What Is 1.21 Repeating As A Fraction
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 4 min read
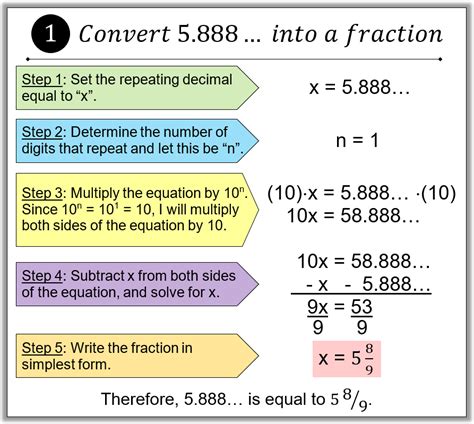
Table of Contents
- What Is 1.21 Repeating As A Fraction
- Table of Contents
- What is 1.212121... as a Fraction? Unlocking the Mystery of Repeating Decimals
- Understanding Repeating Decimals
- The Method: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Generalizing the Method: Converting Any Repeating Decimal
- The Importance of Understanding Repeating Decimals and Fractions
- Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
- Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
- Conclusion: Mastering Repeating Decimals
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is 1.212121... as a Fraction? Unlocking the Mystery of Repeating Decimals
Have you ever encountered a repeating decimal like 1.212121...? It looks simple enough, but converting it into a fraction can seem a bit daunting. Fear not! This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, explaining the underlying concepts and providing you with a step-by-step solution. We'll also explore the broader topic of converting repeating decimals to fractions, equipping you with the skills to tackle similar problems.
Understanding Repeating Decimals
Repeating decimals, also known as recurring decimals, are numbers that have a digit or a group of digits that repeat infinitely after the decimal point. In our case, the digits "21" repeat endlessly. We represent this using a bar over the repeating part: 1.$\overline{21}$. Understanding this notation is crucial for the conversion process.
The Method: A Step-by-Step Guide
The key to converting a repeating decimal to a fraction lies in manipulating algebraic equations. Here's how to convert 1.$\overline{21}$:
Step 1: Assign a Variable
Let's represent the repeating decimal with a variable, say x:
x = 1.$\overline{21}$
Step 2: Multiply to Shift the Decimal
We need to manipulate the equation so that the repeating part aligns. Since the repeating block "21" has two digits, we multiply both sides of the equation by 100:
100x = 121.$\overline{21}$
Step 3: Subtract the Original Equation
Now, subtract the original equation (Step 1) from the equation in Step 2:
100x - x = 121.$\overline{21}$ - 1.$\overline{21}$
This cleverly eliminates the repeating part:
99x = 120
Step 4: Solve for x
Divide both sides by 99 to isolate x:
x = 120/99
Step 5: Simplify the Fraction
Finally, simplify the fraction by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 120 and 99. The GCD is 3. Dividing both the numerator and the denominator by 3, we get:
x = 40/33
Therefore, 1.$\overline{21}$ as a fraction is 40/33.
Generalizing the Method: Converting Any Repeating Decimal
The method described above can be adapted for any repeating decimal. The key is to multiply by a power of 10 that shifts the repeating block to align perfectly. The power of 10 will be 10<sup>n</sup>, where 'n' is the number of digits in the repeating block.
Let's look at a few examples to illustrate this:
Example 1: 0.$\overline{7}$
- x = 0.$\overline{7}$
- 10x = 7.$\overline{7}$
- 10x - x = 7.$\overline{7}$ - 0.$\overline{7}$ => 9x = 7
- x = 7/9
Example 2: 0.$\overline{142857}$
- x = 0.$\overline{142857}$
- 1000000x = 142857.$\overline{142857}$
- 1000000x - x = 142857.$\overline{142857}$ - 0.$\overline{142857}$ => 999999x = 142857
- x = 142857/999999 (This simplifies to 1/7)
Example 3: 2.3$\overline{1}$
This example includes a non-repeating part. We handle it slightly differently:
- x = 2.3$\overline{1}$
- 10x = 23.$\overline{1}$
- 100x = 231.$\overline{1}$
- 100x - 10x = 231.$\overline{1}$ - 23.$\overline{1}$ => 90x = 208
- x = 208/90 = 104/45
Notice how we multiplied by 10 to isolate the repeating part and then by 100 to align it for subtraction. The non-repeating part is incorporated into the final fraction.
The Importance of Understanding Repeating Decimals and Fractions
The ability to convert repeating decimals to fractions is not just a mathematical curiosity; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Engineering and Physics: Precise calculations often require fractional representations for accuracy. Repeating decimals can arise in measurements and calculations involving ratios and proportions.
-
Computer Science: Representing numbers in computers involves translating decimal values into binary formats. Understanding repeating decimals helps in efficient data representation and handling.
-
Finance and Accounting: Accurate calculations of interest, taxes, and other financial computations rely on precise numerical representations. Fractions offer greater accuracy than rounded-off decimal values.
-
Mathematics itself: Converting repeating decimals to fractions is a fundamental concept in number theory and analysis. It underpins further mathematical studies and applications.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
While the method detailed above addresses most common scenarios, some repeating decimals require more sophisticated techniques. For instance, repeating decimals that have a non-repeating part before the repeating block need careful consideration, as demonstrated in the last example. Moreover, understanding the concept of limits and infinite series can offer a deeper understanding of the conversion process.
Troubleshooting Common Mistakes
-
Incorrect Multiplication: Ensure you multiply by the correct power of 10 to align the repeating part effectively. Incorrect multiplication will lead to an incorrect fraction.
-
Simplification Errors: Always simplify the fraction to its lowest terms by finding the greatest common divisor of the numerator and denominator.
-
Ignoring Non-Repeating Parts: Carefully consider and incorporate the non-repeating part of the decimal into the conversion process.
Conclusion: Mastering Repeating Decimals
Converting a repeating decimal like 1.$\overline{21}$ to its fractional equivalent (40/33) is a valuable skill with applications across various fields. Mastering this skill provides a deeper understanding of numbers and their representations, improving your problem-solving abilities in mathematics and beyond. Remember the systematic approach, practice with various examples, and don't be afraid to troubleshoot your way to the correct answer. With practice, you'll confidently navigate the world of repeating decimals and fractions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Silicon
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Takes Up Space And Has Mass
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Is Larger 2 3 Or 3 4
Mar 19, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 10 And 14
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration Of Ca2
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 1.21 Repeating As A Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
