How Many Neutrons Are In Nitrogen
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
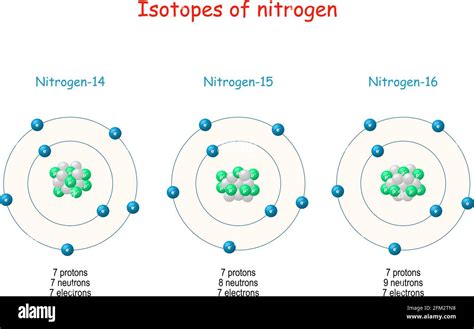
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons Are in Nitrogen? Exploring Isotopes and Nuclear Structure
Nitrogen, a vital element for life, presents a fascinating case study in nuclear structure. Understanding the number of neutrons in a nitrogen atom isn't as straightforward as it might initially seem. This is because nitrogen, like many elements, exists in different isotopic forms. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of nitrogen isotopes, explaining how the neutron count varies and the significance of these variations in various scientific fields.
Understanding Isotopes: The Key to Neutron Count Variability
Before we determine the neutron count in nitrogen, let's establish a fundamental concept: isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron count leads to variations in atomic mass. The number of protons defines the element – in the case of nitrogen, it's always 7. However, the number of neutrons can vary.
Defining Atomic Number and Mass Number
-
Atomic Number (Z): This represents the number of protons in an atom's nucleus. For nitrogen, Z is always 7. This defines nitrogen as nitrogen.
-
Mass Number (A): This is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus (A = Z + N, where N is the number of neutrons). The mass number identifies a specific isotope.
The Common Nitrogen Isotopes: ¹⁴N and ¹⁵N
Nitrogen primarily exists in two stable isotopes:
-
¹⁴N (Nitrogen-14): This is the most abundant isotope, making up approximately 99.63% of naturally occurring nitrogen. Its mass number is 14, indicating 7 protons (atomic number) and 7 neutrons (14 - 7 = 7). Therefore, ¹⁴N has 7 neutrons.
-
¹⁵N (Nitrogen-15): This is the less abundant stable isotope, accounting for about 0.37% of naturally occurring nitrogen. Its mass number is 15, meaning it contains 7 protons and 8 neutrons (15 - 7 = 8). Therefore, ¹⁵N has 8 neutrons.
The Significance of Isotopic Ratios in Various Fields
The relative abundance of ¹⁴N and ¹⁵N isn't just a matter of scientific curiosity; it holds significant implications across various disciplines:
1. Archaeology and Paleoclimatology:
Nitrogen isotopic ratios (¹⁵N/¹⁴N) are powerful tools in archaeology and paleoclimatology. The ratio can reveal information about past diets, environmental conditions, and even ancient agricultural practices. Variations in the ¹⁵N/¹⁴N ratio in human remains, for instance, can reflect changes in dietary protein sources over time. Similarly, analyzing the isotopic composition of ancient plant remains can provide insights into past climates and environmental changes.
2. Geochemistry and Oceanography:
Nitrogen isotopes play a crucial role in geochemical cycles. The distribution and ratios of ¹⁴N and ¹⁵N in various environmental compartments (atmosphere, oceans, soils) provide clues about nitrogen cycling processes, nutrient flows, and pollution sources. Oceanographers, for example, use nitrogen isotope ratios to trace nutrient inputs from terrestrial sources and understand the impact of human activities on marine ecosystems.
3. Medicine and Biology:
Nitrogen isotopes find applications in medical research and biological studies. ¹⁵N-labeled compounds are used as tracers to track metabolic pathways and study the uptake and utilization of nitrogen in biological systems. This technique is invaluable for understanding various biological processes, from protein synthesis to nitrogen fixation in plants.
4. Agriculture and Soil Science:
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plant growth. Understanding nitrogen isotopes in soil helps determine the effectiveness of nitrogen fertilizers and their impact on plant nutrition. The isotopic composition of nitrogen in plants can be used to assess nitrogen uptake efficiency and identify potential nutrient deficiencies.
Unstable Isotopes of Nitrogen: A Glimpse into Radioactive Decay
While ¹⁴N and ¹⁵N are stable isotopes, several radioactive isotopes of nitrogen exist. These isotopes are unstable and undergo radioactive decay, transforming into other elements over time. These unstable isotopes include:
-
¹³N (Nitrogen-13): This isotope has 7 protons and 6 neutrons. It decays through positron emission.
-
¹⁶N (Nitrogen-16): This isotope contains 7 protons and 9 neutrons. It decays through beta decay.
-
¹⁷N (Nitrogen-17): This isotope possesses 7 protons and 10 neutrons and also decays through beta decay.
These radioactive isotopes, although less common, find applications in various scientific fields, such as medical imaging and nuclear research. Their short half-lives limit their practical applications, but their unique decay properties make them valuable tools in specific research areas.
Beyond the Basics: Nuclear Forces and Isotopic Stability
The stability or instability of a nitrogen isotope is determined by the balance of nuclear forces within the nucleus. The strong nuclear force, which attracts protons and neutrons, must overcome the electromagnetic force, which repels protons. In isotopes with an optimal neutron-to-proton ratio, the strong force dominates, leading to stability. However, when the neutron-to-proton ratio is imbalanced, the repulsive electromagnetic force can destabilize the nucleus, resulting in radioactive decay. The different isotopes of nitrogen highlight the delicate balance of these forces in determining nuclear stability.
Applications of Isotopic Analysis Techniques
The determination of nitrogen isotope ratios requires specialized techniques like:
-
Mass Spectrometry: This technique separates isotopes based on their mass-to-charge ratio, allowing accurate measurement of isotopic abundances.
-
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): This combines gas chromatography with mass spectrometry to separate and analyze different nitrogen-containing compounds, allowing for isotopic analysis at a molecular level.
-
Stable Isotope Ratio Mass Spectrometry (SIRMS): This highly precise technique is specifically designed to measure the ratios of stable isotopes, providing highly accurate data for various applications.
These techniques are crucial for providing the quantitative data needed for the applications discussed earlier.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Nitrogen's Nuclear Structure
In summary, the number of neutrons in nitrogen is not a single answer but depends on the specific isotope being considered. While the most abundant isotope, ¹⁴N, has 7 neutrons, the less abundant ¹⁵N has 8. The variations in neutron count lead to differences in atomic mass and have significant implications across various fields, from archaeology to medicine. Understanding these isotopic variations and the underlying principles of nuclear structure provides a deeper appreciation for the complexity and importance of this essential element. Further research into nitrogen isotopes continues to reveal new insights and applications, further highlighting the ongoing significance of this area of scientific study. The utilization of advanced analytical techniques ensures the accurate measurement of isotopic ratios, strengthening the reliability of results in various scientific endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Why Does Ionisation Energy Decrease Down A Group
Mar 21, 2025
-
How To Find Number Of Molecules
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Percent Of 75 Is 3
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Do You Call A Group Of Penguins
Mar 21, 2025
-
35 Is What Percent Of 80
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Are In Nitrogen . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
