How Many Arcseconds Are In One Degree
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
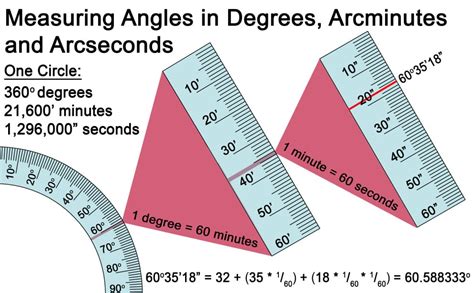
Table of Contents
How Many Arcseconds Are in One Degree? A Deep Dive into Angular Measurement
Understanding angular measurement is crucial in various fields, from astronomy and navigation to surveying and even computer graphics. One of the fundamental units in this system is the arcsecond, a tiny fraction of a degree. But how many arcseconds are actually in one degree? This article will delve into this question, exploring the intricacies of angular measurement and its applications. We'll cover the conversion process, examine related units, and explore the significance of arcseconds in different contexts.
Understanding Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds
Before we delve into the precise number of arcseconds in a degree, let's establish a foundational understanding of the angular measurement system. The degree (°), a familiar unit, represents 1/360th of a full circle. This system, dating back to ancient Babylonian astronomy, has proven remarkably enduring and adaptable.
However, a degree itself is quite a large unit for many applications. To measure finer angles, the degree is further subdivided:
- Arcminute ('): One degree is divided into 60 arcminutes. Think of this as the "minutes" in an angular clock.
- Arcsecond (''): Each arcminute is further subdivided into 60 arcseconds. This is the "seconds" in our angular clock, representing a truly minute angle.
This sexagesimal system (base-60) might seem unusual compared to our decimal system (base-10), but its historical roots and practical applications continue to justify its use.
The Calculation: Arcseconds in a Degree
Now, armed with this knowledge, let's answer the central question: how many arcseconds are in one degree?
The calculation is straightforward:
1 degree = 60 arcminutes 1 arcminute = 60 arcseconds
Therefore:
1 degree = 60 arcminutes * 60 arcseconds/arcminute = 3600 arcseconds
There are 3600 arcseconds in one degree. This seemingly simple conversion factor is crucial for many precise measurements.
The Significance of Arcseconds
The arcsecond, despite its minuscule size, holds significant importance across various disciplines:
Astronomy and Astrophysics
In astronomy, the arcsecond is essential for measuring the angular sizes of celestial objects and the distances between them. The apparent size of stars, planets, and galaxies are often expressed in arcseconds. For example, the angular diameter of the Moon as seen from Earth is roughly 31 arcminutes (or about 1860 arcseconds). However, measuring the precise angular separation between stars, or the tiny wobble of a star due to an orbiting exoplanet, requires the extreme precision of arcseconds and even milliarcseconds (1/1000th of an arcsecond).
Geodesy and Surveying
Precise land surveying and mapping require measurements accurate to the arcsecond level. The positions of points on the Earth's surface, particularly in large-scale mapping projects, are often determined using angles measured in arcseconds. Errors of even a few arcseconds can significantly impact the accuracy of maps and geographical information systems (GIS).
Navigation
While GPS and other modern technologies rely primarily on decimal degrees, the concept of arcseconds and their conversion still find application in certain navigational calculations, particularly in historical or specialized contexts. Accurate navigation, especially at sea or in air, demands precise angular measurements.
Optics and Photography
In optics and photography, the resolving power of a telescope or camera lens is often expressed in terms of its ability to distinguish between two closely spaced points. The smaller the angle it can resolve (measured in arcseconds), the higher its resolution. This is critical for capturing fine details in images, especially in astronomical observation.
Computer Graphics and Gaming
While not as directly apparent, the principles of angular measurement, including arcseconds, influence the rendering of 3D graphics in computer games and other applications. Precise calculations of angles are crucial for creating realistic and immersive visuals, particularly in simulations and virtual reality.
Milliarcseconds and Microarcseconds: Even Finer Measurements
The precision demands of modern science often push beyond the capabilities of even the arcsecond. This leads to the use of smaller units:
-
Milliarcsecond (mas): 1/1000th of an arcsecond. This unit is vital in high-precision astronomy for measuring the positions of stars and other celestial bodies with extreme accuracy. Techniques like Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) can achieve precision at the milliarcsecond level.
-
Microarcsecond (µas): 1/1,000,000th of an arcsecond. Measurements at this level are achieved through advanced techniques and are crucial for investigating minute variations in celestial phenomena.
These increasingly precise measurements reflect the constant push for greater accuracy in scientific observation and technological advancement.
Converting Between Angular Units: Practical Examples
Let's illustrate the conversion process with some practical examples:
Example 1: Convert 12,960 arcseconds to degrees.
Since 1 degree = 3600 arcseconds, we divide the number of arcseconds by 3600:
12,960 arcseconds / 3600 arcseconds/degree = 3.6 degrees
Example 2: Convert 2.5 degrees to arcseconds.
We multiply the number of degrees by 3600:
2.5 degrees * 3600 arcseconds/degree = 9000 arcseconds
Example 3: Convert 30 arcminutes to arcseconds.
We multiply the number of arcminutes by 60:
30 arcminutes * 60 arcseconds/arcminute = 1800 arcseconds
Beyond the Basics: Radians and Other Units
While the degree-minute-second system is widely used, another crucial angular unit is the radian. A radian is defined as the angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. Radians are particularly useful in calculus and other mathematical contexts because they simplify many trigonometric formulas. The conversion between radians and degrees involves the constant π (approximately 3.14159).
Understanding the relationships between these different angular units provides a comprehensive grasp of angular measurement.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Arcseconds
The seemingly small arcsecond plays a disproportionately large role in numerous fields. Its minute size makes it crucial for high-precision measurements, pushing the boundaries of our understanding in astronomy, geodesy, and other areas. From measuring the vast distances of the cosmos to precisely mapping the Earth's surface, the arcsecond remains a fundamental unit in our quest for ever-increasing accuracy. Understanding its relationship to degrees and other angular units is essential for anyone working with spatial data or engaging in precision measurements. The 3600 arcseconds in a single degree represent more than just a simple conversion; they represent a critical component in our ability to understand and interact with the world around us, both big and small.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Centimeters Is 4 Meters
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Sulfer Have
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 70 Percent Of 45
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is Force A Vector Or Scalar
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Pounds In 40 Ounces
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Arcseconds Are In One Degree . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
