Is Radius The Same As Diameter
listenit
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
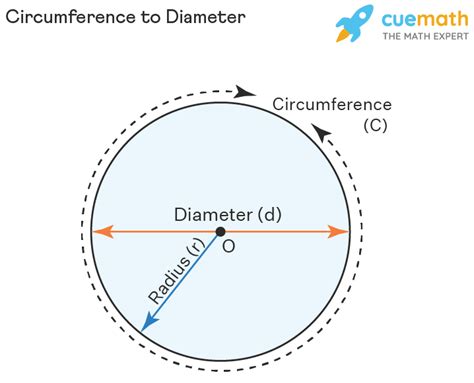
Table of Contents
Is Radius the Same as Diameter? Understanding Circle Geometry
The question, "Is radius the same as diameter?" is a common one, especially for those new to geometry. While they're both crucial components in understanding circles, the answer is a definitive no. Radius and diameter are distinct measurements, related yet fundamentally different. This article will delve deep into the definitions, relationships, and applications of both terms, clarifying any misconceptions and solidifying your understanding of circle geometry. We'll explore the concepts through various examples and illustrations, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the subject.
Defining Radius and Diameter
Let's start with clear and concise definitions:
Radius: The radius of a circle is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference (edge). Think of it as a line segment extending from the heart of the circle to its outer boundary. A circle possesses infinitely many radii, all of equal length. We often represent the radius with the lowercase letter 'r'.
Diameter: The diameter of a circle is a straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and connects two points on the circumference. It's essentially twice the length of the radius. Like the radius, a circle has infinitely many diameters, all of equal length. We usually denote the diameter with the lowercase letter 'd'.
Key Difference: The fundamental difference is the starting and ending points. The radius starts at the center and ends at the circumference, while the diameter starts and ends at the circumference, always passing through the center. This seemingly small difference leads to significant implications in calculations and applications.
The Relationship Between Radius and Diameter
The relationship between the radius (r) and the diameter (d) of a circle is mathematically expressed as:
d = 2r or r = d/2
This simple formula highlights the direct proportionality: the diameter is always twice the length of the radius. This relationship forms the cornerstone of numerous circle-related calculations.
Applications of Radius and Diameter
The concepts of radius and diameter are fundamental in various fields, impacting our daily lives in more ways than you might initially think. Let's explore some key applications:
1. Calculating Circumference and Area
The radius and diameter play pivotal roles in calculating the circumference (distance around the circle) and area (space enclosed by the circle).
-
Circumference (C): The formula for circumference involves the radius or diameter:
- C = 2πr (using radius)
- C = πd (using diameter)
Where 'π' (pi) is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159.
-
Area (A): The formula for the area of a circle utilizes the radius:
- A = πr²
Notice that the area calculation relies solely on the radius. While you can use the diameter-radius relationship to indirectly calculate the area from the diameter, using the radius directly is simpler and more efficient.
2. Engineering and Design
In engineering and design, the radius and diameter are critical parameters in various applications:
- Wheel Design: The diameter of a wheel determines its overall size and the distance it covers in one revolution. The radius plays a role in determining the wheel's curvature and strength.
- Pipe Sizing: In plumbing and other industries, pipe diameter is a crucial specification, determining the flow rate of liquids or gases.
- Circular Structures: The radius and diameter are essential in designing circular structures such as bridges, tunnels, and stadiums.
- Manufacturing: The precision manufacturing of circular parts, such as bearings and gears, relies on accurate control of radius and diameter.
3. Cartography and Navigation
Radius and diameter are integral to geographic calculations:
- Map Projections: Representing the Earth (a sphere) on a flat map necessitates understanding the Earth's radius.
- GPS Systems: GPS calculations utilize a spherical model of the Earth, requiring knowledge of the Earth's radius for accurate positioning.
- Navigation: Understanding the radius of a turning circle is crucial for safe vehicle navigation.
4. Astronomy
In astronomy, these concepts are crucial for understanding celestial bodies:
- Orbital Calculations: Calculating the orbits of planets and satellites requires considering the radius and diameter of their orbits and the celestial bodies themselves.
- Star Sizes: The diameter of stars is a critical factor in classifying and studying them.
5. Everyday Life
Beyond these technical applications, radius and diameter subtly influence our daily lives:
- Clocks and Watches: The radius of a clock face contributes to its aesthetic design.
- Pizza Slices: The radius is used to determine the area of a pizza slice.
- Circular Gardens: Designing circular flower beds often involves specifying the desired radius or diameter.
Misconceptions and Clarifications
A common misconception is that radius and diameter are interchangeable. While they are related, they are not interchangeable. Using the wrong value in a calculation can lead to incorrect results. Always be mindful of whether the problem requires the radius or the diameter, and use the appropriate formula accordingly.
Conclusion
While related, the radius and diameter of a circle are fundamentally different measurements. Understanding this distinction, along with their relationship (d = 2r), is crucial for accurately calculating circumference, area, and solving problems involving circular shapes. The concepts of radius and diameter have broad applications across diverse fields, from engineering and design to astronomy and everyday life. Mastering these concepts enhances your understanding of geometry and opens doors to solving many real-world problems involving circular shapes. Remember to always carefully distinguish between radius and diameter to ensure accurate calculations and successful problem-solving. Precise application of these concepts guarantees efficiency and correctness in any context involving circle geometry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 14
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is 6 To The Power Of 0
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Oxidation State Of S In H2so4
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Is Water A Liquid At Room Temp
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is The Number Zero A Rational Number
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Radius The Same As Diameter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
