What Are The 3 Properties Of Water
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 7 min read
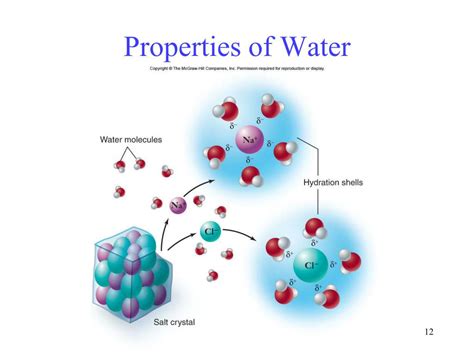
Table of Contents
- What Are The 3 Properties Of Water
- Table of Contents
- What are the 3 Properties of Water? Exploring the Unique Characteristics of H₂O
- 1. High Specific Heat Capacity: Water's Temperature Buffer
- Why is High Specific Heat Capacity Important?
- The Hydrogen Bond Connection: Understanding the Mechanism
- 2. Cohesion and Adhesion: Water's Stickiness and Surface Tension
- Cohesion: Water Sticks to Water
- Adhesion: Water Sticks to Other Substances
- The Hydrogen Bond Factor Again: The Molecular Basis
- 3. Excellent Solvent Properties: The Universal Solvent
- How Water Dissolves Substances
- The Importance of Water's Solvent Properties
- Beyond Simple Dissolution: Water's Complex Interactions
- Conclusion: The Extraordinary Properties of Water
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What are the 3 Properties of Water? Exploring the Unique Characteristics of H₂O
Water. It's the essence of life, covering most of our planet's surface and making up a significant portion of our bodies. But beyond its obvious importance, water possesses a fascinating array of unique properties that stem from its seemingly simple molecular structure: two hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to a single oxygen atom (H₂O). While many properties of water could be discussed, we will focus on three key characteristics: high specific heat capacity, cohesion and adhesion, and excellent solvent properties. Understanding these properties is crucial to grasping the fundamental role water plays in biological systems and the environment.
1. High Specific Heat Capacity: Water's Temperature Buffer
One of the most remarkable properties of water is its high specific heat capacity. This refers to the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius (or one Kelvin). Water has an exceptionally high specific heat capacity (approximately 4.18 J/g°C), significantly higher than most other substances. This means that water can absorb or release a large amount of heat energy with only a small change in temperature.
Why is High Specific Heat Capacity Important?
This seemingly simple property has profound consequences:
-
Temperature Regulation: Water's high specific heat capacity acts as a temperature buffer, preventing drastic temperature fluctuations. This is crucial for maintaining stable temperatures in aquatic environments, protecting aquatic life from extreme temperature changes. It also plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate, moderating temperature swings between day and night and across seasons. Coastal regions, for instance, experience less extreme temperature variations than inland areas due to the influence of the ocean's high heat capacity.
-
Biological Significance: Within organisms, water's high specific heat capacity is critical for maintaining a stable internal temperature. Our bodies are largely composed of water, and this property helps prevent rapid changes in body temperature, protecting our cells and tissues from thermal damage. This is especially important for maintaining enzyme activity, as many enzymes function optimally only within a narrow temperature range.
-
Heat Transfer: The high specific heat capacity of water makes it an efficient medium for heat transfer. This property is exploited in many industrial and technological applications, including cooling systems in power plants and automobiles.
The Hydrogen Bond Connection: Understanding the Mechanism
The exceptional specific heat capacity of water is directly linked to the hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules. Because of the polar nature of the water molecule (oxygen is slightly negative and hydrogen is slightly positive), water molecules are attracted to each other through these relatively weak, but collectively powerful, hydrogen bonds. These bonds require a significant amount of energy to break, which is why it takes a lot of heat energy to raise the temperature of water. When heat is added, the energy is initially used to break these hydrogen bonds rather than increasing the kinetic energy of the molecules (which would manifest as a temperature increase).
2. Cohesion and Adhesion: Water's Stickiness and Surface Tension
Water molecules exhibit strong cohesion and adhesion properties. Cohesion refers to the attraction between molecules of the same substance, while adhesion refers to the attraction between molecules of different substances. Both of these properties are essential for many biological processes and environmental phenomena.
