Is An Element A Pure Substance
listenit
Mar 28, 2025 · 5 min read
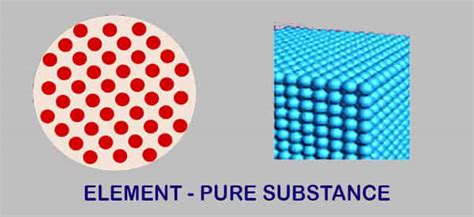
Table of Contents
Is an Element a Pure Substance? A Deep Dive into Chemistry
The question, "Is an element a pure substance?" might seem straightforward to some, but a deeper understanding requires exploring the fundamental concepts of chemistry. The answer is a resounding yes, but the reasoning behind it unveils the very essence of matter and its classification. This article will delve into the definitions of elements and pure substances, exploring their characteristics, differentiating them from mixtures, and highlighting the importance of this classification in chemistry and beyond.
Understanding Pure Substances
A pure substance is a form of matter that has a constant chemical composition and distinct chemical properties. This means that its constituent parts are the same throughout, and it cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical methods like filtration or distillation. Pure substances have a fixed melting point and boiling point, unlike mixtures. The properties of a pure substance remain consistent regardless of the sample's origin or preparation method. Examples of pure substances include elements and compounds.
Key Characteristics of Pure Substances:
- Uniform composition: The chemical makeup is consistent throughout the entire sample.
- Distinct properties: Each pure substance possesses unique physical and chemical properties that can be used to identify it.
- Fixed melting and boiling points: These points remain constant under standard pressure.
- Cannot be separated by physical means: Only chemical methods can break down pure substances into simpler components.
Exploring Elements: The Building Blocks of Matter
Elements are the fundamental building blocks of all matter. They are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Each element is defined by its atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. The periodic table organizes all known elements according to their atomic number and properties, revealing periodic trends in their behavior.
Key Characteristics of Elements:
- Unique atomic number: This number determines the element's identity and distinguishes it from all others.
- Cannot be broken down chemically: They cannot be separated into simpler substances using chemical reactions.
- Specific properties: Each element possesses characteristic physical and chemical properties, such as reactivity, density, and melting point.
- May exist as atoms or molecules: Some elements exist as individual atoms (e.g., noble gases), while others form molecules composed of identical atoms (e.g., oxygen, O₂).
The Difference Between Elements and Compounds
While both elements and compounds are pure substances, there's a crucial difference. Compounds are formed when two or more elements chemically combine in fixed proportions. The resulting substance has entirely different properties than the individual elements that compose it. For instance, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from the elements hydrogen and oxygen. The properties of water are vastly different from those of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
Elements can be combined to create a huge variety of compounds, showcasing the complexity and versatility of matter. This chemical bonding is a fundamentally different process from the physical mixing of substances, which creates mixtures rather than compounds.
Distinguishing Elements from Compounds:
| Feature | Element | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Single type of atom | Two or more types of atoms |
| Formation | Cannot be broken down chemically | Formed by chemical reaction |
| Properties | Unique to the element | Different from constituent elements |
| Separation | Cannot be separated chemically | Can be separated chemically (though often difficult) |
Differentiating Pure Substances from Mixtures
Mixtures, unlike pure substances, are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. They can be separated by physical means, and their composition is not fixed. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform, like sand and water).
Key Differences between Pure Substances and Mixtures:
| Feature | Pure Substance | Mixture |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fixed and uniform | Variable and may be uniform or non-uniform |
| Separation | Cannot be separated physically | Can be separated physically |
| Properties | Distinct and constant | Vary depending on composition |
| Melting/Boiling Point | Fixed | Range of melting/boiling points |
The Importance of Classifying Substances
The classification of substances as elements, compounds, or mixtures is essential for numerous reasons in various fields:
- Understanding chemical reactions: Knowing the composition of reactants allows prediction of products and understanding the reaction mechanisms.
- Material science: Classifying materials allows for the development of new materials with specific properties.
- Environmental science: Identifying pollutants and understanding their behavior is crucial for environmental protection.
- Medicine and pharmacology: Understanding the chemical composition of drugs and their interactions is fundamental to medicine.
- Forensic science: Analyzing substances helps in crime investigations.
Exploring Different Types of Elements
Elements can be further classified based on their properties:
- Metals: Typically shiny, solid at room temperature (except mercury), good conductors of heat and electricity, malleable, and ductile. Examples include iron, copper, gold, and aluminum.
- Nonmetals: Generally poor conductors of heat and electricity, may be solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature, and often brittle. Examples include oxygen, carbon, sulfur, and chlorine.
- Metalloids (semimetals): Exhibit properties of both metals and nonmetals, and their conductivity can vary depending on conditions. Examples include silicon, germanium, and arsenic.
- Noble gases (inert gases): Very unreactive and exist as monatomic gases at room temperature. Examples include helium, neon, and argon.
Advanced Concepts and Isotopes
While the atomic number defines an element, it's crucial to consider isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. This means they have the same number of protons but different mass numbers. While isotopes have slightly different physical properties, they share the same chemical properties, maintaining the elemental identity.
Conclusion: The Defining Role of Purity
To reiterate, an element is indeed a pure substance. This classification is not merely an academic exercise; it's the cornerstone of our understanding of matter. The consistent chemical composition and the inability to decompose elements chemically are defining characteristics that underpin all aspects of chemistry and related scientific fields. The study of elements, their properties, and their interactions lays the foundation for countless scientific and technological advancements. From developing new materials to understanding the complexities of life, the classification and understanding of elements as pure substances remain fundamental to scientific progress. The purity of an element is essential for its consistent properties and reactivity, making it a building block of our world and a subject of continuous scientific exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Intermolecular Force Is The Weakest
Mar 31, 2025
-
How To Calculate Molar Mass Of A Gas
Mar 31, 2025
-
The Weaker The Acid The Stronger The Conjugate Base
Mar 31, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Does Barium Have
Mar 31, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 4 Out Of 20
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is An Element A Pure Substance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
