Number Of Electrons In Carbon -12
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
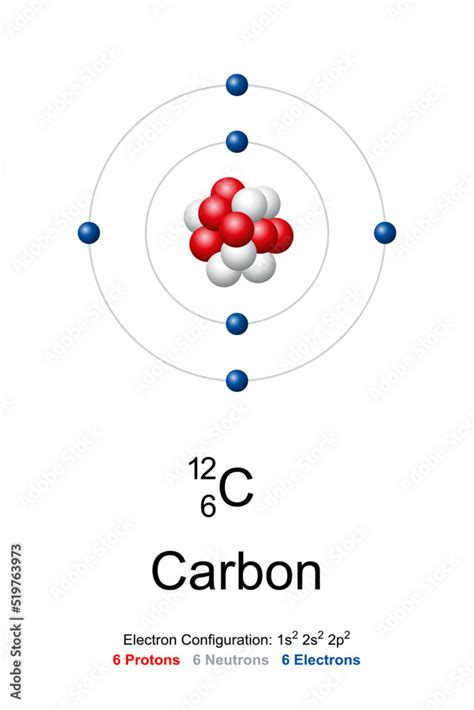
Table of Contents
The Number of Electrons in Carbon-12: A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter is crucial in various scientific fields. This article delves into the specifics of carbon-12, focusing on the number of electrons it possesses and exploring the broader context of atomic structure, isotopes, and their significance.
What is Carbon-12?
Carbon-12 (¹²C) is the most abundant isotope of carbon, making up approximately 99% of the carbon found in nature. It's an essential element for life as we know it, forming the backbone of organic molecules and playing a crucial role in numerous biological processes. The "12" in its designation represents its mass number, which is the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Atoms are composed of three subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons determines the element's atomic number and its identity.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. Their number generally equals the number of protons in a neutral atom, ensuring an overall neutral charge.
Determining the Number of Electrons in Carbon-12
The atomic number of carbon is 6. This means that a neutral carbon atom has six protons in its nucleus. Since a neutral atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, a neutral carbon-12 atom possesses six electrons.
This fundamental principle applies to all isotopes of carbon, including carbon-12, carbon-13, and carbon-14. The number of electrons directly correlates with the atomic number, defining the chemical behavior and properties of the element.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Count
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This variation affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties (to a significant degree). The different isotopes of carbon are:
- Carbon-12 (¹²C): 6 protons, 6 neutrons, 6 electrons (most abundant)
- Carbon-13 (¹³C): 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons
- Carbon-14 (¹⁴C): 6 protons, 8 neutrons, 6 electrons (radioactive)
Notice that despite the variations in neutrons, the number of electrons remains constant at six for all isotopes of carbon. This consistency in electron number is what defines their shared chemical behavior.
Electron Configuration and Chemical Bonding
The arrangement of electrons in an atom's energy levels is known as its electron configuration. This configuration significantly influences the atom's reactivity and the types of chemical bonds it can form. For carbon-12, the electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p². This means:
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the lowest energy level (n=1), specifically the s orbital.
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2), in the s orbital.
- 2p²: Two electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2), in the p orbitals.
This configuration explains carbon's unique ability to form four covalent bonds, leading to the vast diversity of organic molecules. The four valence electrons (the electrons in the outermost shell) can participate in bonding with other atoms.
Covalent Bonding and Carbon's Versatility
Carbon's ability to form four covalent bonds stems directly from its electron configuration. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms to achieve a stable electron configuration (often an octet, eight electrons in the outermost shell). This shared electron structure is responsible for the incredible structural variety seen in organic compounds.
Carbon's ability to bond with itself (catenation) and with numerous other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur, is the basis of the diversity of life and countless synthetic materials. This capacity is a direct consequence of the specific number of electrons – six – and the resulting electron configuration.
Significance of Carbon-12 in Science and Technology
Carbon-12 holds significant importance in various scientific and technological fields:
- Standard for Atomic Mass: Carbon-12 is the standard upon which the atomic mass unit (amu) is defined. One amu is defined as 1/12 the mass of a single carbon-12 atom.
- Radiocarbon Dating: Carbon-14, a radioactive isotope of carbon, is used in radiocarbon dating to determine the age of organic materials. While carbon-14 has a different number of neutrons, its electron count remains the same as carbon-12.
- Organic Chemistry: Carbon-12 forms the basis of organic chemistry, the study of carbon-containing compounds. Its unique bonding capabilities lead to the vast array of organic molecules found in living organisms and synthetic materials.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: NMR spectroscopy utilizes the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei, including ¹³C, to analyze the structure and composition of molecules. The electrons surrounding the nucleus play a crucial role in shielding the nucleus from the external magnetic field, influencing the NMR signals obtained.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Atomic Structure
The seemingly simple fact that carbon-12 has six electrons is fundamental to understanding its chemical behavior, its importance in biological systems, and its wide-ranging applications in various fields. The number of electrons, coupled with the atom's nuclear composition and electron configuration, dictates its properties and roles in the universe. This detailed exploration underscores the critical link between fundamental atomic structure and the macroscopic properties and applications we observe in the world around us. By understanding the number of electrons in carbon-12 and the principles of atomic structure, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the universe and the building blocks that make it all possible. Further study into isotopic variations and electron behavior is essential to expanding our scientific knowledge and developing new technologies. The six electrons in carbon-12 are, therefore, far more than just a number; they are the key to understanding a fundamental element of life and the universe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Highest Human Body Temperature Ever Recorded
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Translation Occur In The Nucleus
Mar 17, 2025
-
X 2 3x 2 X 1
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Osmosis And Dialysis
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Smallest Unit Of An Element
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Electrons In Carbon -12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
