What Is One Sixth As A Decimal
listenit
Apr 02, 2025 · 5 min read
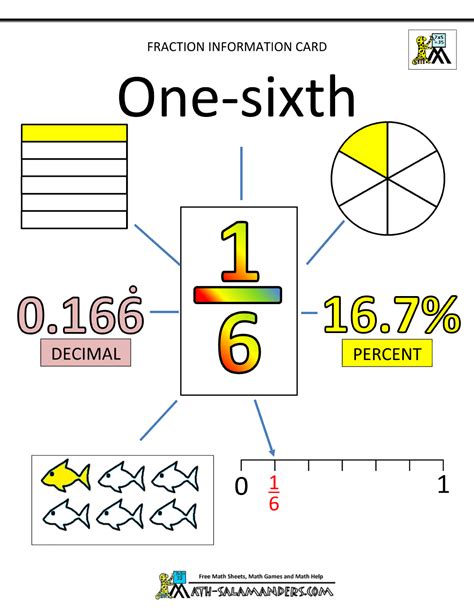
Table of Contents
What is One Sixth as a Decimal? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding fractions and their decimal equivalents is fundamental to mathematics and numerous real-world applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion of the fraction one-sixth (1/6) into its decimal representation, exploring various methods and their underlying principles. We'll also examine the practical applications of this conversion and address frequently asked questions.
Understanding Fractions and Decimals
Before we dive into the conversion of 1/6, let's refresh our understanding of fractions and decimals. A fraction represents a part of a whole, expressed as a ratio of two integers: the numerator (top number) and the denominator (bottom number). A decimal is a way of writing a number using a base-ten system, where digits to the right of the decimal point represent tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
Converting a fraction to a decimal involves dividing the numerator by the denominator. This process can yield a terminating decimal (a decimal with a finite number of digits) or a repeating decimal (a decimal with a digit or group of digits that repeat infinitely).
Converting 1/6 to a Decimal: The Long Division Method
The most straightforward method for converting 1/6 to a decimal is through long division. We divide the numerator (1) by the denominator (6):
1 ÷ 6 = ?
Since 6 does not divide evenly into 1, we add a decimal point and a zero to the dividend (1), making it 1.0. Now we perform the long division:
0.1666...
6 | 1.0000
- 0
10
- 6
40
- 36
40
- 36
40
- 36
...
As you can see, the remainder is always 4, leading to an infinitely repeating decimal: 0.1666... This is often represented as 0.16̅6 or 0.16̄, where the bar indicates the repeating digit or digits.
Understanding Repeating Decimals
The repeating decimal nature of 1/6's decimal equivalent is a key characteristic. Not all fractions convert to terminating decimals; some produce repeating decimals, reflecting the inherent relationship between the numerator and denominator. The denominator's prime factorization plays a critical role: if the denominator contains prime factors other than 2 and 5 (the prime factors of 10), the resulting decimal will be repeating. Since 6's prime factorization is 2 x 3, containing the prime factor 3, we obtain a repeating decimal.
Alternative Methods for Conversion
While long division is the most fundamental approach, other methods can be employed to convert 1/6 to a decimal:
- Using a Calculator: Most calculators can directly perform the division 1 ÷ 6, providing the decimal equivalent (0.16666... or a similar representation). However, understanding the underlying process remains crucial.
- Conversion to an Equivalent Fraction: While not directly converting to a decimal, we can convert 1/6 to an equivalent fraction with a denominator that is a power of 10. However, this is not possible with 1/6 as 10 only has 2 and 5 as prime factors.
Practical Applications of 1/6 as a Decimal
The decimal equivalent of 1/6 finds application in various fields:
- Engineering and Design: Precise calculations involving ratios and proportions frequently necessitate the use of decimal equivalents.
- Finance and Accounting: Calculations involving interest rates, discounts, or profit margins might involve fractions that need conversion to decimals for easier computation.
- Data Analysis and Statistics: Working with datasets often requires converting fractions into decimals for statistical analysis and representation.
- Scientific Calculations: Many scientific formulas and equations utilize decimal numbers for precision and ease of computation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is 0.1666... an exact representation of 1/6?
A1: No, 0.1666... is an approximation of 1/6. The decimal representation is infinitely repeating, so any finite representation will be an approximation.
Q2: How many decimal places should I use when representing 1/6 as a decimal?
A2: The required number of decimal places depends on the context. For most applications, using a few decimal places (e.g., 0.167) is sufficient, but for high-precision calculations, more decimal places might be necessary. The number of decimal places required is determined by the accuracy needed for the specific application.
Q3: What are some common errors made when converting fractions to decimals?
A3: Common errors include: incorrectly placing the decimal point, truncating the decimal representation prematurely (especially with repeating decimals), and misinterpreting repeating decimal patterns.
Q4: How can I check if my decimal conversion is accurate?
A4: You can check the accuracy of your conversion by multiplying the decimal by the original denominator. If the result is approximately equal to the numerator, then the conversion is accurate. For example, 0.1666... * 6 ≈ 1.
Q5: Are there any other fractions that produce repeating decimals?
A5: Yes, many fractions produce repeating decimals. Generally, any fraction whose denominator contains prime factors other than 2 and 5 will yield a repeating decimal. Examples include 1/3, 1/7, 1/9, and many others.
Conclusion
Converting fractions to decimals is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications. The conversion of 1/6 to its decimal equivalent (0.16̅6) exemplifies the process of long division and highlights the concept of repeating decimals. Understanding this conversion is crucial for accuracy and efficiency in various mathematical, scientific, and practical contexts. By mastering this fundamental concept, you enhance your mathematical proficiency and equip yourself to tackle more complex calculations and applications. Remember to always consider the required level of precision depending on the context of your problem.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Explain Why Chemical Equations Have To Be Balanced
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Do You Write 10 As A Fraction
Apr 03, 2025
-
Why Are Ionic Substances Soluble In Water
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Ml In A Dropper
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Many Bonds Does Boron Make
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is One Sixth As A Decimal . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
