Number Of Valence Electrons In Beryllium
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
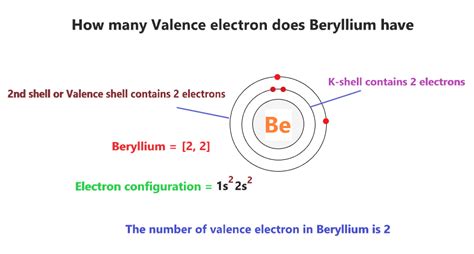
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Beryllium: Unveiling the Secrets of its Valence Electrons
Beryllium, a fascinating element residing in the alkaline earth metal family, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic configuration, particularly the number of valence electrons, is crucial to comprehending its chemical behavior and properties. This comprehensive exploration delves into the intricacies of beryllium's valence electrons, exploring its atomic structure, bonding characteristics, and the implications of its electronic configuration for its various applications.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Reactivity
Before we dive into the specifics of beryllium, let's establish a foundational understanding of valence electrons. These are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom, also known as the valence shell. They are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. The number of valence electrons dictates an atom's tendency to gain, lose, or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, typically resembling that of a noble gas. This stable configuration is often referred to as the octet rule (eight electrons in the outer shell), although exceptions exist, particularly for elements in the first few rows of the periodic table.
Beryllium's Atomic Structure and Electronic Configuration
Beryllium (Be), with an atomic number of 4, possesses four electrons. Its electronic configuration is 1s²2s². This means that it has two electrons in the first shell (1s²) and two electrons in the second shell (2s²). Critically, the two electrons in the outermost shell (2s²) are its valence electrons. This configuration explains much of beryllium's chemical behavior.
The Significance of the 2s² Configuration
The fact that beryllium only possesses two valence electrons is significant. Unlike many other elements that strive for a full octet, beryllium often forms compounds where it achieves a stable electron configuration by losing these two valence electrons. This results in the formation of a +2 cation (Be²⁺), a characteristic feature of its reactivity.
Beryllium's Chemical Bonding: A Consequence of its Valence Electrons
The presence of only two valence electrons significantly influences the types of bonds beryllium forms. Beryllium predominantly exhibits covalent bonding, sharing electrons with other atoms to achieve a more stable configuration. While it can lose its two valence electrons to form ionic bonds, this is less prevalent than covalent bonding, especially with non-metals.
Covalent Bonding in Beryllium Compounds
The covalent nature of beryllium's bonding is exemplified in compounds like beryllium chloride (BeCl₂). In this compound, beryllium shares its two valence electrons with two chlorine atoms, each chlorine atom contributing one electron to form two covalent bonds. This results in a linear molecular geometry for BeCl₂. The covalent nature of beryllium's bonding is also demonstrated in organoberyllium compounds, where beryllium bonds with carbon atoms.
The Limitations of the Octet Rule with Beryllium
It is important to note that beryllium, being a small atom, often does not strictly adhere to the octet rule. Its small size allows it to form stable compounds with less than eight electrons in its valence shell. This is a key distinction between beryllium and other elements in its group, highlighting its unique chemical characteristics.
Applications of Beryllium: Leveraging its Properties
The unique properties stemming from its electronic configuration and low atomic weight make beryllium valuable in various applications. Its high strength-to-weight ratio, high thermal conductivity, and transparency to X-rays are key attributes contributing to its utilization in:
-
Aerospace: Beryllium alloys find use in aircraft components and spacecraft structures, where light weight and high strength are crucial.
-
Nuclear Reactors: Its low neutron absorption cross-section makes beryllium ideal for use as a neutron reflector and moderator in nuclear reactors.
-
Electronics: Beryllium's high thermal conductivity is exploited in heat sinks for electronic devices, ensuring efficient heat dissipation.
-
X-ray Optics: Its transparency to X-rays makes it a valuable material in X-ray windows and optical components used in X-ray equipment.
-
Military Applications: Beryllium's combination of strength and light weight makes it valuable in military applications, including in guided missiles and high-speed aircraft components.
Comparing Beryllium to other Alkaline Earth Metals
Beryllium's behavior contrasts with that of other alkaline earth metals, such as magnesium and calcium. While magnesium and calcium readily form ionic compounds by losing their two valence electrons, beryllium shows a stronger tendency toward covalent bonding. This difference highlights the influence of atomic size and electronegativity. Beryllium's smaller size and higher electronegativity lead to a greater polarization of its bonds, favoring covalent character.
The Environmental and Health Considerations of Beryllium
Despite its many valuable applications, beryllium presents significant health and environmental concerns. Beryllium is a known toxic and carcinogenic element. Inhalation of beryllium dust can lead to serious lung diseases, including berylliosis, a chronic and often debilitating condition. Therefore, handling beryllium requires strict safety precautions and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
Conclusion: The Crucial Role of Valence Electrons in Defining Beryllium
In summary, the two valence electrons of beryllium are the cornerstone of its unique chemical and physical properties. Its tendency to form covalent bonds, its unique atomic structure, and its distinctive reactivity, all stem from this fundamental characteristic. Understanding the number of valence electrons and their implications is paramount to appreciating the multifaceted role of beryllium in various scientific and technological applications, while remaining mindful of its inherent toxicity and environmental implications. The careful management and utilization of this element require a deep understanding of its fundamental chemistry and a robust commitment to safety protocols. Further research into beryllium's properties and its interaction with other elements will undoubtedly continue to reveal new insights and potential applications, while highlighting the vital role its two valence electrons play in shaping its unique identity among the elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Oz Is 500 Ml Of Water
Mar 18, 2025
-
7 5a 4 1 14 8a
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Head Of The Femur Articulates With The
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 2
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Determines The Shape Of A Protein
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Valence Electrons In Beryllium . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
