Integral Of 1 Cos X 2
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
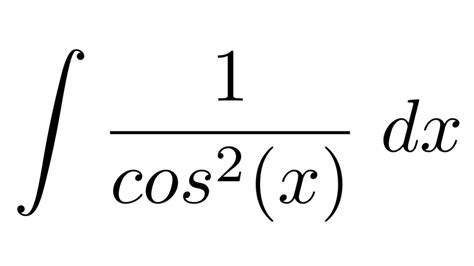
Table of Contents
The Indefinite Integral of 1/(cos²x): A Comprehensive Guide
The integral of 1/(cos²x), often written as ∫sec²(x)dx, is a fundamental integral in calculus with significant applications across various fields, including physics and engineering. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of solving this integral, explore its various approaches, and examine its practical applications.
Understanding the Integral and its Significance
The expression 1/(cos²x) represents the square of the secant function, sec²(x). Therefore, the integral we're aiming to solve is the indefinite integral of sec²(x) with respect to x. This seemingly simple integral holds significant importance due to its connection to the derivative of the tangent function.
Why is this integral important?
- Foundation of Calculus: It serves as a cornerstone integral within introductory calculus, demonstrating the powerful inverse relationship between differentiation and integration.
- Applications in Physics and Engineering: It frequently appears in solving differential equations that model oscillatory motion, wave phenomena, and other physical processes.
- Trigonometric Identities: Understanding its solution strengthens your grasp of trigonometric identities and their application within calculus.
Solving the Integral: The Direct Approach
The most straightforward approach to solving ∫sec²(x)dx leverages the fundamental theorem of calculus. We recall that the derivative of tan(x) is sec²(x):
d/dx [tan(x)] = sec²(x)
Therefore, by the fundamental theorem of calculus, the antiderivative (indefinite integral) of sec²(x) is tan(x). We add the constant of integration, 'C', to account for the family of antiderivatives:
∫sec²(x)dx = tan(x) + C
This solution is concise and elegant, highlighting the beauty and efficiency of calculus.
Exploring Alternative Approaches
While the direct approach is the most efficient, exploring alternative methods can enhance understanding and problem-solving skills.
Using Trigonometric Identities
We could attempt to solve the integral using trigonometric identities to manipulate the integrand into a more manageable form. However, in this case, the direct application of the known derivative proves to be far more efficient. Attempts to employ identities might lead to more complex expressions without significant advantage.
Numerical Integration Techniques
For cases where an analytical solution is unattainable, numerical integration techniques become necessary. Methods like the trapezoidal rule, Simpson's rule, or more advanced techniques like Gaussian quadrature can provide approximate solutions. However, for ∫sec²(x)dx, these are unnecessary due to the readily available analytical solution.
Applications of the Integral
The integral ∫sec²(x)dx= tan(x) + C finds widespread applications in numerous fields:
1. Physics: Simple Harmonic Motion
Simple harmonic motion (SHM) describes oscillatory motion, such as a mass on a spring or a pendulum swinging with small angles. The differential equations governing SHM often involve trigonometric functions, and the integral of sec²(x) plays a crucial role in solving these equations to find the displacement, velocity, or acceleration as a function of time.
For example, consider a simple pendulum. The equation of motion can involve terms that require the integration of sec²(x) to determine the pendulum's angular displacement over time.
2. Engineering: Curvature and Geometry
In engineering applications involving curves, the integral of sec²(x) might appear when calculating the curvature of a curve defined by a parametric equation involving trigonometric functions. Curvature is a measure of how sharply a curve bends, and its calculation often involves derivatives and integrals of trigonometric functions.
Consider the design of a rollercoaster track. The curvature at various points along the track can be determined using integral calculus, where integrals involving sec²(x) could be encountered.
3. Calculus: Solving Differential Equations
Many differential equations in science and engineering contain trigonometric functions. The integral of sec²(x) becomes an essential tool when solving such equations using techniques like separation of variables or integrating factors. These equations model various physical phenomena, ranging from wave propagation to the behavior of electrical circuits.
The integral appears frequently in solving second-order linear differential equations with constant coefficients, which model many physical systems exhibiting oscillations or vibrations.
Dealing with Definite Integrals
While the focus has been on the indefinite integral, the concept readily extends to definite integrals. If we need to evaluate the definite integral of sec²(x) from a to b, we simply evaluate the antiderivative, tan(x), at the limits of integration:
∫(from a to b) sec²(x)dx = tan(b) - tan(a)
This assumes that the function is continuous over the interval [a,b]. We must be mindful of discontinuities at x = (2n+1)π/2, where n is an integer, as the tangent function is undefined at these points.
Advanced Considerations and Extensions
Complex Analysis:
The integral ∫sec²(z)dz in the complex plane offers a different perspective. Complex analysis allows us to extend the concept of integration to complex numbers. Here, the result will involve complex numbers and requires a more nuanced understanding of complex functions and their integration techniques.
Generalized Integrals:
The concept extends to generalized integrals (improper integrals), where the limits of integration might be infinite or the integrand might have singularities. Careful consideration of limits and convergence is necessary in these cases.
Conclusion: Mastering the Integral of 1/(cos²x)
The integral of 1/(cos²x), or ∫sec²(x)dx, is a fundamental integral in calculus with far-reaching applications. While its solution—tan(x) + C—is straightforward, understanding its derivation and various approaches enriches one's comprehension of calculus and its power. Its importance spans various fields, from physics and engineering to advanced mathematical concepts. Mastering this integral is not only a key element in mastering introductory calculus but also a stepping stone towards more advanced topics and problem-solving capabilities. Therefore, thoroughly understanding this seemingly simple integral is crucial for anyone pursuing further studies in mathematics, science, or engineering.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Atomic Number For Magnesium
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Gcf Of 20 And 16
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Conjugate Acid Of Hco3
Mar 16, 2025
-
A Ma Or An Ma Degree
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is 3 Square Root Of 3
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of 1 Cos X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
