What Is The Absolute Value Of -6
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
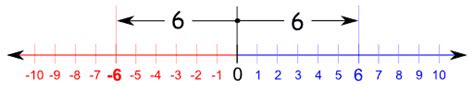
Table of Contents
What is the Absolute Value of -6? A Deep Dive into Absolute Value
The seemingly simple question, "What is the absolute value of -6?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of a fundamental mathematical concept: absolute value. While the answer itself is straightforward (6), understanding the why behind it unveils crucial insights into its applications in various fields, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and beyond. This comprehensive article will delve into the meaning of absolute value, explore its properties, and illustrate its significance with real-world examples.
Understanding Absolute Value: Distance from Zero
At its core, the absolute value of a number represents its distance from zero on the number line. This distance is always non-negative, regardless of whether the number is positive or negative. Therefore, the absolute value of -6 is 6, because -6 is 6 units away from zero.
We represent the absolute value of a number using vertical bars: |x|. So, |-6| = 6. Similarly, |6| = 6. The absolute value function essentially "strips away" the negative sign, leaving only the magnitude of the number.
Visualizing Absolute Value on the Number Line
Imagine a number line stretching infinitely in both directions. Zero sits at the center. Positive numbers extend to the right, and negative numbers extend to the left. The absolute value of any number is the distance you'd need to travel along this line to reach that number from zero.
- Positive numbers: For positive numbers like 5, the absolute value is simply the number itself: |5| = 5.
- Negative numbers: For negative numbers like -5, the absolute value is the positive equivalent: |-5| = 5.
- Zero: The absolute value of zero is zero: |0| = 0.
Defining Absolute Value Mathematically
Formally, the absolute value function can be defined as follows:
|x| = { x, if x ≥ 0 {-x, if x < 0
This piecewise function states that:
- If x is greater than or equal to zero (non-negative), the absolute value of x is x itself.
- If x is less than zero (negative), the absolute value of x is the negative of x (making it positive).
Properties of Absolute Value
Absolute value possesses several crucial properties that are essential for understanding its behavior and applications:
- Non-negativity: |x| ≥ 0 for all real numbers x. The absolute value is always greater than or equal to zero.
- Identity property: |x| = x if x ≥ 0. The absolute value of a non-negative number is the number itself.
- Even function: |-x| = |x| for all real numbers x. The absolute value function is an even function, meaning it is symmetric about the y-axis.
- Multiplicative property: |xy| = |x||y| for all real numbers x and y. The absolute value of a product is the product of the absolute values.
- Triangle inequality: |x + y| ≤ |x| + |y| for all real numbers x and y. This inequality states that the absolute value of a sum is less than or equal to the sum of the absolute values.
Applications of Absolute Value
The concept of absolute value extends far beyond simple arithmetic. It plays a critical role in numerous areas:
1. Measuring Distance and Differences
Absolute value is fundamental in calculating distances. For example, the distance between two points on a number line, say a and b, is given by |a - b|. This ensures the distance is always positive, regardless of the order of the points.
2. Error Analysis and Tolerance
In engineering and science, absolute value helps quantify errors and tolerances. The absolute difference between a measured value and an expected value indicates the magnitude of the error, independent of whether the measurement is too high or too low.
3. Computer Programming
Absolute value functions are built-in features in most programming languages. They are essential for tasks like:
- Finding the distance between two points in a coordinate system.
- Implementing algorithms that require only the magnitude of a quantity.
- Handling numerical errors and comparisons.
4. Physics and Engineering
Absolute value finds applications in various physical phenomena, such as:
- Calculating the magnitude of vectors: Vectors have both magnitude and direction; absolute value gives the magnitude.
- Analyzing oscillations and vibrations: The amplitude of an oscillation is often represented using absolute value.
- Determining the absolute error in measurements.
5. Statistics and Probability
In statistics, absolute value is used in calculations involving:
- Mean absolute deviation: A measure of the variability of data.
- Median absolute deviation: Another measure of variability, less sensitive to outliers.
- L1 norm: Used in regression analysis and other statistical techniques.
6. Calculus and Analysis
Absolute value appears in various advanced mathematical concepts, including:
- Piecewise functions: Defining functions with different behaviors in different intervals.
- Derivatives and integrals: The derivative of the absolute value function is not defined at zero, leading to interesting analytical challenges.
- Optimization problems: Absolute value can be used to formulate constraints and objectives.
Solving Equations and Inequalities Involving Absolute Value
Solving equations and inequalities that include absolute value requires careful consideration of the definition of absolute value.
Example 1: Solving an equation
Solve for x: |x - 3| = 5
This equation means that the distance between x and 3 is 5. Thus, x can be either 8 (5 units to the right of 3) or -2 (5 units to the left of 3). The solutions are x = 8 and x = -2.
Example 2: Solving an inequality
Solve for x: |x + 2| < 4
This inequality states that the distance between x and -2 is less than 4. This means x must be between -6 and 2. The solution is -6 < x < 2.
Advanced Concepts: Absolute Value and Complex Numbers
The concept of absolute value extends even to complex numbers. For a complex number z = a + bi, where 'a' and 'b' are real numbers and 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1), the absolute value (or modulus) of z is denoted as |z| and is calculated as:
|z| = √(a² + b²)
This represents the distance of the complex number from the origin in the complex plane.
Conclusion: The Importance of Absolute Value
The absolute value of -6, while seemingly simple, serves as a gateway to understanding a powerful and ubiquitous mathematical concept. Its properties and applications span numerous fields, highlighting its significance in various branches of mathematics, science, engineering, and computer science. Understanding absolute value is not merely about calculating distances; it's about grasping a fundamental tool for representing magnitudes, handling errors, and solving a wide range of problems across diverse disciplines. From the basic number line to advanced calculus and beyond, the absolute value function plays a crucial, often understated, role in the mathematical landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Muscle Subdivides The Ventral Body Cavity
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Are Three Main Ideas Of The Cell Theory
Mar 28, 2025
-
Hcl Ba Oh 2 Balanced Equation
Mar 28, 2025
-
7x 2y 13 X 2y 11
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is Digesting Food A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Absolute Value Of -6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
