Is Neon A Liquid Solid Or Gas
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
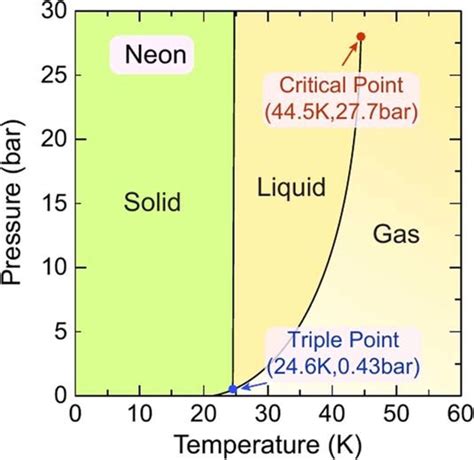
Table of Contents
Is Neon a Liquid, Solid, or Gas? Exploring the States of Matter
Neon, a noble gas with the chemical symbol Ne and atomic number 10, is famously known for its vibrant red-orange glow in neon signs. But beyond its illuminating properties, understanding its physical state at different temperatures and pressures is crucial to appreciating its unique characteristics. This comprehensive article delves into the question: is neon a liquid, solid, or gas? and explores the conditions under which it exists in each state. We’ll also delve into its properties and applications, explaining why its gaseous state is most prevalent in everyday life.
Neon's Existence as a Gas: The Most Common State
Under standard conditions of temperature and pressure (STP), which are typically defined as 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 atmosphere (atm), neon exists as a gas. This is because its atoms have weak intermolecular forces (London dispersion forces, to be precise). These forces are weak because neon atoms have a complete outer electron shell, making them exceptionally unreactive and stable. This lack of strong attraction between atoms allows them to move freely and independently, characterizing the gaseous state.
Understanding Intermolecular Forces and Neon's Inert Nature
The behavior of a substance, including its state of matter, is largely dictated by the strength of the forces between its constituent particles. In neon's case, the extremely weak London dispersion forces are insufficient to overcome the kinetic energy of its atoms at room temperature. This means the atoms are constantly moving around rapidly, resulting in the chaotic, expansive nature of a gas. Neon's inert nature, stemming from its full electron shell, further contributes to the weakness of these intermolecular interactions.
Neon Gas: Applications and Properties
The gaseous nature of neon at STP makes it incredibly versatile. Its most well-known application is in neon lighting. The gas is contained within glass tubes, and when an electrical current passes through it, the electrons in the neon atoms become excited to higher energy levels. As these electrons fall back to their ground state, they emit photons of light, producing the characteristic reddish-orange glow.
Beyond lighting, neon gas finds applications in:
- Lasers: Neon is a component in helium-neon lasers, which produce a stable, coherent beam of light used in various applications, including barcode scanners and laser pointers.
- Cryogenics: While not liquid neon itself, neon's low boiling point makes it useful in cryogenic refrigeration systems. Though not as potent as liquid helium, it offers significant cooling capacity.
- Diving Gas Mixtures: While not a primary component, small amounts of neon can be added to diving gas mixtures for specific applications, primarily because of its low solubility in blood and tissues.
Neon as a Liquid: Achieving the Condensed Phase
To transition neon from its gaseous state to a liquid, we need to reduce its kinetic energy. This can be achieved by lowering the temperature. At atmospheric pressure, neon's boiling point is -246.08 °C (-410.94 °F). This means that below this temperature, neon will exist as a liquid.
The Importance of Temperature and Pressure in State Changes
The temperature at which a substance changes state (e.g., boiling point, melting point) is heavily influenced by pressure. While -246.08 °C is the boiling point at 1 atm, this point will change if the pressure is altered. Increasing the pressure generally increases the boiling point and the melting point, as it requires more energy to overcome the stronger intermolecular forces.
Liquid Neon: Properties and Applications
Liquid neon, while less common than its gaseous form, has important applications due to its extremely low temperature:
- Cryogenic Cooling: Liquid neon is a powerful cryogenic refrigerant, finding use in scientific research requiring extremely low temperatures, such as cooling superconducting magnets and other sensitive equipment.
- Medical Applications: Although less common than liquid nitrogen, liquid neon can theoretically be used in cryosurgery, although liquid nitrogen is the more established option.
It's important to note that handling liquid neon requires careful precautions due to its extremely low temperature. Direct contact can cause severe frostbite.
Neon as a Solid: The Frozen State
To further reduce the kinetic energy of neon atoms and solidify the substance, we need to lower the temperature even further. At atmospheric pressure, neon's melting point is -248.59 °C (-415.46 °F). Below this temperature, neon exists as a solid. The solid form is a crystalline structure where the neon atoms are arranged in a regular pattern, with the weak London dispersion forces holding them in place.
Solid Neon: Properties and Applications
Solid neon, like liquid neon, is primarily utilized in scientific research requiring extremely low temperatures. Its applications overlap significantly with those of liquid neon, mainly focusing on cryogenic applications and low-temperature experimentation. It’s worth noting that the practical applications of solid neon are limited compared to its gaseous and liquid forms.
The Phase Diagram: Visualizing Neon's States
A phase diagram is a graphical representation of the different states of a substance as a function of temperature and pressure. Neon's phase diagram shows the conditions under which it exists as a solid, liquid, or gas. The diagram clearly illustrates the triple point, where all three phases coexist in equilibrium, and the critical point, beyond which the distinction between liquid and gas disappears. Understanding neon’s phase diagram is essential for predicting its behavior under varying conditions.
Conclusion: Neon Primarily Exists as a Gas
While neon can exist in liquid and solid states under specific conditions of low temperature and, in some cases, high pressure, its most common and prevalent state under normal environmental conditions is gas. Its inert nature, stemming from its complete electron shell, and the resulting weak intermolecular forces, lead to the characteristic properties of a gas at ambient temperatures and pressures. However, the ability of neon to transition to liquid and solid phases at extremely low temperatures makes it a valuable resource in various scientific and industrial applications. Understanding these different states and the conditions that govern them is essential to appreciating neon's unique properties and its multifaceted applications. Its usefulness extends beyond just its iconic presence in luminous signs, showcasing its importance in diverse fields like cryogenics and laser technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is The Limiting Reactant The One With Less Moles
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 24 And 32
Apr 05, 2025
-
Highest Common Factor Of 28 And 42
Apr 05, 2025
-
Which Chamber Of The Heart Has The Thickest Wall
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 3 And A Half Feet
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Neon A Liquid Solid Or Gas . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
