How Many Protons Does Platinum Have
listenit
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
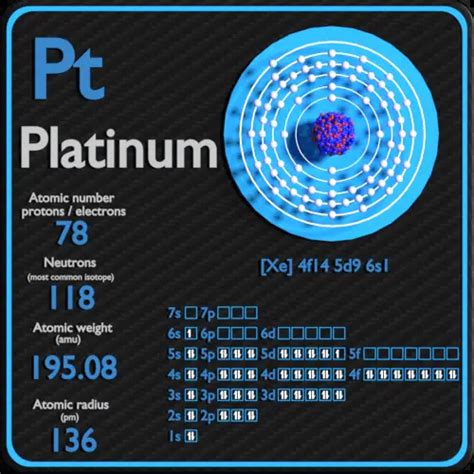
Table of Contents
How Many Protons Does Platinum Have? Understanding Atomic Structure and Platinum's Properties
Platinum, a lustrous, silvery-white metal, holds a prominent position in various industries, from jewelry to automotive catalytic converters. Understanding its fundamental properties, particularly its atomic structure, is crucial to appreciating its unique characteristics and applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the core question: how many protons does platinum have? We'll explore the concept of atomic number, delve into the unique properties of platinum stemming from its proton count, and examine its significance in various scientific fields.
Understanding Atomic Number and Protons
Before answering the central question, let's establish a fundamental understanding of atomic structure. Every atom, the basic building block of matter, consists of a nucleus containing positively charged particles called protons and neutral particles called neutrons. Orbiting this nucleus are negatively charged particles called electrons.
The atomic number of an element is defined as the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom of that element. This number is unique to each element and defines its identity on the periodic table. It's essentially the element's fingerprint, differentiating it from all other elements. The number of protons directly dictates the chemical properties of the element, as the protons determine the number of electrons required to balance the charge and thus influence how an atom interacts with other atoms.
Platinum's Atomic Number and Proton Count
Now, let's address the primary question: how many protons does platinum have?
Platinum's atomic number is 78. This means that every atom of platinum contains 78 protons in its nucleus. This fundamental characteristic is unchanging; it's what makes platinum, platinum. Any atom with 78 protons will exhibit the chemical and physical properties associated with platinum, regardless of the number of neutrons (which determine the isotope) or electrons (which influence the ion's charge).
Isotopes of Platinum: Neutrons and Atomic Mass
While the number of protons remains constant for a given element, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Platinum has several naturally occurring isotopes, each with a different atomic mass. Atomic mass is the total mass of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. For instance, the most abundant isotope of platinum is Platinum-195, meaning it has 78 protons and 117 neutrons (195 - 78 = 117). Other isotopes, such as Platinum-194 and Platinum-196, also exist in smaller proportions.
Properties of Platinum Stemming from its 78 Protons
The 78 protons in platinum's nucleus directly influence its unique properties, making it highly valuable in numerous applications:
1. High Density and Melting Point:
The strong nuclear forces holding together the 78 protons and associated neutrons result in a high nuclear density. This translates to a high overall density for platinum, making it a heavy metal. Similarly, the strong bonds within the platinum atom contribute to its high melting point, requiring significant energy to break the metallic bonds.
2. Excellent Electrical Conductivity:
The arrangement of electrons in platinum's electron shells, dictated by the 78 protons, facilitates excellent electrical conductivity. The readily available electrons can move freely, carrying electrical current effectively.
3. High Resistance to Corrosion:
Platinum's chemical inertness, a property directly tied to its electronic configuration determined by the proton number, makes it highly resistant to corrosion. It doesn't readily react with most acids or bases, maintaining its stability even under harsh conditions. This resistance is crucial for its applications in chemical processes and jewelry.
4. Catalytic Activity:
Platinum's catalytic activity, its ability to accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed itself, is linked to its electronic structure. The specific arrangement of electrons, influenced by the 78 protons, allows platinum to act as an intermediary in many important chemical reactions. This catalytic property is fundamental to its use in catalytic converters, where it helps convert harmful exhaust gases into less toxic substances.
Applications of Platinum: Leveraging its Unique Properties
The unique combination of properties stemming from its 78 protons makes platinum indispensable in a variety of applications across diverse industries:
1. Jewelry and Ornaments:
Platinum's inherent beauty, combined with its resistance to tarnish and corrosion, makes it a highly sought-after metal for jewelry and ornaments. Its durability ensures that platinum jewelry retains its lustrous appearance for generations.
2. Automotive Catalytic Converters:
Platinum's catalytic properties are crucial in reducing harmful emissions from automobiles. It acts as a catalyst to convert harmful pollutants like carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides into less harmful substances, contributing to cleaner air.
3. Chemical Industry:
Platinum's resistance to corrosion and its catalytic properties make it essential in various chemical processes. It's used as a catalyst in several industrial reactions, including the production of nitric acid and the refining of petroleum.
4. Medical Applications:
Platinum compounds have found applications in chemotherapy drugs used in cancer treatment. Their unique interactions with biological systems make them effective in targeting and destroying cancerous cells. Cisplatin, a platinum-based drug, is a widely used anticancer agent.
5. Electronics:
Platinum's excellent electrical conductivity makes it valuable in electronic components. It's used in electrical contacts, spark plugs, and other applications requiring high conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
6. Laboratory Equipment:
Platinum's inertness makes it suitable for laboratory equipment used in handling corrosive chemicals. Crucibles and electrodes made of platinum are commonly used in various laboratory procedures.
Platinum's Significance in Scientific Research
Platinum plays a vital role in scientific research, particularly in:
- Analytical Chemistry: Platinum electrodes are widely used in electrochemical analysis due to their excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Catalysis Research: Platinum is a model catalyst for studying fundamental catalytic processes, leading to advancements in catalysis science and technology.
- Material Science: The investigation of platinum's properties and behavior contributes to the development of new materials with enhanced performance.
- Nanotechnology: Platinum nanoparticles are being studied for their unique properties and potential applications in various areas, including medicine and electronics.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Platinum's Atomic Structure
Understanding that platinum has 78 protons is fundamental to grasping its unique properties and diverse applications. This number dictates its atomic identity, influencing its density, melting point, electrical conductivity, resistance to corrosion, and catalytic activity. These properties, in turn, make platinum a crucial element in various industries, from jewelry and automotive applications to medicine and scientific research. The exploration of platinum's atomic structure continues to drive scientific innovation and technological advancements across numerous fields. The 78 protons within each platinum atom are not just a number; they are the foundation of this remarkable element's versatility and importance in our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Grams In 8 Kilograms
Apr 02, 2025
-
12x 4y 20 Solve For Y
Apr 02, 2025
-
Most Reactive Group On The Periodic Table
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Solve Multi Step Inequalities
Apr 02, 2025
-
Percent Composition Of Mg No3 2
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Does Platinum Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
