Fraction As A Sum Of Unit Fractions
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
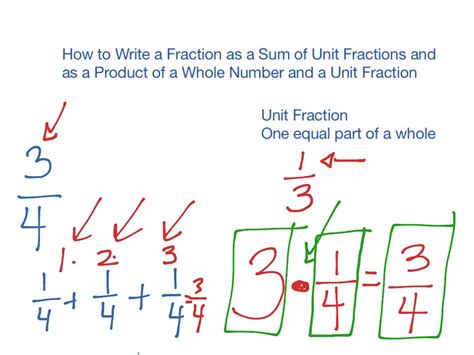
Table of Contents
Fractions as a Sum of Unit Fractions: An Exploration of Ancient Mathematics and Modern Applications
The representation of fractions as a sum of unit fractions – fractions with a numerator of 1 – is a fascinating area of mathematics with a rich history and surprising contemporary relevance. This exploration delves into the intricacies of this ancient mathematical problem, examining its historical context, various solution methods, and its unexpected applications in modern fields.
A Journey Through History: The Roots of Unit Fraction Decomposition
The fascination with expressing fractions as sums of unit fractions dates back to ancient Egypt. Egyptian mathematicians, lacking the sophisticated fractional notation we use today, developed a unique system primarily employing unit fractions (like 1/2, 1/3, 1/4, etc.) and the fraction 2/3. The Rhind Papyrus, a mathematical text dating back to around 1650 BCE, provides extensive evidence of this system. This papyrus contains tables detailing the decomposition of fractions of the form 2/n into sums of distinct unit fractions, offering a glimpse into their ingenious methods.
The "Greedy Algorithm": A Simple Approach
One of the simplest methods for expressing a fraction as a sum of unit fractions is the greedy algorithm. This algorithm iteratively subtracts the largest possible unit fraction from the given fraction until the remainder is zero or a unit fraction itself.
For example, let's decompose 5/7:
- The largest unit fraction less than or equal to 5/7 is 1/2 (5/7 - 1/2 = 3/14).
- The largest unit fraction less than or equal to 3/14 is 1/5 (3/14 - 1/5 = 1/70).
- The remaining fraction is 1/70, a unit fraction.
Therefore, 5/7 = 1/2 + 1/5 + 1/70.
While straightforward, the greedy algorithm doesn't always produce the shortest or most elegant sum. Often, it leads to a longer series of unit fractions than other methods.
Beyond the Greedy Algorithm: Exploring Sophisticated Techniques
The limitations of the greedy algorithm spurred the development of more sophisticated techniques for decomposing fractions into sums of unit fractions. These methods often involve intricate mathematical manipulations and recursive processes.
The Fibonacci Method and its Variations
The renowned Fibonacci sequence indirectly influences some unit fraction decomposition methods. While not a direct algorithm, understanding the properties of Fibonacci numbers can offer insights into finding efficient decompositions. Certain recursive approaches leverage relationships between the numerator and denominator to strategically choose unit fractions, often resulting in more concise representations.
Finding Optimal Solutions: A Complex Computational Problem
Determining the optimal decomposition – the representation with the fewest number of unit fractions – is a computationally challenging problem. As the input fraction becomes more complex (larger numerator and denominator), the search space for optimal solutions explodes exponentially, making exhaustive searches impractical for larger fractions. Advanced algorithms and heuristics are employed to tackle this complexity, often leveraging number theory concepts and optimization techniques.
The Continued Fraction Approach: A Powerful Tool
Continued fractions provide a powerful framework for decomposing fractions. A continued fraction represents a fraction as a sequence of integers, enabling systematic decomposition into unit fractions. The process involves repeated application of the Euclidean algorithm, resulting in a unique continued fraction representation. This representation can then be transformed into a sum of unit fractions through a straightforward procedure.
The advantages of the continued fraction approach include:
- Uniqueness: Each fraction has a unique continued fraction representation.
- Efficiency: Often leads to relatively short sums of unit fractions.
- Algorithmic Simplicity: The steps involved are clearly defined and easily implemented.
Applications in Modern Mathematics and Computer Science
Despite its ancient origins, the study of unit fraction decomposition continues to hold relevance in modern mathematical and computational contexts.
Applications in Number Theory
Unit fraction decomposition intertwines with various aspects of number theory, including the study of Diophantine equations, which involve finding integer solutions to polynomial equations. The techniques used for decomposing fractions contribute to solving certain types of Diophantine equations and understanding the structure of number systems.
Applications in Computer Science and Algorithm Design
The problem of finding optimal unit fraction decompositions has inspired the development of efficient algorithms and data structures within computer science. Researchers explore algorithms that approximate optimal solutions efficiently, balancing computational cost with solution quality. These algorithms have potential applications in areas such as resource allocation, scheduling, and network optimization.
Beyond the Practical: A Window into Mathematical Beauty
The study of unit fractions isn't purely utilitarian. It offers a window into the inherent beauty and elegance of mathematics. The pursuit of concise and elegant representations of fractions as sums of unit fractions reveals intriguing patterns and relationships within the number system. It encourages exploration, problem-solving, and the appreciation of mathematical structures.
Exploring Further: Open Problems and Research Directions
Despite centuries of research, several open problems remain within the field of unit fraction decomposition. Some key areas of ongoing research include:
- Finding Optimal Decompositions: Developing more efficient algorithms to consistently find the shortest possible sum of unit fractions for arbitrary fractions.
- Exploring Variations: Investigating variations of the problem, such as restricting the set of allowed unit fractions or imposing constraints on the coefficients.
- Connecting to Other Mathematical Fields: Exploring deeper connections between unit fraction decomposition and other areas of mathematics, such as algebraic number theory and graph theory.
Conclusion: A Timeless Mathematical Puzzle
The representation of fractions as sums of unit fractions, a concept originating in ancient Egypt, remains a vibrant area of mathematical investigation. From its historical context in the Rhind Papyrus to its modern applications in number theory and computer science, this problem continues to fascinate and challenge mathematicians. The exploration of different algorithms, the pursuit of optimal solutions, and the connections to other mathematical fields ensure that this ancient mathematical puzzle will continue to be a rich source of research and discovery for years to come. The inherent beauty and elegance of the problem, coupled with its surprising relevance in modern contexts, make it a captivating topic for both mathematicians and enthusiasts alike. The journey through the intricacies of unit fraction decomposition reveals the enduring power of mathematical exploration and its ability to bridge ancient and modern mathematical thought.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Figure Diameter With Circumference
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 245
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 1 3 Plus 1 4
Mar 25, 2025
-
The Study Of The Cells Is Called
Mar 25, 2025
-
Can Mixtures Be Separated By Physical Means
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Fraction As A Sum Of Unit Fractions . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