Cohesion: Water Sticks to Water
The cohesive forces between water molecules are responsible for several important features:
-
Surface Tension: The strong cohesive forces at the surface of water create surface tension, a phenomenon where the surface of the liquid acts like a stretched elastic membrane. This allows certain insects, such as water striders, to walk on water. Surface tension also plays a role in capillary action.
-
Water Transport in Plants: Cohesion is crucial for the transport of water from the roots to the leaves of plants through a process called transpiration. Water molecules adhere to each other, forming a continuous column that extends from the roots to the leaves. As water evaporates from the leaves, the cohesive forces pull more water up from the roots.
Adhesion: Water Sticks to Other Substances
Water's ability to adhere to other substances is also critical:
-
Capillary Action: Capillary action is the ability of water to move against gravity in narrow tubes or porous materials. This phenomenon is driven by both cohesion and adhesion. The adhesion of water to the walls of the tube pulls the water upward, and the cohesive forces between water molecules pull the rest of the water column along. Capillary action is essential for the movement of water in plants, soil, and other porous materials.
-
Wetting: Adhesion contributes to water's ability to wet surfaces. This is important in many biological and technological contexts. For example, the adhesion of water to our skin allows it to remain hydrated.
The Hydrogen Bond Factor Again: The Molecular Basis
Just as with specific heat capacity, hydrogen bonds are the key to understanding water's cohesive and adhesive properties. The polar nature of water molecules allows them to form hydrogen bonds not only with each other but also with other polar molecules and ions. This interaction underpins the powerful forces of cohesion and adhesion.
3. Excellent Solvent Properties: The Universal Solvent
Water is often called the "universal solvent" because of its exceptional ability to dissolve a wide variety of substances. This property stems from its polar nature and its ability to form hydrogen bonds.
How Water Dissolves Substances
Water's polarity allows it to interact with both ionic compounds and polar molecules:
-
Dissolving Ionic Compounds: When an ionic compound, such as salt (NaCl), is added to water, the polar water molecules surround the ions, separating them from each other and preventing them from reforming a crystal lattice. The positive ends of water molecules are attracted to the negative ions (e.g., Cl⁻), and the negative ends are attracted to the positive ions (e.g., Na⁺). This process is called hydration.
-
Dissolving Polar Molecules: Water can also dissolve many polar molecules, such as sugars and alcohols. The polar water molecules form hydrogen bonds with the polar groups on the solute molecules, effectively surrounding and separating them.
The Importance of Water's Solvent Properties
Water's solvent properties are essential for:
-
Biological Processes: Water acts as the solvent for many biochemical reactions that occur within cells. Nutrients, waste products, and enzymes are all dissolved in water, allowing them to be transported and react with each other. Without water's solvent properties, many essential biological processes would be impossible.
-
Environmental Processes: Water plays a critical role in dissolving and transporting minerals and other substances in the environment. This is essential for nutrient cycling and the overall functioning of ecosystems.
-
Chemical Reactions: Many chemical reactions require water as a solvent to facilitate the interaction of reactants. This is particularly true for reactions that occur in aqueous solutions.
Beyond Simple Dissolution: Water's Complex Interactions
It's important to note that water's solvent properties are not simply about dissolving substances; they involve complex interactions and dynamic equilibria between water molecules and the dissolved substances. The properties of the resulting solutions, such as pH and conductivity, are influenced by the nature of the dissolved substances and their interactions with water.
Conclusion: The Extraordinary Properties of Water
The three properties of water discussed—high specific heat capacity, cohesion and adhesion, and excellent solvent properties—are interconnected and crucial for life on Earth. These properties arise from the unique structure of the water molecule and the resulting hydrogen bonding. Understanding these properties is fundamental to comprehending the vital role water plays in biological systems, environmental processes, and countless technological applications. The seemingly simple molecule of H₂O is, in fact, extraordinarily complex and essential for the existence of life as we know it. Further research continues to unveil the subtle nuances of water's behaviour, further highlighting its importance and complexity. From the microscopic level to the macroscopic scale, water's influence is undeniable and pervasive. Its unique properties continue to fascinate scientists and inspire innovation across diverse fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Percentage Of 6 5
Mar 22, 2025
-
Difference Between Normal And Binomial Distribution
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Constant Term In A Polynomial
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Do You Factor 2x 2 5x 3
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is Magnesium A Solid Liquid Or Gas
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The 3 Properties Of Water . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
