What Is Lcm Of 9 And 15
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
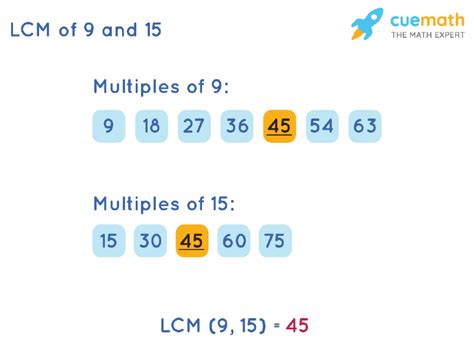
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 9 and 15? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and different methods for calculating the LCM opens up a world of mathematical possibilities. This article delves into the intricacies of finding the LCM of 9 and 15, exploring various methods and highlighting their practical applications. We’ll go beyond a simple answer and explore the broader significance of LCMs in mathematics and everyday life.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 9 and 15, let's solidify our understanding of what an LCM actually is. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of the numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that both numbers divide into evenly.
Think of it like this: imagine you have two gears, one with 9 teeth and the other with 15 teeth. The LCM represents the number of rotations it takes for both gears to simultaneously return to their starting positions. This analogy highlights the practical applications of LCMs in various fields, including engineering and scheduling.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method for finding the LCM of relatively small numbers like 9 and 15 is by listing their multiples.
Step 1: List the multiples of 9:
9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, ...
Step 2: List the multiples of 15:
15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, ...
Step 3: Identify the smallest common multiple:
By comparing the two lists, we can see that the smallest number that appears in both lists is 45. Therefore, the LCM of 9 and 15 is 45.
This method is effective for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome and inefficient when dealing with larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more efficient and systematic method for finding the LCM, especially for larger numbers, involves prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
Step 1: Find the prime factorization of 9:
9 = 3 x 3 = 3²
Step 2: Find the prime factorization of 15:
15 = 3 x 5
Step 3: Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
The prime factors involved are 3 and 5. The highest power of 3 is 3² (from the factorization of 9), and the highest power of 5 is 5¹ (from the factorization of 15).
Step 4: Multiply the highest powers:
LCM(9, 15) = 3² x 5 = 9 x 5 = 45
This method provides a more elegant and scalable solution compared to listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It clearly demonstrates the underlying mathematical structure behind the LCM.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers are closely related. The GCD is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. There's a handy formula connecting the LCM and GCD:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
Where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
Step 1: Find the GCD of 9 and 15:
The factors of 9 are 1, 3, and 9. The factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, and 15. The greatest common factor is 3. Therefore, GCD(9, 15) = 3.
Step 2: Apply the formula:
LCM(9, 15) x GCD(9, 15) = 9 x 15 LCM(9, 15) x 3 = 135 LCM(9, 15) = 135 / 3 = 45
This method utilizes the relationship between LCM and GCD, offering another efficient approach to calculating the LCM. Finding the GCD can sometimes be easier than directly finding the LCM, especially for larger numbers. The Euclidean algorithm is a particularly efficient method for finding the GCD of larger numbers.
Euclidean Algorithm for GCD (Advanced)
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for calculating the GCD of two integers. It's particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where prime factorization becomes more complex. Let's illustrate it with 9 and 15:
Step 1: Divide the larger number (15) by the smaller number (9) and find the remainder:
15 ÷ 9 = 1 with a remainder of 6.
Step 2: Replace the larger number with the smaller number (9) and the smaller number with the remainder (6):
Now we find the GCD of 9 and 6.
Step 3: Repeat the process:
9 ÷ 6 = 1 with a remainder of 3.
Step 4: Repeat again:
6 ÷ 3 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
When the remainder is 0, the GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 3. Once you have the GCD, you can use the formula from Method 3 to calculate the LCM.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of LCM extends beyond theoretical mathematics and finds practical applications in various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine you have two events that occur at regular intervals. The LCM helps determine when both events will coincide. For instance, if one event happens every 9 days and another every 15 days, they will occur together again after 45 days.
-
Engineering: In designing gears, the LCM determines the number of rotations needed for gears with different numbers of teeth to synchronize.
-
Music: LCM is used in musical composition to find the least common multiple of rhythmic patterns to create harmoniously synchronized melodies.
Conclusion: More Than Just a Calculation
Finding the LCM of 9 and 15, while seemingly a simple exercise, highlights the power and elegance of mathematical concepts. We explored several methods, from listing multiples to employing prime factorization and the Euclidean algorithm. Each method offers a different perspective, highlighting the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas. The practical applications of LCM demonstrate its relevance beyond the classroom, showcasing its utility in various real-world situations. Understanding these methods equips you not only to solve specific LCM problems but also to appreciate the broader mathematical principles at play. The LCM is far more than just a calculation; it's a fundamental concept with wide-ranging implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 Square Root Of 3
Mar 16, 2025
-
5 1 2 To Improper Fraction
Mar 16, 2025
-
Graph Of X 1 X 1
Mar 16, 2025
-
The Overall Charge Of The Nucleus Is
Mar 16, 2025
-
Number Of Valence Electrons In S
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Lcm Of 9 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
