Terms Like Terms Coefficients And Constants
listenit
Mar 27, 2025 · 5 min read
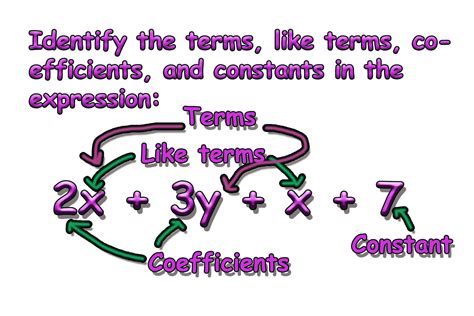
Table of Contents
Understanding Terms, Coefficients, and Constants in Algebra
Algebra, at its core, is about understanding and manipulating relationships between variables and numbers. While it might seem daunting at first, mastering the fundamentals, such as understanding terms, coefficients, and constants, is crucial to building a solid algebraic foundation. This comprehensive guide will delve into these key concepts, providing clear definitions, examples, and practical applications to solidify your understanding.
What is a Term in Algebra?
In algebra, a term is a single number, variable, or the product of numbers and variables. Think of terms as the individual building blocks of algebraic expressions. They are separated by addition or subtraction signs.
Examples of Terms:
- 5: A constant term (a number without a variable)
- x: A variable term (a single variable)
- 3x²: A variable term (a number multiplied by a variable raised to a power)
- -2xy: A variable term (a number multiplied by two variables)
- 7/y: A variable term (a number divided by a variable; this can also be expressed as 7y⁻¹)
Non-Examples of Terms:
- x + 2: This is an expression, not a single term, as it contains two terms separated by a plus sign.
- 3(x + y): This is also an expression, representing the product of a constant and a binomial (an expression with two terms). While it can be simplified, it isn't a single term in its present form.
Understanding terms is fundamental because it forms the basis for simplifying, factoring, and solving algebraic expressions and equations.
Coefficients: The Multipliers in Algebraic Expressions
A coefficient is the numerical factor of a term that's multiplied by a variable or variables. It tells us how many of a particular variable or variable combination we have. It's important to note that if a term only contains a variable, its coefficient is implicitly 1 (e.g., x is the same as 1x).
Examples of Coefficients:
- In the term 3x, the coefficient is 3.
- In the term -5y², the coefficient is -5.
- In the term 12ab, the coefficient is 12.
- In the term x, the coefficient is 1 (it's often implied and not written explicitly).
- In the term -y³, the coefficient is -1.
Coefficients play a vital role in algebraic operations. When adding or subtracting like terms (terms with the same variables raised to the same powers), we add or subtract the coefficients while keeping the variable part the same. This concept is crucial for simplifying expressions. For instance: 3x + 5x = 8x (We add the coefficients 3 and 5).
Constants: The Unchanging Numbers
A constant is a term that contains only a number, without any variables. It's a fixed value that doesn't change. Constants are often represented by numerals. They're the unchanging elements in algebraic expressions.
Examples of Constants:
- 7: A positive constant
- -4: A negative constant
- 0: The zero constant
- 2.5: A constant that's a decimal number
- π: A constant representing pi (approximately 3.14159)
Constants are essential in forming complete algebraic expressions and equations. They provide the numerical context within which the variables operate. They can be added, subtracted, multiplied, or divided according to the order of operations.
Distinguishing Terms, Coefficients, and Constants: A Practical Approach
Let's solidify our understanding by analyzing a few examples:
Example 1: 5x² + 2x - 7
- Terms: 5x², 2x, -7
- Coefficients: 5 (in 5x²), 2 (in 2x)
- Constants: -7
Example 2: -3ab + 4a - 9b + 11
- Terms: -3ab, 4a, -9b, 11
- Coefficients: -3 (in -3ab), 4 (in 4a), -9 (in -9b)
- Constants: 11
Example 3: (1/2)y³ - 6y + 15
- Terms: (1/2)y³, -6y, 15
- Coefficients: 1/2 (in (1/2)y³), -6 (in -6y)
- Constants: 15
Example 4: 4x²y - 7xy² + 2x - 5y + 1
- Terms: 4x²y, -7xy², 2x, -5y, 1
- Coefficients: 4 (in 4x²y), -7 (in -7xy²), 2 (in 2x), -5 (in -5y)
- Constants: 1
By consistently identifying terms, coefficients, and constants, you'll develop a strong foundation for more advanced algebraic concepts.
Applications of Terms, Coefficients, and Constants
Understanding terms, coefficients, and constants extends far beyond basic algebra. These concepts are crucial in various mathematical and scientific fields:
-
Solving Equations: Identifying terms helps in isolating variables and solving for unknowns. For example, to solve the equation 3x + 5 = 14, understanding that 3x and 5 are separate terms allows you to isolate 'x'.
-
Simplifying Expressions: Combining like terms (terms with the same variables and exponents) simplifies complex expressions. Knowing the coefficients allows for efficient simplification.
-
Factoring Polynomials: Identifying the coefficients and constants of polynomials is essential for factoring them into simpler expressions. This is widely used in calculus and other higher-level mathematics.
-
Graphing Equations: Constants and coefficients in linear equations (y = mx + c) directly impact the y-intercept (c) and the slope (m) of the line, defining its position and orientation on a graph.
-
Scientific Modeling: In physics, chemistry, and engineering, algebraic equations often describe relationships between variables. Understanding coefficients allows interpreting the strength and impact of each variable on the overall system.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
As you progress in your algebraic studies, you'll encounter more complex scenarios involving terms, coefficients, and constants. Some of these include:
-
Polynomial Expressions: These are expressions consisting of multiple terms, each being a constant or a variable raised to a non-negative integer power. Identifying coefficients becomes particularly important in polynomial operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
-
Exponential Functions: Coefficients in exponential functions define the rate of growth or decay. Understanding them is crucial in applications like population growth modeling, radioactive decay, and compound interest calculations.
-
Matrices and Vectors: In linear algebra, matrices and vectors are composed of elements that can be interpreted as coefficients or constants, enabling operations like matrix multiplication and vector addition.
Conclusion
Mastering the concepts of terms, coefficients, and constants is the cornerstone of algebraic success. By understanding their definitions, identifying them within expressions, and applying them in various contexts, you’ll gain a strong foundation for tackling more complex algebraic problems and unlocking the power of mathematical modeling in diverse fields. Consistent practice and careful attention to detail are key to solidifying your understanding and building confidence in your algebraic skills. Remember, the seemingly simple concepts of terms, coefficients, and constants are the bedrock upon which a deep understanding of algebra is built. Consistent practice and application will solidify your grasp of these crucial elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Groups 3 12 On The Periodic Table
Mar 30, 2025
-
Lewis Structure Of N Ch3 3
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Name For The Compound N2o5
Mar 30, 2025
-
Is Radius The Same As Diameter
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is 35 In A Fraction
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Terms Like Terms Coefficients And Constants . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
