What Element Has The Symbol 0
listenit
May 12, 2025 · 6 min read
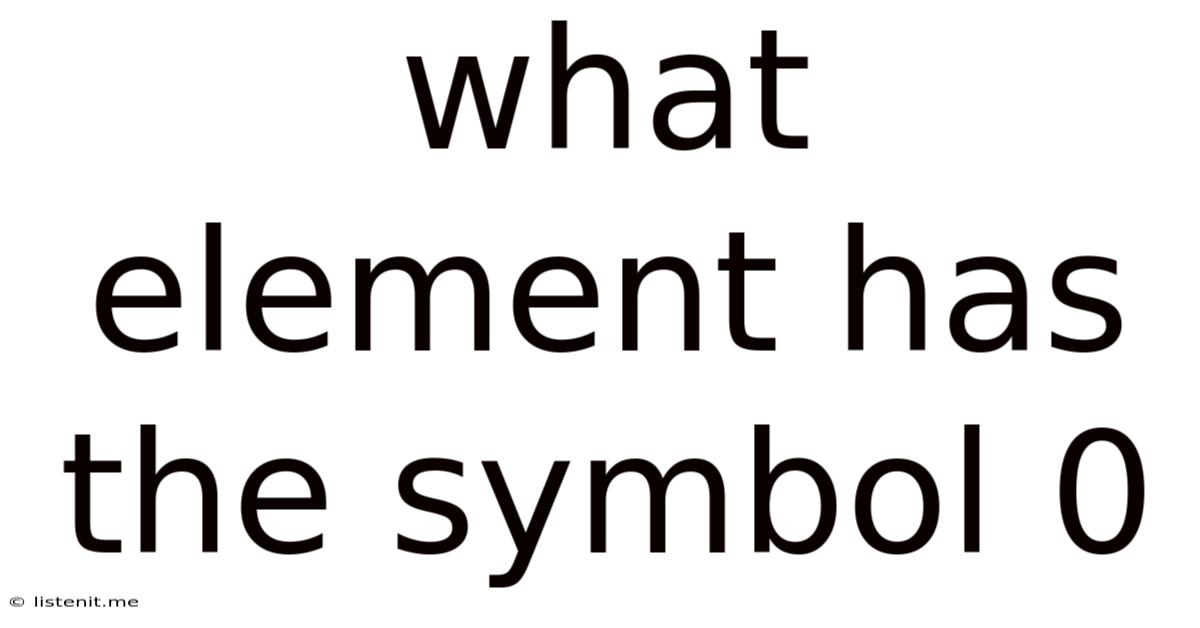
Table of Contents
What Element Has the Symbol O? Unlocking the Secrets of Oxygen
The element with the symbol O is oxygen. This isn't just any element; it's arguably the most crucial element for life as we know it. Understanding oxygen goes beyond simply knowing its symbol; it delves into its properties, its role in various processes, its impact on the environment, and its importance to human existence. This comprehensive article will explore all these facets, providing a detailed look into the fascinating world of oxygen.
Oxygen: An Abundant and Essential Element
Oxygen (O) is a nonmetal in Group 16 of the periodic table, also known as the chalcogens. Its atomic number is 8, meaning it has eight protons in its nucleus. It's highly reactive, readily forming compounds with most other elements. This reactivity stems from its electron configuration, which makes it eager to gain two electrons to achieve a stable octet. This drive for stability underpins many of oxygen's crucial roles in chemical reactions.
Key Properties of Oxygen
-
Gas at Room Temperature: Oxygen exists as a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas under standard conditions. This gaseous nature allows for its easy distribution throughout the atmosphere and its efficient uptake by living organisms.
-
Diatomic Molecule: Oxygen typically exists as a diatomic molecule (O₂), meaning two oxygen atoms are bonded together. This is a crucial aspect of its behavior and reactivity.
-
Allotropes: Besides the common diatomic form (O₂), oxygen also exists as ozone (O₃), a triatomic allotrope. Ozone is a powerful oxidizing agent with a distinct pungent odor, playing a vital role in the stratosphere by absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation.
-
Paramagnetism: Oxygen is paramagnetic, meaning it's weakly attracted to a magnetic field. This property arises from the presence of unpaired electrons in its molecular orbitals.
-
High Electronegativity: Oxygen possesses high electronegativity, meaning it strongly attracts electrons in chemical bonds. This property contributes to its ability to readily form compounds with other elements, often acting as an oxidizing agent.
The Vital Role of Oxygen in Biological Processes
Oxygen's significance is profoundly intertwined with life itself. Its role in respiration is fundamental to the survival of most living organisms.
