Is 3 5 A Rational Number
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
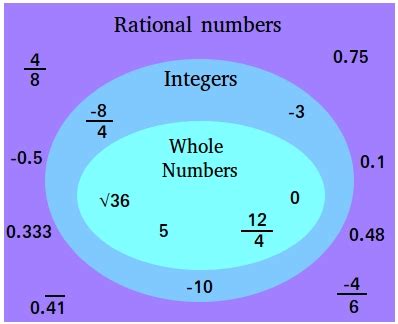
Table of Contents
Is 3/5 a Rational Number? A Deep Dive into Rational and Irrational Numbers
The question, "Is 3/5 a rational number?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer requires a solid grasp of the definitions of rational and irrational numbers. This article will not only definitively answer this question but also delve into the broader concepts of rational and irrational numbers, providing a comprehensive understanding of their properties and differences.
Understanding Rational Numbers
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, and q is not equal to zero. The key here is the ability to express the number precisely as a ratio of two integers. This seemingly simple definition opens up a vast world of numbers.
Examples of Rational Numbers
- Integers: All integers are rational numbers. For example, 5 can be written as 5/1, -3 as -3/1, and 0 as 0/1.
- Fractions: Obvious examples include fractions like 1/2, 3/4, and -2/7. The numerator and denominator are both integers.
- Terminating Decimals: Decimal numbers that terminate (end) are also rational. For example, 0.75 can be expressed as 3/4, and 0.125 as 1/8.
- Repeating Decimals: Decimals that have a repeating pattern, such as 0.333... (1/3) or 0.142857142857... (1/7), are rational. The repeating pattern indicates a relationship that can be expressed as a fraction.
Properties of Rational Numbers
- Closure under Addition: The sum of two rational numbers is always a rational number.
- Closure under Subtraction: The difference between two rational numbers is always a rational number.
- Closure under Multiplication: The product of two rational numbers is always a rational number.
- Closure under Division: The quotient of two rational numbers (where the divisor is not zero) is always a rational number.
Understanding Irrational Numbers
An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, and q is not equal to zero. These numbers are non-repeating and non-terminating decimals. Their decimal representations go on forever without ever falling into a predictable pattern.
Examples of Irrational Numbers
- √2: The square root of 2 is a classic example. Its decimal representation is approximately 1.41421356..., continuing infinitely without repeating.
- π (Pi): The ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately 3.14159..., is another famous irrational number. It's non-repeating and non-terminating.
- e (Euler's number): The base of the natural logarithm, approximately 2.71828..., is also irrational.
- φ (Golden Ratio): Approximately 1.6180339887..., appears frequently in geometry and nature.
Properties of Irrational Numbers
Irrational numbers, unlike rational numbers, do not possess closure properties under the standard arithmetic operations. The sum, difference, product, or quotient of two irrational numbers may be rational or irrational. For example:
- √2 * √2 = 2 (irrational * irrational = rational)
- √2 + (-√2) = 0 (irrational + irrational = rational)
- √2 * √8 = 4 (irrational * irrational = rational)
Back to the Original Question: Is 3/5 a Rational Number?
Given the definitions above, the answer is a resounding yes. 3/5 perfectly fits the definition of a rational number. Both 3 and 5 are integers, and 5 (the denominator) is not zero. Therefore, 3/5 can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, satisfying the criterion for being a rational number.
Furthermore, 3/5 can be easily converted to a decimal: 0.6. This is a terminating decimal, another characteristic of rational numbers.
Distinguishing Rational from Irrational Numbers: A Practical Approach
Identifying whether a number is rational or irrational can sometimes be challenging, especially with complex numbers or those represented as decimals. Here’s a practical approach:
-
Check for Fraction Representation: Can the number be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0? If yes, it's rational.
-
Examine Decimal Representation: If the number is given as a decimal:
- Terminating Decimal: If the decimal terminates (ends), it's rational.
- Repeating Decimal: If the decimal repeats a pattern infinitely, it's rational.
- Non-Terminating, Non-Repeating Decimal: If the decimal continues infinitely without repeating, it's irrational.
-
Consider Known Irrational Numbers: If the number involves square roots of non-perfect squares (e.g., √2, √3, √5), π, e, or other known irrational constants, it's likely irrational unless further simplification is possible.
The Importance of Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
The distinction between rational and irrational numbers is fundamental in mathematics. It has implications across various fields:
- Calculus: Understanding these number types is crucial for limits, derivatives, and integrals.
- Real Analysis: The real number system is built upon the concept of rational and irrational numbers.
- Algebra: Solving equations and inequalities often involves working with both rational and irrational numbers.
- Geometry: Many geometric calculations, such as finding the area or circumference of a circle, involve irrational numbers like π.
- Computer Science: Representing and manipulating these numbers in computer systems requires different approaches due to their inherent properties.
Conclusion
In summary, 3/5 is definitively a rational number. This article has not only answered the specific question but also provided a comprehensive overview of rational and irrational numbers, explaining their properties, differences, and significance in mathematics and other fields. By understanding the core concepts and the methods for identifying rational and irrational numbers, you can confidently navigate mathematical problems involving these essential number types. Remember the key characteristic: rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, while irrational numbers cannot. This simple yet profound distinction is the foundation for a deeper understanding of the number system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of And 18
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Elements Has The Largest Atomic Radius
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The 3 Main Ideas Of Cell Theory
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Are The Most Reactive Metals On The Periodic Table
Mar 25, 2025
-
30 L Equals How Many Gallons
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 3 5 A Rational Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
