What Is The Gcf Of 20 And 16
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
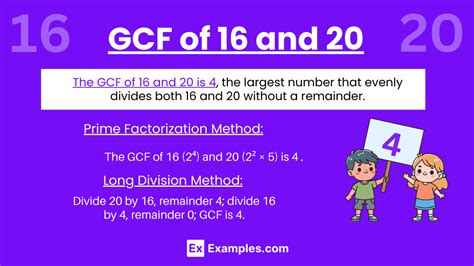
Table of Contents
What is the GCF of 20 and 16? A Deep Dive into Greatest Common Factors
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it is crucial for a strong foundation in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will explore the GCF of 20 and 16, delving into multiple approaches to arrive at the solution and exploring the broader applications of GCF in various mathematical contexts. We'll also look at how understanding GCF can enhance problem-solving skills and provide a deeper appreciation for number theory.
Understanding Greatest Common Factors (GCF)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the GCF of 20 and 16, let's define what a greatest common factor actually is. The GCF, also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest number that divides exactly into two or more numbers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that is a factor of all the numbers in question.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. The factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The common factors of 12 and 18 are 1, 2, 3, and 6. The greatest of these common factors is 6, therefore the GCF of 12 and 18 is 6.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 20 and 16
There are several reliable methods to determine the GCF of 20 and 16. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Factors
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list all the factors of each number and then identify the largest factor common to both.
- Factors of 20: 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20
- Factors of 16: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
The common factors of 20 and 16 are 1, 2, and 4. The greatest of these is 4. Therefore, the GCF of 20 and 16 is 4.
2. Prime Factorization
This method involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves. Then, we identify the common prime factors and multiply them together to find the GCF.
- Prime factorization of 20: 2 x 2 x 5 = 2² x 5
- Prime factorization of 16: 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 2⁴
The common prime factor is 2. The lowest power of 2 present in both factorizations is 2². Therefore, the GCF is 2² = 4.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
This is a more efficient method for larger numbers. The Euclidean algorithm is based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal.
Let's apply it to 20 and 16:
- 20 = 1 x 16 + 4
- 16 = 4 x 4 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 4, therefore the GCF of 20 and 16 is 4.
Applications of GCF in Real-World Scenarios
Understanding GCF extends beyond simple arithmetic exercises. It has practical applications in various fields:
1. Simplifying Fractions
GCF is essential for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. To simplify a fraction, we divide both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF. For example, to simplify the fraction 20/16, we divide both by their GCF, which is 4: 20/4 = 5 and 16/4 = 4, resulting in the simplified fraction 5/4.
2. Geometry and Measurement
GCF is useful in solving geometry problems involving area and perimeter calculations. For example, if you need to tile a rectangular floor with square tiles of equal size, finding the GCF of the length and width of the floor will determine the largest possible square tile that can be used without any cutting or waste.
3. Sharing and Division Problems
GCF helps solve problems involving fair sharing. If you have 20 apples and 16 oranges to distribute equally among several people, the GCF will tell you the maximum number of people you can share them with equally without having any leftovers of either fruit. In this case, the GCF of 20 and 16 (4) indicates you can share them equally among 4 people.
4. Number Theory and Cryptography
GCF plays a vital role in advanced mathematical fields such as number theory and cryptography. Algorithms like the Euclidean algorithm are fundamental to many cryptographic systems, ensuring secure data transmission.
Extending the Concept: GCF of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the GCF of more than two numbers. For instance, to find the GCF of 20, 16, and 12:
Method 1: Listing Factors: Find the factors of each number and identify the largest common factor.
Method 2: Prime Factorization: Find the prime factorization of each number, and identify the common prime factors raised to their lowest powers.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm (extended): First, find the GCF of two numbers using the Euclidean Algorithm, and then find the GCF of the result and the third number, and so on.
Conclusion: Mastering GCF for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding the greatest common factor is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency. Whether you're simplifying fractions, solving geometry problems, or delving into more advanced mathematical concepts, the ability to efficiently calculate GCF is invaluable. By mastering various methods like listing factors, prime factorization, and the Euclidean algorithm, you equip yourself with versatile tools to tackle a wide range of mathematical challenges. The seemingly simple task of finding the GCF of 20 and 16 opens the door to a deeper appreciation of number theory and its far-reaching applications. Remember, practice is key to solidifying your understanding and improving your skills. Continuously challenge yourself with different problems, and you will find your mathematical abilities growing exponentially.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 And 10
Mar 17, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 40
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Convert Wavelength To Meters
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Argon
Mar 17, 2025
-
1 1 X 2 Power Series
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Gcf Of 20 And 16 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
