What Is A Prime Factorization Of 44
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
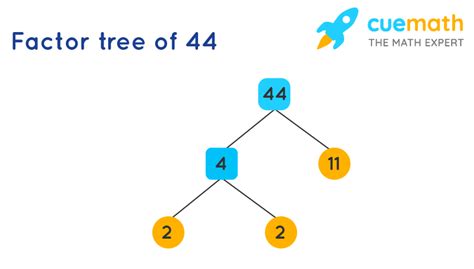
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 44? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Prime factorization. The term itself might sound intimidating, conjuring up images of complex mathematical equations and endless calculations. But the core concept is surprisingly straightforward, and understanding it unlocks a world of mathematical possibilities. This article will explore the prime factorization of 44, delve into the foundational concepts of prime numbers and factorization, and show you how to apply this knowledge to other numbers. We'll even explore some advanced applications and related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 44, let's establish a solid understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The sequence continues infinitely.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Greater than 1: 1 is not considered a prime number.
- Infinite Sequence: There are infinitely many prime numbers.
Understanding prime numbers is crucial because they are the building blocks of all other whole numbers through a process called prime factorization.
What is Factorization?
Factorization, also known as prime factorization or integer factorization, is the process of breaking down a composite number (a number greater than 1 that is not prime) into its prime factors. These factors are the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, equal the original number. Think of it like dissecting a number into its fundamental prime components.
Example: Let's factorize the number 12. 12 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 3. Therefore, the prime factorization of 12 is 2² x 3.
Prime Factorization of 44: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's apply this knowledge to find the prime factorization of 44. We'll use a method called the factor tree.
-
Start with the number: Begin with the number 44.
-
Find the smallest prime factor: The smallest prime number that divides 44 is 2. 44 divided by 2 is 22.
-
Continue factoring: Now we have 22. Again, the smallest prime factor of 22 is 2. 22 divided by 2 is 11.
-
Reach a prime number: We're left with 11, which is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 44 is 2 x 2 x 11, which can be written more concisely as 2² x 11.
Visualizing with a Factor Tree
A factor tree provides a visual representation of the factorization process:
44
/ \
2 22
/ \
2 11
This tree clearly shows how 44 breaks down into its prime factors: 2, 2, and 11.
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization
A fundamental theorem in number theory states that every composite number has a unique prime factorization. This means that no matter what method you use to factorize a number, you'll always arrive at the same set of prime factors (though the order might differ). This uniqueness is incredibly important in various mathematical applications.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers play a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. The security of these systems relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms related to prime factorization are used in various computer science applications, including data compression and hashing.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, forming the basis for numerous theorems and proofs.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Understanding prime factorization is vital for working with modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus).
-
Simplifying Fractions: Prime factorization helps simplify fractions to their lowest terms. By factoring the numerator and denominator, you can identify common factors that cancel out.
Beyond 44: Factoring Larger Numbers
While factoring small numbers like 44 is relatively straightforward, factoring very large numbers can be computationally intensive. For extremely large numbers, even the most powerful computers may take an extraordinarily long time to find the prime factorization. This computational challenge is what makes certain cryptographic systems secure.
Advanced Techniques for Prime Factorization
For larger numbers, more sophisticated techniques are required beyond simple trial division. Some of these include:
-
Trial Division: A basic method of testing divisibility by progressively larger prime numbers. It's inefficient for large numbers.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: A method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It's useful for generating a list of potential divisors.
-
Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that's more efficient than trial division for finding some factors of a composite number.
-
General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large numbers. It's a complex algorithm used to factor numbers with hundreds of digits.
Conclusion: The Importance of Prime Factorization
The prime factorization of 44, as we've seen, is 2² x 11. While seemingly simple, this concept underpins much of number theory and has far-reaching applications in various fields. Understanding prime numbers and the process of prime factorization provides a crucial foundation for further exploration in mathematics and computer science. From cryptography to simplifying fractions, the ability to decompose numbers into their prime components is a fundamental skill with lasting value. The exploration of prime factorization offers a glimpse into the fascinating world of number theory, revealing the elegant structure hidden within the seemingly simple act of dividing numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 20 Is 17
Mar 26, 2025
-
Find Parametric Equations For The Tangent Line To The Curve
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Find The Radius Of A Circle Using Circumference
Mar 26, 2025
-
Ground State Electron Configuration For Bromine
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 2 Go Into 19
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Prime Factorization Of 44 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
