number. This is the key to understanding how many protons are in gold.
The periodic table, a beautifully organized chart of elements, arranges elements based on their increasing atomic numbers. Each element occupies a specific position, reflecting its unique atomic structure and properties.
Gold's Atomic Number: Unraveling the Mystery
Now, let's focus on gold (Au). Gold's atomic number is 79. This means that every atom of gold contains 79 protons in its nucleus. This is not merely a coincidence; it's the defining characteristic that sets gold apart from all other elements. The presence of 79 protons dictates gold's unique chemical and physical properties, such as its malleability, ductility, high density, and characteristic yellow luster.
The Significance of 79 Protons
The 79 protons in a gold atom are not just a numerical value; they are responsible for:
-
Defining Gold's Identity: The 79 protons are the definitive characteristic that makes it gold. Changing the number of protons transforms the element into something else entirely.
-
Determining Chemical Behavior: The arrangement of electrons, which is dictated by the number of protons, determines how gold interacts with other elements and forms chemical bonds. This is what allows gold to be relatively unreactive, contributing to its resistance to corrosion.
-
Influencing Physical Properties: The number of protons, along with the number of neutrons and electrons, significantly influences the density, melting point, and other physical attributes of gold. The large number of protons contributes to gold's high density.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Count
While the number of protons defines an element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Gold has several isotopes, all with 79 protons but varying numbers of neutrons. The most common isotope of gold is Gold-197 (¹⁹⁷Au), with 79 protons and 118 neutrons.
The different isotopes of gold have very similar chemical properties because the number of protons and electrons remains the same. However, their physical properties, such as mass and radioactive decay behavior, can differ slightly. Some gold isotopes are radioactive, meaning they undergo decay over time, transforming into other elements.
Beyond Protons: The Role of Electrons and Neutrons
While protons define the element, electrons and neutrons also play crucial roles:
-
Electrons: These negatively charged particles determine the atom's chemical behavior. They participate in chemical bonding and interactions with other atoms. Gold's electronic configuration accounts for its low reactivity.
-
Neutrons: These neutral particles contribute to the atom's mass and stability. The number of neutrons can affect the stability of an isotope, leading to radioactive decay in some cases. The different neutron counts in gold isotopes don't significantly change its chemical properties.
Gold's Properties and Applications: A Consequence of Atomic Structure
The unique atomic structure of gold, particularly its 79 protons, leads to a set of distinctive properties that have made it highly valued throughout history.
-
Malleability and Ductility: Gold can be easily hammered into thin sheets (malleability) and drawn into wires (ductility), owing to its specific atomic arrangement and bonding.
-
High Density: Gold is a very dense metal, thanks in part to the presence of a large number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
-
Electrical Conductivity: Gold is an excellent conductor of electricity, which is linked to the behavior of its electrons.
-
Inertness: Gold is relatively unreactive, which means it resists corrosion and tarnishing, contributing to its durability and value.
These properties explain gold's wide range of applications, including jewelry, electronics, dentistry, and investments. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for use in electronics, while its beauty and malleability have made it a prized material for jewelry for millennia.
Conclusion: The Proton's Reign in Gold's Identity
In summary, the answer to the question "How many protons are in the element gold?" is definitively 79. This atomic number is the defining characteristic of gold, differentiating it from all other elements. The 79 protons are the core of gold's identity, determining its chemical behavior and contributing significantly to its unique physical properties. The number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes of gold, but the 79 protons remain constant, upholding gold's place on the periodic table and its status as a precious and versatile metal. Understanding the atomic structure of gold, particularly the role of its 79 protons, provides a deeper appreciation for this remarkable element and its enduring significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Integral Of X 2e X 2
Mar 17, 2025
-
In What Type Of Rock Are Fossils Usually Found
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Are The Common Factors Of 36 And 60
Mar 17, 2025
-
Draw The Product Of The Hydration Of 2 Butene
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lewis Acid And Base Vs Bronsted
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Are In The Element Gold . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
