What Is A Shape Called With 11 Sides
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
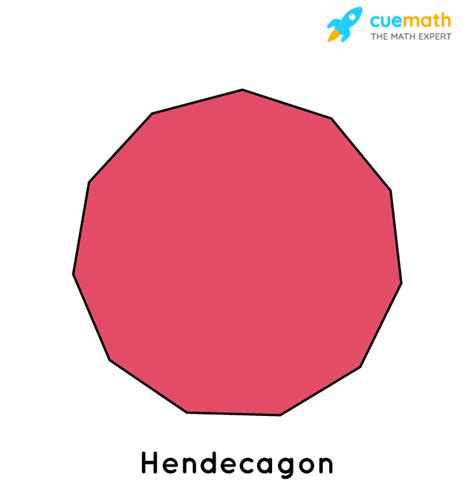
Table of Contents
What is a Shape Called with 11 Sides? Understanding Hendecagons
Have you ever wondered about the name of a shape with 11 sides? While common shapes like triangles, squares, and pentagons are easily recognizable, venturing into the realm of polygons with more sides can lead to less familiar terminology. This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of hendecagons, exploring their properties, characteristics, and applications. Prepare to expand your geometrical knowledge!
Defining the Hendecagon: An 11-Sided Polygon
A hendecagon, also known as an undecagon, is a polygon with eleven sides and eleven angles. The term "hendecagon" is derived from the Greek words "hendeka," meaning eleven, and "gonia," meaning angle. Similarly, "undecagon" uses the Latin prefix "undec," also signifying eleven. Both terms are perfectly acceptable and used interchangeably.
Understanding Polygons: A Quick Refresher
Before we dive deeper into the specifics of hendecagons, let's establish a foundational understanding of polygons in general. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a set of straight line segments. The segments are called sides, and the points where the segments meet are called vertices or corners. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- Nonagon: 9 sides
- Decagon: 10 sides
- Hendecagon/Undecagon: 11 sides
- Dodecagon: 12 sides
And the list continues, with names becoming less common as the number of sides increases.
Properties of a Hendecagon
Like all polygons, a hendecagon possesses several key properties:
Interior Angles
The sum of the interior angles of any polygon can be calculated using the formula: (n - 2) * 180°, where 'n' is the number of sides. For a hendecagon (n = 11), the sum of its interior angles is: (11 - 2) * 180° = 1620°.
If the hendecagon is regular, meaning all its sides and angles are equal, each interior angle measures 1620° / 11 ≈ 147.27°.
Exterior Angles
The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, regardless of whether it's regular or irregular, always equals 360°. In a regular hendecagon, each exterior angle measures 360° / 11 ≈ 32.73°.
Diagonals
A diagonal is a line segment connecting two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. The number of diagonals in a polygon can be calculated using the formula: n(n - 3) / 2, where 'n' is the number of sides. For a hendecagon, the number of diagonals is: 11(11 - 3) / 2 = 44.
Regular vs. Irregular Hendecagons
Hendecagons can be categorized into two main types:
Regular Hendecagon
A regular hendecagon is a hendecagon where all its sides are of equal length, and all its interior angles are equal in measure. It possesses a high degree of symmetry. Constructing a perfect regular hendecagon using only a compass and straightedge is impossible, as 11 is not a Fermat prime.
Irregular Hendecagon
An irregular hendecagon is a hendecagon where its sides and angles are not all equal. It lacks the symmetry of a regular hendecagon and can take on a wide variety of shapes and forms.
Construction of a Hendecagon
Constructing a precise hendecagon, especially a regular one, is challenging. While it's impossible to construct a regular hendecagon using only a compass and straightedge, approximate constructions are possible using various methods, including:
- Using a protractor: Measure each interior angle (approximately 147.27°) and construct the sides accordingly. This method is relatively simple but lacks precision.
- Using geometric software: Computer-aided design (CAD) software provides precise tools for constructing regular and irregular hendecagons.
- Approximation methods: Various mathematical formulas and iterative processes can be used to approximate the construction of a regular hendecagon. These methods often involve trigonometric calculations.
Real-World Applications of Hendecagons
While not as prevalent as other polygons, hendecagons do appear in various contexts:
- Tessellations: Although a regular hendecagon cannot tessellate (tile a plane without gaps or overlaps), irregular hendecagons can be used in certain tessellation designs.
- Architectural design: While less common than other shapes, hendecagons can occasionally appear in architectural structures, particularly in decorative elements or unique designs.
- Art and design: Hendecagons can be found in various artistic creations, from mosaics and stained-glass windows to abstract art. Its unusual number of sides gives it a distinctive visual appeal.
- Engineering and design: While infrequent, hendecagons might feature in specific engineering or design applications where the precise geometry is beneficial. For instance, in the construction of specialized gears or intricate mechanical components.
Hendecagrams: Stars and Polygrams
Related to hendecagons are hendecagrams, which are star polygons formed by connecting vertices of a hendecagon in a specific pattern. Just as with other star polygons, these can exhibit various levels of complexity and visual appeal. The construction of hendecagrams often requires advanced geometric knowledge.
Conclusion: Embracing the Uniqueness of the Hendecagon
The hendecagon, though less familiar than some of its polygonal counterparts, holds a unique place in the world of geometry. Its eleven sides and angles offer a fascinating exploration into the properties and characteristics of polygons with a larger number of sides. Understanding the hendecagon enriches our appreciation for the diversity and complexity of geometric shapes and their applications in various fields. Whether it's its mathematical properties, its potential in design, or its relative rarity, the hendecagon presents an intriguing subject worthy of further investigation. The complexity of creating accurate hendecagons also highlights the power of computer-aided design tools in achieving precise geometric constructions, surpassing the limitations of traditional methods. From its definition to its applications, the hendecagon demonstrates the continuous and fascinating world of mathematics and geometry, even extending to star polygons and tessellations. Its unusual nature keeps it interesting and engaging, suitable for exploration by students, mathematicians, and design enthusiasts alike. Its uniqueness, challenges in construction, and potential applications make it a significant element within geometry and further applications across other disciplines. By understanding the hendecagon, we gain a deeper appreciation for the world of polygons and their diverse properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Event Had An Enormous Effect On Us Workplace Safety
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 2 5 As A Percent
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Is Element Different From Compound
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 18 24 As A Percent
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 70 Percent Of 200
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Shape Called With 11 Sides . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
