How Many Protons Electrons And Neutrons Does Nitrogen Have
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
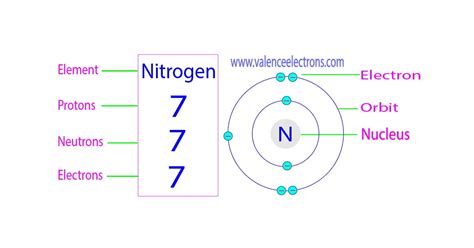
Table of Contents
How Many Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons Does Nitrogen Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Nitrogen, a vital element for life as we know it, plays a crucial role in various biological processes and industrial applications. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons it possesses, is fundamental to grasping its chemical behavior and properties. This article will delve deep into the atomic composition of nitrogen, exploring its isotopes and explaining how this elemental makeup contributes to its significance in the natural world and human endeavors.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Basics
Before we delve into the specifics of nitrogen, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. Atoms, the fundamental building blocks of matter, are composed of three subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons generally equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
Nitrogen's Atomic Number and Protons
Nitrogen's atomic number is 7. This means a nitrogen atom possesses 7 protons in its nucleus. This number is unchanging and is what definitively identifies an atom as nitrogen, distinguishing it from all other elements on the periodic table. The atomic number is a fundamental characteristic that dictates the element's chemical properties and how it interacts with other elements.
Nitrogen's Electrons: Orbitals and Chemical Behavior
A neutral nitrogen atom also contains 7 electrons. These electrons occupy specific energy levels or shells surrounding the nucleus. The electron configuration of nitrogen is 1s²2s²2p³. This configuration explains nitrogen's chemical behavior. The outermost shell (2s²2p³) contains five electrons – three unpaired electrons in the 2p orbitals. These unpaired electrons are crucial because they readily participate in chemical bonding, making nitrogen highly reactive and capable of forming strong covalent bonds with other atoms. This characteristic is reflected in the diversity of nitrogen compounds found in nature and utilized in various industrial processes. The tendency of nitrogen to form three covalent bonds is evident in molecules like ammonia (NH₃) and in the nitrogen gas molecule itself (N₂), where two nitrogen atoms share three pairs of electrons forming a strong triple bond.
Nitrogen's Neutrons: Isotopes and Mass Number
The number of neutrons in a nitrogen atom isn't fixed; it varies depending on the isotope. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. The most common isotope of nitrogen is Nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N), which has 7 neutrons. The mass number (14) is the sum of protons and neutrons. However, another stable isotope exists, Nitrogen-15 (¹⁵N), which contains 8 neutrons.
While ¹⁴N constitutes approximately 99.6% of naturally occurring nitrogen, ¹⁵N represents the remaining percentage. Both isotopes are stable, meaning they don't undergo radioactive decay. The difference in neutron number, though seemingly small, can influence certain chemical reactions and physical properties, albeit subtly. This difference in isotopic composition is utilized in various scientific techniques, such as isotopic tracing in biological and environmental studies.
The Significance of Nitrogen's Atomic Composition
The specific atomic composition of nitrogen – its 7 protons, its variable number of neutrons (most commonly 7), and its 7 electrons – directly impacts its properties and its role in the world around us. Let's explore some key aspects:
1. Biological Importance:
- Amino Acids and Proteins: Nitrogen is a crucial component of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. Proteins are essential for virtually all biological processes, from structural support to enzymatic activity. The nitrogen in amino acids forms the backbone of these crucial molecules.
- Nucleic Acids (DNA and RNA): Nitrogen is a fundamental element in the structure of DNA and RNA, the molecules that carry genetic information. Nitrogenous bases like adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine (or uracil in RNA) incorporate nitrogen atoms into their molecular structures.
- Ammonia (NH₃): A key nitrogen compound, ammonia, is produced by the decomposition of organic matter and serves as a crucial nutrient for plants.
- Nitrates and Nitrites: These nitrogen-containing compounds are vital components of the nitrogen cycle, providing a usable form of nitrogen for plant growth.
2. Industrial Applications:
- Fertilizers: Nitrogen is a key component of fertilizers, supplying plants with the essential nitrogen they need for optimal growth. The Haber-Bosch process, a crucial industrial process, synthesizes ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen, providing a large-scale source of nitrogen for fertilizer production.
- Explosives: Certain nitrogen compounds, such as nitrates and nitrites, are utilized in the manufacture of explosives due to their energy-releasing properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: Many pharmaceuticals incorporate nitrogen atoms into their molecular structures, highlighting its essential role in the creation of medicines.
3. Atmospheric Significance:
- Atmospheric Nitrogen (N₂): Approximately 78% of Earth's atmosphere is composed of molecular nitrogen (N₂). This nitrogen, despite its abundance, is relatively inert due to its strong triple bond. However, this gaseous nitrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth's atmospheric pressure and temperature.
Conclusion: Nitrogen – A Foundation of Life and Industry
The seemingly simple numbers – 7 protons, 7 electrons, and most commonly 7 neutrons – that define a nitrogen atom belie its extraordinary significance. This atomic composition underlies nitrogen's crucial role in biological processes, sustaining life on Earth, and its widespread applications in various industries. Understanding nitrogen's atomic structure, its isotopes, and how this structure dictates its chemical properties and reactivity provides a fundamental appreciation for the importance of this element in our world. From the intricate workings of living organisms to the vast scale of industrial processes, nitrogen's presence is undeniable, making its atomic composition a subject worthy of in-depth study and continuous exploration. Further research into nitrogen isotopes, their variations, and their impact on different environments and processes continues to expand our understanding of this vital element.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Potassium Iodide Covalent Or Ionic
Apr 05, 2025
-
Common Denominator Of 3 4 5
Apr 05, 2025
-
20 Is What Percent Of 400
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Protons Are In A Sulfur Atom
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 2 25
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Electrons And Neutrons Does Nitrogen Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
