Integrate 1 X 2 3 2
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
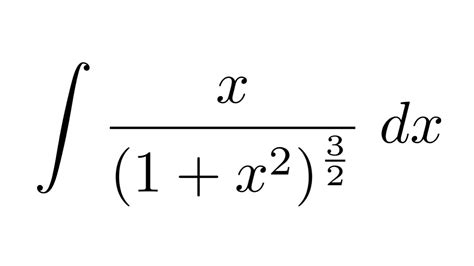
Table of Contents
Integrating 1 x 2 x 3 x 2: A Deep Dive into Multiplication and its Applications
The seemingly simple expression "1 x 2 x 3 x 2" represents a fundamental concept in mathematics: multiplication. While the calculation itself is straightforward (resulting in 12), the underlying principles and the far-reaching applications of multiplication extend far beyond this basic arithmetic operation. This article will explore the intricacies of multiplication, delve into its various applications across different fields, and analyze its importance in problem-solving and advanced mathematical concepts.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Multiplication
Multiplication, at its core, is a form of repeated addition. When we say "1 x 2," we are essentially adding 1 to itself 2 times (1 + 1 = 2). Similarly, "1 x 2 x 3 x 2" can be interpreted as:
- 1 x 2 = 2 (Adding 1 two times)
- 2 x 3 = 6 (Adding 2 three times)
- 6 x 2 = 12 (Adding 6 two times)
This repeated addition approach is useful for understanding the concept, especially for beginners. However, as numbers become larger, this method becomes inefficient. This is where the power and efficiency of multiplication truly shine.
The Commutative and Associative Properties
Multiplication possesses two crucial properties that simplify calculations and enhance understanding:
-
Commutative Property: The order of the numbers in a multiplication problem does not affect the outcome. For example, 2 x 3 is the same as 3 x 2. This property is particularly helpful in simplifying complex calculations. In our example, we could rearrange the terms: (1 x 2) x (3 x 2) = (2) x (6) = 12, or (1 x 3) x (2 x 2) = 3 x 4 = 12.
-
Associative Property: The grouping of numbers in a multiplication problem does not affect the outcome. For instance, (1 x 2) x 3 is the same as 1 x (2 x 3). This allows us to strategically group numbers for easier computation. In our example, we can group the numbers in various ways to arrive at the same answer.
Applications of Multiplication Across Diverse Fields
The seemingly simple act of multiplying numbers underpins numerous aspects of our lives and numerous complex fields of study. Its applications range from everyday tasks to advanced scientific calculations.
Everyday Applications
Multiplication is integral to everyday activities, often without us even realizing it:
- Shopping: Calculating the total cost of multiple items. If you buy 3 apples at $2 each, you multiply 3 x $2 = $6.
- Cooking: Doubling or tripling recipes. If a recipe calls for 2 cups of flour, multiplying by 2 or 3 allows you to easily adjust the recipe to serve more people.
- Construction and Engineering: Calculating the area or volume of structures and materials. This is essential for designing buildings, roads, and many other structures. Area is calculated using multiplication (length x width), while volume uses multiplication (length x width x height).
- Finance: Calculating interest, discounts, and taxes. These calculations heavily rely on multiplication.
Scientific and Technological Applications
Multiplication plays a crucial role in various scientific and technological disciplines:
- Physics: Calculating forces, velocities, and energies. Many physics formulas involve multiplication. For example, calculating kinetic energy involves multiplying mass and velocity squared (KE = 1/2 * mv²).
- Chemistry: Calculating molar masses and stoichiometric ratios. These calculations are essential for understanding chemical reactions and their products.
- Computer Science: Performing matrix operations, which are fundamental to computer graphics, machine learning, and many other areas. Matrix multiplication is a core operation in these fields.
- Engineering: Designing and analyzing systems and structures. From circuit design to bridge building, multiplication is used extensively.
- Data Analysis: Calculating statistical measures like means and variances often involve multiplication.
Advanced Mathematical Concepts
Multiplication forms the foundation for numerous advanced mathematical concepts:
- Algebra: Solving equations and inequalities often involves multiplication and division.
- Calculus: Derivatives and integrals, which are fundamental to calculus, involve multiplication and other operations.
- Linear Algebra: Matrix multiplication, vector multiplication, and scalar multiplication are crucial components of linear algebra.
- Probability and Statistics: Calculating probabilities, expected values, and other statistical measures involves multiplication.
Extending the Concept: Beyond Simple Multiplication
While "1 x 2 x 3 x 2" is a simple example, the principles of multiplication extend to more complex scenarios:
- Multiplication with Decimals and Fractions: The same rules apply, but careful attention must be paid to decimal placement and fraction simplification.
- Multiplication with Negative Numbers: The rules for multiplying with negative numbers are essential: a negative number multiplied by a positive number results in a negative number, while a negative number multiplied by a negative number results in a positive number.
- Exponents and Powers: Exponents represent repeated multiplication. For example, 2³ means 2 x 2 x 2. Understanding exponents is crucial for many advanced mathematical concepts.
- Factorials: The factorial of a number (denoted by !) is the product of all positive integers less than or equal to that number. For example, 5! = 5 x 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 120. Factorials are widely used in probability and combinatorics.
Problem Solving with Multiplication
Multiplication is a key tool for problem-solving. Many real-world problems can be effectively modeled and solved using multiplication.
Example 1: Area Calculation
Imagine you need to calculate the area of a rectangular room that measures 10 feet by 12 feet. The area is simply calculated by multiplying the length and width: 10 feet x 12 feet = 120 square feet.
Example 2: Unit Conversion
Suppose you need to convert 5 kilometers to meters. Knowing that there are 1000 meters in a kilometer, you multiply 5 km x 1000 meters/km = 5000 meters.
Example 3: Cost Calculation
If you buy 15 items at $5 each, the total cost is 15 x $5 = $75.
Multiplication in Programming and Algorithms
Multiplication is a fundamental operation in computer programming and algorithm design. Many programming languages have built-in functions for multiplication, making it easy to implement in various applications.
- Looping and Iteration: Multiplication can be implemented using loops, where a value is repeatedly added to itself a certain number of times.
- Arrays and Matrices: Multiplication is extensively used in array and matrix operations, which are fundamental to many computer science algorithms.
- Game Development: Calculating positions, velocities, and collisions in games often involves multiplication.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Multiplication
From the simple calculation of "1 x 2 x 3 x 2" to the complex computations underpinning advanced scientific research and technological innovations, multiplication remains a cornerstone of mathematics and its applications. Understanding its fundamental principles, properties, and diverse applications is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the world of numbers and problem-solving. Its efficiency and power are unmatched in simplifying complex calculations and providing solutions to a vast array of problems across various disciplines. Mastering multiplication is not just about learning arithmetic; it's about unlocking a gateway to a deeper understanding of the mathematical world and its influence on our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit Weight Of Water In Lb Ft3
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is Study Of Cells Called
Mar 22, 2025
-
Where Does Carbon Dioxide Enter The Plant
Mar 22, 2025
-
How Many Arcseconds Are In One Degree
Mar 22, 2025
-
Does Electronegativity Increase Down A Group
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integrate 1 X 2 3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
