How Many Bonds Does Boron Make
listenit
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
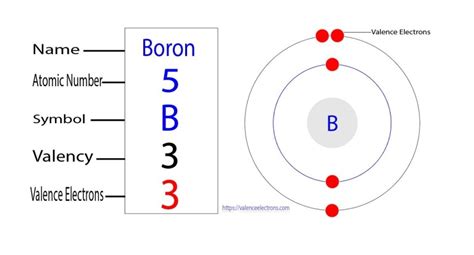
Table of Contents
How Many Bonds Does Boron Make? Understanding Boron's Bonding Behavior
Boron, a fascinating element residing in Group 13 of the periodic table, presents a unique challenge to our understanding of chemical bonding. Unlike its heavier congeners, aluminum, gallium, indium, and thallium, which predominantly exhibit a +3 oxidation state, boron displays a more nuanced bonding behavior. The question, "How many bonds does boron make?" doesn't have a simple, single-number answer. Instead, the number of bonds boron forms is highly dependent on its chemical environment and the nature of the interacting atoms. This article delves into the complexities of boron bonding, exploring its tendency to form electron-deficient compounds and the factors that influence its bonding capabilities.
Boron's Electronic Configuration and its Implications for Bonding
Boron possesses an electronic configuration of 1s²2s²2p¹. This configuration suggests that boron has only three valence electrons available for bonding. Therefore, one might initially expect boron to exclusively form three covalent bonds, achieving a stable octet. However, this simplistic view fails to capture the richness and complexity of boron chemistry.
The Octet Rule and its Limitations in Boron Chemistry
The octet rule, while a useful guideline for understanding the bonding in many elements, frequently breaks down when applied to boron. Boron readily forms compounds with only three bonds, leading to electron-deficient structures. These electron-deficient species are characterized by fewer than eight valence electrons around the boron atom. This deficiency explains the unique reactivity and bonding characteristics of boron compounds.
Electron-Deficient Bonding in Boron Compounds
The formation of electron-deficient compounds is a hallmark of boron's chemical behavior. This is often observed in boron's halides (BF3, BCl3, BBr3, BI3) and other compounds.
Boron Trihalides: A Case Study in Electron Deficiency
Let's consider boron trifluoride (BF3) as a prime example. Boron in BF3 forms three sigma bonds with three fluorine atoms. However, this leaves the boron atom with only six valence electrons, two short of a complete octet. To compensate for this electron deficiency, BF3 acts as a Lewis acid, readily accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base, such as ammonia (NH3). This interaction leads to the formation of a coordinate covalent bond, expanding the coordination number of boron to four.
BF3 + NH3 → F3B-NH3
This adduct formation illustrates boron's capability to expand its coordination number beyond three when provided with sufficient electron density from a Lewis base.
Other Examples of Electron-Deficient Boron Compounds
Electron deficiency isn't limited to the trihalides. Boranes (compounds containing boron and hydrogen) also exhibit this characteristic. For instance, diborane (B2H6) possesses a unique structure involving three-center two-electron bonds. These bonds arise from the electron deficiency of boron and represent a fascinating deviation from the conventional two-center two-electron bonds.
Factors Influencing the Number of Bonds Formed by Boron
Several factors influence the number of bonds boron forms:
1. Electronegativity of the Bonded Atom
The electronegativity of the atom bonding with boron significantly impacts the number of bonds formed. Highly electronegative atoms such as fluorine tend to attract the electron density away from boron, leading to stronger electron deficiency and the possibility of forming more bonds upon interaction with Lewis bases. Less electronegative atoms may not exert as strong of a pull, leaving boron in a state where fewer additional bonds are favorable.
2. Steric Effects
The size and shape of the ligands bonded to boron influence its bonding behavior. Bulky ligands can hinder the approach of other atoms or molecules, limiting the number of bonds that boron can potentially form.
3. Nature of the Reaction
The reaction conditions, including the presence of other reactants, solvents, and temperature, play a critical role in determining the final bonding state of boron.
4. Presence of Lewis Bases
The availability of Lewis bases profoundly influences boron's bonding. As seen with BF3, the presence of Lewis bases can lead to the formation of adducts, effectively increasing the number of bonds around the boron atom from three to four.
Boron's Coordination Number: Beyond Three
While boron typically forms three bonds, leading to an electron-deficient state, its coordination number can be greater than three under certain circumstances. The coordination number represents the number of atoms directly bonded to boron. The formation of adducts with Lewis bases, as described earlier, increases the coordination number to four. Further, boron can exhibit higher coordination numbers in more complex structures.
Organoboron Compounds and Higher Coordination Numbers
In organoboron compounds, boron can achieve higher coordination numbers depending on the nature of the organic ligands. Steric and electronic factors play a significant role in determining the final coordination number.
Conclusion: The Versatility of Boron Bonding
The question of how many bonds boron makes is not answered by a single number. While boron typically forms three covalent bonds, resulting in electron-deficient species, it displays considerable versatility in its bonding behavior. The number of bonds can increase upon interaction with Lewis bases, reaching higher coordination numbers in certain situations. The electronegativity of the bonding partner, steric effects, reaction conditions, and the presence of Lewis bases all exert significant influence on boron's bonding capabilities. The complexity of boron's bonding makes it a fascinating area of study, highlighting the limitations of simple bonding models and showcasing the diversity of chemical interactions. Understanding these factors helps in predicting and explaining the properties and reactivity of a wide range of boron-containing compounds, which find applications in numerous fields, including medicine, materials science, and catalysis. Further research continues to unravel the subtle intricacies of this remarkable element's bonding behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Natural Resources In The Northeast Region
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Negative Square Root Of 64
Apr 04, 2025
-
Anything That Takes Up Space And Has Mass Is
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Mm Are In 50 Cm
Apr 04, 2025
-
3x 2y 16 In Slope Intercept Form
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Bonds Does Boron Make . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
