Integral Of 1 Y 1 2
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
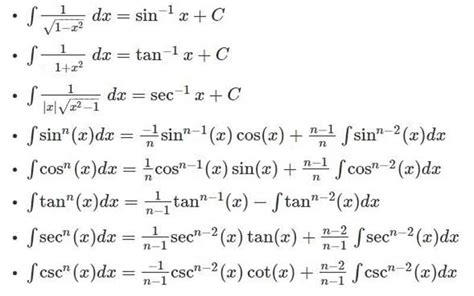
Table of Contents
The Integral of 1/(y(y+2)): A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple integral, ∫ 1/(y(y+2)) dy, presents a fantastic opportunity to delve into several crucial calculus concepts. This guide will comprehensively explore the solution, highlighting the techniques involved and demonstrating how to approach similar problems. We'll cover partial fraction decomposition, a vital method for integrating rational functions, and discuss the broader implications of this seemingly straightforward integral.
Understanding the Problem: ∫ 1/(y(y+2)) dy
Our task is to find the antiderivative of the function 1/(y(y+2)). This is a rational function—a ratio of two polynomials. Direct integration isn't immediately obvious; we need a strategy to simplify the integrand. This is where partial fraction decomposition comes into play.
Partial Fraction Decomposition: Breaking Down the Rational Function
Partial fraction decomposition is a powerful technique used to express a rational function as a sum of simpler rational functions. This simplification is crucial because simpler rational functions are often much easier to integrate. The process relies on factoring the denominator and then expressing the original fraction as a sum of fractions with simpler denominators.
Steps:
-
Factor the Denominator: Our denominator is already factored: y(y+2).
-
Set up the Partial Fraction Decomposition: Since we have two distinct linear factors in the denominator, we set up the decomposition as follows:
1/(y(y+2)) = A/y + B/(y+2)
where A and B are constants we need to determine.
-
Find the Constants A and B: To find A and B, we clear the fractions by multiplying both sides by the original denominator, y(y+2):
1 = A(y+2) + By
-
Solve for A and B: We can use two common methods to solve for A and B:
-
Method 1: Equating Coefficients: Expand the right side and equate the coefficients of the corresponding powers of y:
1 = Ay + 2A + By 1 = (A+B)y + 2A
This gives us a system of two linear equations:
A + B = 0 (coefficient of y) 2A = 1 (constant term)
Solving this system, we find A = 1/2 and B = -1/2.
-
Method 2: Substituting Values: We can strategically substitute values of y to solve for A and B. Let's try y = 0:
1 = A(0+2) + B(0) => A = 1/2
Now let's try y = -2:
1 = A(-2+2) + B(-2) => B = -1/2
-
-
Rewrite the Integral: Now that we've found A and B, we can rewrite the original integral as:
∫ 1/(y(y+2)) dy = ∫ (1/2)/y dy + ∫ (-1/2)/(y+2) dy
Integrating the Simpler Fractions
The resulting integrals are straightforward to solve using basic integration rules:
-
∫ (1/2)/y dy = (1/2) ∫ (1/y) dy = (1/2) ln|y| + C₁ (where C₁ is the constant of integration)
-
∫ (-1/2)/(y+2) dy = (-1/2) ∫ 1/(y+2) dy = (-1/2) ln|y+2| + C₂ (where C₂ is the constant of integration)
Combining the Results and the Final Answer
Combining the results from the two integrals and consolidating the constants of integration (C₁ + C₂ = C), we obtain the final solution:
∫ 1/(y(y+2)) dy = (1/2) ln|y| - (1/2) ln|y+2| + C
This can be further simplified using logarithmic properties:
∫ 1/(y(y+2)) dy = (1/2) ln|y/(y+2)| + C
Expanding the Horizons: Variations and Extensions
The techniques employed here are applicable to a wide range of similar integrals. Let's explore some variations:
1. Different Denominator: Consider an integral with a different denominator, such as ∫ 1/(y(y-3)(y+1)) dy. The partial fraction decomposition would involve three terms, each with a linear denominator. The process remains similar, but the system of equations for solving for the constants becomes slightly larger.
2. Repeated Linear Factors: Integrals with repeated linear factors in the denominator require a modified approach to partial fraction decomposition. For example, in ∫ 1/(y²(y+2)) dy, we would decompose it as A/y + B/y² + C/(y+2).
3. Quadratic Factors: If the denominator contains irreducible quadratic factors (factors that cannot be factored further using real numbers), the partial fraction decomposition will involve terms with linear numerators over the quadratic factors. For example, ∫ (3y+2)/(y(y²+1)) dy would necessitate a decomposition of the form A/y + (By+C)/(y²+1).
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
While this specific integral might not directly represent a readily observable physical phenomenon, the underlying technique of partial fraction decomposition finds applications in various fields:
-
Electrical Engineering: Circuit analysis often involves solving differential equations, and partial fraction decomposition simplifies the process of finding inverse Laplace transforms.
-
Chemical Engineering: Solving systems of differential equations that model chemical reactions frequently uses this technique.
-
Physics: In analyzing damped harmonic oscillations or solving problems involving forces, the technique may be necessary.
-
Probability and Statistics: Partial fraction decomposition can simplify calculations involving probability distributions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals
The integral ∫ 1/(y(y+2)) dy, seemingly simple at first glance, offers a valuable learning experience. Through mastering the technique of partial fraction decomposition, we've not only solved the integral but also acquired a valuable tool applicable across various branches of mathematics and science. Remember to practice solving various integrals with different types of denominators to fully grasp this essential calculus technique. This is fundamental to further mathematical explorations, particularly within the realms of differential equations and advanced calculus. The seemingly simple problem presented here acts as a gateway to deeper understanding and more complex applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 18
Mar 28, 2025
-
Do You Have To Add Water To Acid
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Fraction Of 70
Mar 28, 2025
-
Light Is A Transverse Or Longitudinal Wave
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Are Chromosomes Called When They Look Like Xs
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of 1 Y 1 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
