The Quotient Of A Number And
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
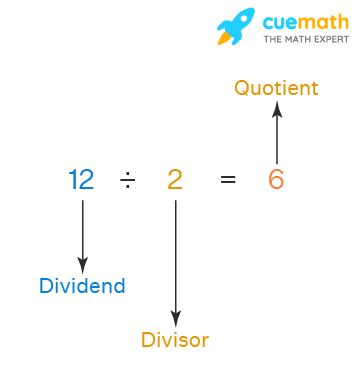
Table of Contents
The Quotient of a Number and: A Deep Dive into Division and its Applications
The seemingly simple concept of "the quotient of a number and" opens up a vast world of mathematical exploration. This seemingly basic phrase encapsulates the fundamental operation of division, a cornerstone of arithmetic that extends its influence far beyond simple calculations. Understanding the quotient, its implications, and its diverse applications across various fields is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of mathematics and its real-world relevance.
Understanding the Quotient
Before delving into the complexities, let's solidify the basics. A quotient is the result obtained by dividing one number (the dividend) by another number (the divisor). In the phrase "the quotient of a number and," the "number" acts as the dividend, and the term following "and" represents the divisor. For example:
- The quotient of 12 and 3 is 4 (because 12 ÷ 3 = 4).
- The quotient of 25 and 5 is 5 (because 25 ÷ 5 = 5).
- The quotient of 100 and 20 is 5 (because 100 ÷ 20 = 5).
This simple definition lays the groundwork for exploring the broader applications and interpretations of quotients.
Beyond Simple Division: Exploring Different Contexts
The concept of a quotient extends beyond simple integer division. Let's explore various contexts where understanding quotients is critical:
1. Fractions and Rational Numbers:
Fractions are fundamentally representations of quotients. A fraction, such as ¾, can be interpreted as the quotient of 3 divided by 4. Understanding this relationship is crucial for performing operations with fractions, converting them to decimals, and comprehending their numerical value. The quotient in this context provides the numerical representation of a part-to-whole relationship.
2. Decimals and Division:
The process of long division allows us to express the quotient of two numbers as a decimal. This is especially useful when dealing with situations where the dividend isn't perfectly divisible by the divisor, resulting in a remainder. The decimal representation provides a more precise numerical value than expressing the answer solely as a whole number and a remainder. For instance, the quotient of 7 and 3 is 2.333... (a repeating decimal).
3. Algebra and Variables:
In algebra, quotients frequently involve variables. For instance, the expression 'x/y' represents the quotient of x and y. Understanding how to manipulate and simplify such expressions is fundamental to algebraic operations, equation solving, and working with functions. The quotient in this context becomes a dynamic value dependent on the values of the variables.
4. Rate and Ratio Problems:
Quotients are instrumental in solving problems involving rates and ratios. Speed, for example, is calculated as the quotient of distance and time (speed = distance/time). Similarly, unit prices are calculated by dividing the total cost by the quantity. In these contexts, the quotient represents a rate or a ratio that compares two different quantities.
5. Geometry and Measurement:
Quotients appear frequently in geometric calculations. For instance, the area of a triangle is calculated as half the product of the base and the height (Area = ½ * base * height), which indirectly involves the quotient if the height is expressed as a fraction or decimal. Also, understanding ratios and proportions in similar figures involves manipulating quotients of corresponding lengths.
6. Data Analysis and Statistics:
Quotients play a critical role in data analysis and statistics. Averages, such as the mean, are calculated by dividing the sum of values by the number of values. Ratios and proportions are used to compare different data sets, and percentages are essentially quotients expressed as fractions of 100. For instance, calculating a batting average in baseball or a grade point average involves determining quotients.
Advanced Applications of Quotients
The significance of quotients transcends elementary arithmetic. Let's explore some more advanced applications:
1. Calculus:
Quotients form the foundation of calculus, particularly in differential calculus where the concept of a derivative involves the limit of a quotient. The derivative measures the instantaneous rate of change of a function and is fundamentally defined as a quotient of infinitesimally small changes.
2. Abstract Algebra:
In abstract algebra, quotients are crucial in the formation of quotient groups and quotient rings. These structures arise when a larger algebraic structure is partitioned into equivalence classes, and operations are defined on these classes. This concept is central to understanding group theory and ring theory.
3. Computer Science:
Quotients are essential in computer algorithms and data structures. Hashing algorithms, used for efficient data retrieval, often involve the modulo operation, which is essentially a quotient calculation. Moreover, many algorithms in computer graphics and image processing rely on calculations involving quotients.
Real-World Examples of Quotients
To further illustrate the pervasiveness of quotients, consider these real-world applications:
-
Cooking: Recipes often require dividing ingredients, such as halving a recipe or dividing a cake into equal slices. The quotient determines the quantity of each ingredient needed.
-
Finance: Calculating interest rates, unit costs, profit margins, and analyzing financial statements all rely heavily on quotient calculations.
-
Engineering: Designing structures, calculating forces, and analyzing material properties frequently involves quotients. Engineers use ratios and proportions extensively, which are essentially quotients.
-
Physics: Many physical laws involve ratios and proportions, such as the relationship between force, mass, and acceleration (F = ma).
-
Medicine: Dosage calculations in medicine frequently require dividing medication quantities to ensure proper administration. Understanding quotients is crucial for accurate dosage calculations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Quotients
While the concept of a quotient is relatively straightforward, some common issues can arise:
-
Division by Zero: This is a fundamental error in mathematics. Dividing any number by zero is undefined. It’s crucial to always check for zero divisors before performing calculations.
-
Handling Remainders: Understanding how to express a quotient when the dividend isn't perfectly divisible by the divisor is crucial. Depending on the context, the remainder might be ignored, expressed as a fraction, or converted into a decimal.
-
Interpreting Results: The meaning of a quotient depends entirely on the context. Understanding the units involved and the quantities being compared is crucial for correctly interpreting the numerical result.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous Quotient
The quotient, at first glance, seems a simple concept. However, its depth and breadth are remarkable. From the elementary arithmetic of fractions to the complexities of calculus and abstract algebra, quotients play a pivotal role in mathematics and its myriad applications. A solid grasp of quotients is essential for success in many fields, and understanding its versatile nature is key to unlocking deeper insights into the world around us. This understanding extends beyond mere calculation; it empowers us to analyze, interpret, and solve problems across disciplines. The journey of exploring the quotient doesn't end here; continuous exploration and application will further refine this fundamental mathematical concept's significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 10 To The Power Of 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 And 10
Mar 17, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 40
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Convert Wavelength To Meters
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Argon
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Quotient Of A Number And . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
