How Many Neutrons Are In C14
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
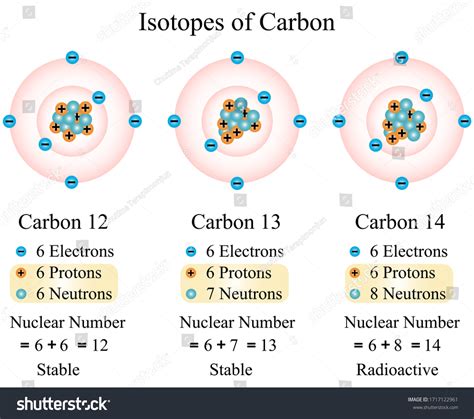
Table of Contents
How Many Neutrons are in C14? Exploring Isotopes and Nuclear Structure
Carbon-14, or ¹⁴C, is a fascinating isotope with significant applications in various fields, notably archaeology and environmental science. Understanding its nuclear structure, particularly the number of neutrons it contains, is crucial to grasping its properties and applications. This article delves deep into the topic, explaining not just the answer to the central question but also providing a comprehensive understanding of isotopes, atomic structure, and the significance of Carbon-14.
Understanding Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Before we dive into the specifics of Carbon-14, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. Every atom consists of three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; all carbon atoms have 6 protons.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the atom's nucleus. Unlike protons, the number of neutrons can vary within the same element, leading to isotopes.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells. The number of electrons typically equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
What are Isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons. This difference in neutron number affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties. Many elements exist in nature as a mixture of isotopes.
For example, carbon has three naturally occurring isotopes:
- Carbon-12 (¹²C): Contains 6 protons and 6 neutrons (12 - 6 = 6). This is the most abundant isotope of carbon (approximately 99%).
- Carbon-13 (¹³C): Contains 6 protons and 7 neutrons (13 - 6 = 7). A small percentage of naturally occurring carbon is ¹³C.
- Carbon-14 (¹⁴C): Contains 6 protons and 8 neutrons (14 - 6 = 8). This is a radioactive isotope, meaning it undergoes radioactive decay.
How Many Neutrons are in C14? The Answer
The mass number of an isotope, written as a superscript before the element symbol (e.g., ¹⁴C), represents the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Therefore, Carbon-14 (¹⁴C) has 8 neutrons.
Calculating the Number of Neutrons
To calculate the number of neutrons in any isotope, simply subtract the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number:
Number of neutrons = Mass number - Atomic number
In the case of ¹⁴C:
Number of neutrons = 14 - 6 = 8
The Significance of Carbon-14: Radiocarbon Dating
The radioactive nature of Carbon-14 is what makes it incredibly important in various scientific disciplines. Specifically, its half-life of approximately 5,730 years allows scientists to utilize it for radiocarbon dating.
Radiocarbon Dating Explained
Cosmic rays constantly bombard the Earth's atmosphere, creating Carbon-14. This ¹⁴C is incorporated into living organisms through photosynthesis and the food chain. While an organism is alive, the concentration of ¹⁴C remains relatively constant. However, once the organism dies, the intake of ¹⁴C ceases, and the existing ¹⁴C begins to decay through beta decay.
By measuring the remaining ¹⁴C in a sample (like an ancient artifact or fossil), scientists can estimate the time elapsed since the organism's death. The ratio of ¹⁴C to ¹²C in the sample is compared to the ratio in living organisms to determine the age.
Limitations of Radiocarbon Dating
While a powerful tool, radiocarbon dating has limitations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy decreases with older samples due to the significantly reduced amount of ¹⁴C. Reliable dating typically extends to around 50,000 years. Beyond that, the amount of ¹⁴C remaining is too small to provide accurate results.
- Contamination: Contamination of the sample with modern carbon can skew results. Careful sample preparation and handling are crucial.
- Reservoir Effects: Variations in the atmospheric concentration of ¹⁴C over time can also affect accuracy. Calibration curves are used to account for these variations.
Carbon-14 in Other Applications
Besides radiocarbon dating, Carbon-14 finds application in:
- Tracing Metabolic Pathways: ¹⁴C-labeled molecules can be used to study metabolic processes in biological systems. By tracking the movement of the labeled carbon atoms, researchers can gain insights into how organisms utilize nutrients and other molecules.
- Environmental Science: ¹⁴C can be used to study environmental processes, such as the movement of groundwater and the cycling of carbon in ecosystems.
- Medicine: While less common than other isotopes, Carbon-14 has been used in specific medical applications such as studying drug metabolism.
Understanding Isotopes beyond Carbon-14
The principles discussed regarding Carbon-14 apply to isotopes of other elements as well. Isotopes of hydrogen, oxygen, and uranium, for example, have their own specific properties and applications. Some isotopes are stable, while others are radioactive, undergoing decay at varying rates. The number of neutrons, along with the number of protons, determines the isotope's properties and behavior.
Further Exploration: Isotope Abundance and Nuclear Stability
The abundance of different isotopes in nature is not random. It is influenced by factors like nuclear stability. Isotopes with a neutron-to-proton ratio close to 1 are generally more stable. As you move away from this ideal ratio, isotopes tend to be less stable and may undergo radioactive decay to achieve a more stable configuration. This decay involves the emission of particles like beta particles (electrons) or alpha particles (helium nuclei) or the capture of electrons. The type of decay depends on whether the isotope has too many neutrons or too many protons.
The study of nuclear stability and decay is a complex field involving quantum mechanics and nuclear physics. However, understanding the basic principles allows us to appreciate the significance of isotopes, including Carbon-14, and their importance in various scientific disciplines.
Conclusion: The Importance of Carbon-14 and Isotope Studies
The question of how many neutrons are in Carbon-14 is a seemingly simple one, with a straightforward answer: eight. However, understanding this answer requires a grasp of fundamental atomic structure, the concept of isotopes, and the unique properties of radioactive isotopes. Carbon-14, with its radioactive nature and relatively long half-life, has become an invaluable tool in archaeology, environmental science, and other scientific fields. Its application in radiocarbon dating has revolutionized our understanding of history and prehistory, allowing us to date artifacts and fossils with remarkable accuracy. The broader study of isotopes and their properties continues to be crucial for advancing knowledge across various scientific disciplines, highlighting the profound significance of this seemingly small subatomic particle. Further research into isotope behavior and nuclear stability will undoubtedly continue to yield significant insights and practical applications in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Factor 1 X 3
Mar 29, 2025
-
How To Find A Boiling Point
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is 85 In Fraction Form
Mar 29, 2025
-
The Coefficients In A Chemical Equation Represent The
Mar 29, 2025
-
Maximum Number Of Electrons In P Orbital
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Neutrons Are In C14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
