Sum Of The Interior Angles Of A Heptagon
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
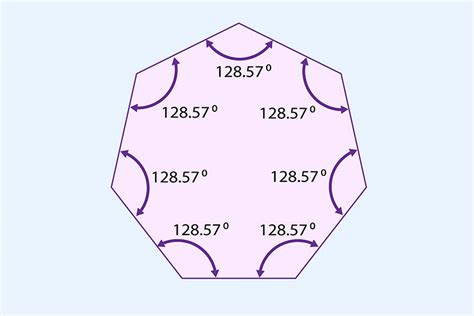
Table of Contents
The Sum of the Interior Angles of a Heptagon: A Comprehensive Guide
The heptagon, a polygon with seven sides and seven angles, holds a fascinating place in geometry. Understanding its properties, particularly the sum of its interior angles, is crucial for various mathematical applications and problem-solving. This comprehensive guide will delve into the calculation, proof, and applications of the sum of the interior angles of a heptagon, providing you with a thorough understanding of this geometric concept.
Understanding Polygons and Their Angles
Before we dive into the specifics of heptagons, let's establish a foundational understanding of polygons and their angles. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a set of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the segments meet are called the vertices. Polygons are classified according to the number of sides they possess: triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), heptagons (7 sides), octagons (8 sides), and so on.
Each polygon possesses both interior angles and exterior angles. Interior angles are the angles formed inside the polygon at each vertex. Exterior angles are formed by extending one side of the polygon at each vertex. The sum of the interior angles is a key characteristic of any polygon, and it's directly related to the number of sides it has.
Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles of a Polygon
A fundamental formula exists to determine the sum of the interior angles of any polygon, regardless of its shape or regularity. This formula is:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' represents the number of sides of the polygon.
This formula holds true for all convex polygons – polygons where all interior angles are less than 180°. Non-convex polygons, which contain at least one interior angle greater than 180°, require a slightly different approach, but the underlying principle remains consistent.
Applying the Formula to a Heptagon
A heptagon, having seven sides (n = 7), allows us to directly apply the formula to find the sum of its interior angles:
(7 - 2) * 180° = 5 * 180° = 900°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of any heptagon is 900°. This is true regardless of whether the heptagon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles vary).
Proof of the Formula: Triangulation Method
The formula (n - 2) * 180° can be elegantly proven using a method called triangulation. Consider any polygon with 'n' sides. We can divide this polygon into a series of triangles by drawing diagonals from one vertex to all other non-adjacent vertices. Notice that this creates (n - 2) triangles.
Since the sum of the interior angles of any triangle is always 180°, the sum of the interior angles of the (n - 2) triangles will be (n - 2) * 180°. Crucially, the sum of the angles in these triangles perfectly matches the sum of the interior angles of the original polygon. This establishes the validity of our formula.
Visualizing Triangulation in a Heptagon
Let's visualize this with a heptagon. Start at any vertex. You can draw four diagonals to divide the heptagon into five triangles. Each triangle has interior angles summing to 180°. Therefore, the total sum of the interior angles of the heptagon is 5 * 180° = 900°.
Regular Heptagons: A Special Case
While the 900° sum applies to all heptagons, regular heptagons exhibit unique properties. In a regular heptagon, all sides are equal in length, and all interior angles are equal in measure. Since the sum of the interior angles is 900°, each individual interior angle of a regular heptagon measures:
900° / 7 ≈ 128.57°
This precise angle is crucial in various applications, from tiling patterns to architectural designs.
Applications of Heptagon Angle Properties
The understanding of heptagon angles has significant implications in various fields:
1. Architecture and Design:
Heptagons, both regular and irregular, appear in architectural designs, creating unique visual effects and structural elements. Accurate calculation of angles is essential for constructing stable and aesthetically pleasing structures.
2. Computer Graphics and Game Development:
In computer graphics and game development, precise calculations of polygon angles are critical for rendering accurate 2D and 3D models. Understanding the properties of heptagons contributes to creating realistic and visually appealing virtual environments.
3. Tessellations and Tilings:
While regular heptagons cannot tessellate (completely cover a surface without gaps or overlaps), irregular heptagons can be used to create intricate and fascinating tiling patterns. Precise angle calculations are crucial for achieving these complex designs.
4. Engineering and Manufacturing:
In engineering and manufacturing, accurate angle calculations are paramount. Understanding heptagon angles can be relevant in designing specific mechanical parts or components.
5. Crystallography:
Certain crystal structures exhibit heptagonal symmetry. Understanding the angles in heptagons is vital for analyzing and modeling these structures.
Solving Problems Involving Heptagons
Many geometrical problems involve finding missing angles or sides within a heptagon. Knowing the sum of the interior angles (900°) is a critical starting point for solving these problems. Often, the problem will provide some information about other angles or side lengths, and by using geometric principles and algebraic techniques, you can solve for the unknowns.
For example, you might be given a heptagon with six known angles and asked to find the seventh. Simply subtract the sum of the six known angles from 900° to find the value of the missing angle.
Beyond the Heptagon: Extending the Concept
The principles applied to heptagons extend to all polygons. Understanding the formula (n - 2) * 180° and the triangulation method is crucial for calculating the sum of interior angles for any polygon, regardless of the number of sides. This knowledge forms a fundamental basis for further exploration in geometry and related fields.
Conclusion: Mastering the Heptagon's Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a heptagon, 900°, is a fundamental concept in geometry with broad applications. Understanding its calculation, proof, and implications across various disciplines allows for a deeper appreciation of geometrical principles and their practical relevance. This knowledge forms a strong foundation for further explorations into polygon geometry and related mathematical fields. By mastering these concepts, you equip yourself with valuable tools for solving complex problems and understanding the geometric world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Solve Equations With Feet
Mar 16, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 30
Mar 16, 2025
-
Where Is The Mass Of An Atom Located
Mar 16, 2025
-
How To Graph Y 1 2x 1
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Can Fit In The Second Shell
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of The Interior Angles Of A Heptagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