Respiration: The Engine of Life
Aerobic respiration, the process of using oxygen to break down glucose and release energy, is the primary energy source for most organisms. This complex process occurs in the mitochondria, the powerhouses of cells. The reaction can be summarized as:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy
This equation shows how glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) reacts with oxygen (O₂) to produce carbon dioxide (CO₂), water (H₂O), and a significant amount of energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). This energy fuels all cellular processes, enabling growth, movement, and reproduction.
Oxygen's Role Beyond Respiration
Beyond respiration, oxygen plays other crucial roles in biological systems. It's a component of water (H₂O), an essential solvent for biological reactions. It's also involved in various metabolic processes, including the oxidation of fats and proteins. Furthermore, oxygen is a key reactant in many enzymatic reactions, driving essential biochemical pathways.
Oxygen in the Environment and Its Impact
Oxygen constitutes approximately 21% of Earth's atmosphere. This abundance is a consequence of photosynthesis, a process by which plants and other photosynthetic organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
Photosynthesis: The Source of Atmospheric Oxygen
The equation for photosynthesis is essentially the reverse of respiration:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This process is responsible for maintaining the oxygen levels in our atmosphere and is critical for the survival of oxygen-dependent life forms. The balance between photosynthesis and respiration maintains a relatively stable level of atmospheric oxygen.
The Ozone Layer: A Protective Shield
The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, plays a critical role in absorbing harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. This absorption is crucial in protecting life on Earth from the damaging effects of UV radiation. Ozone depletion, caused primarily by the release of ozone-depleting substances, poses a significant threat to the environment and human health.
Industrial Applications of Oxygen
Oxygen's reactivity and abundance make it a crucial element in many industrial processes. Its use spans various sectors, demonstrating its versatility and importance beyond biological systems.
Combustion and Welding
Oxygen is essential for combustion, the process of rapid oxidation that releases heat and light. This property is exploited in various industrial applications, including power generation, metal refining, and welding. Oxy-fuel welding, for instance, uses a mixture of oxygen and fuel gas to achieve extremely high temperatures for joining metals.
Chemical Synthesis
Oxygen serves as a crucial reactant in countless chemical syntheses. It's used in the production of various chemicals, including nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and many organic compounds. Its oxidizing power facilitates numerous reactions, providing a vital component for chemical manufacturing.
Medical Applications
Oxygen is crucial in medical applications, particularly in providing respiratory support to patients with breathing difficulties. Oxygen therapy is essential in various medical conditions, improving oxygen saturation levels and enhancing tissue oxygenation.
Water Treatment
Oxygen is used in water treatment processes to break down organic matter and eliminate pollutants. Its oxidizing properties help to improve water quality, making it safe for consumption and other uses.
Oxygen Deficiency and its Consequences
While oxygen is essential for life, its deficiency can have severe consequences. Hypoxia, a condition characterized by insufficient oxygen supply to the body's tissues, can result in various health issues, depending on the severity and duration of the deficiency.
Hypoxia: The Dangers of Oxygen Deprivation
Mild hypoxia can cause fatigue, headaches, and dizziness. Severe hypoxia, however, can lead to organ damage, coma, and even death. High-altitude environments, where atmospheric oxygen pressure is lower, are particularly prone to inducing hypoxia.
The Future of Oxygen Research
Research on oxygen continues to expand our understanding of its properties, functions, and applications. Exploring new avenues of oxygen research holds immense potential for various fields.
Advances in Oxygen Therapy
Ongoing research is focused on developing more efficient and targeted oxygen therapies, improving the delivery of oxygen to tissues and enhancing treatment efficacy. This includes exploring new methods of oxygen delivery and developing novel oxygen carriers.
Environmental Impact of Oxygen
Research continues to investigate the environmental impact of oxygen production and consumption. Understanding the balance between oxygen production and consumption is crucial for maintaining a healthy ecosystem. This involves research into the effects of pollution on oxygen levels and the development of sustainable oxygen production methods.
Exploring Oxygen in Extreme Environments
Research into the presence and role of oxygen in extreme environments, such as deep oceans and space, helps to unravel the conditions that support life and explore the potential for life beyond Earth. This research includes investigating the adaptations of organisms to low-oxygen environments and exploring the potential for oxygen-based life in other planetary systems.
In conclusion, the element with the symbol O, oxygen, is far more than just a chemical symbol; it's a fundamental component of life, a driving force in countless natural and industrial processes, and a subject of ongoing scientific exploration. Its abundance, reactivity, and crucial role in biological systems solidify its importance in the world around us, making its study an enduring quest for scientific understanding and technological advancement. The vast applications and ongoing research surrounding oxygen highlight its continued significance for the future of humanity and our planet.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Do Cot On Ti 84
May 12, 2025
-
Distance From Jupiter To The Sun In Au
May 12, 2025
-
3x 4y 12 Slope Intercept Form
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does Chlorine Have In Its Outer Shell
May 12, 2025
-
Which Gas Has The Slowest Rate Of Diffusion
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Element Has The Symbol 0 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.