How To Figure Diameter With Circumference
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
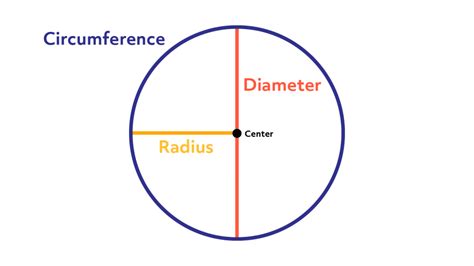
Table of Contents
How to Figure Diameter with Circumference: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the diameter of a circle using its circumference is a fundamental concept in mathematics and has widespread applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the relationship between diameter and circumference, delve into different methods for calculating diameter from circumference, and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also examine scenarios where this calculation is crucial and discuss potential challenges you might encounter.
Understanding the Fundamental Relationship
Before diving into the calculations, it's crucial to grasp the core relationship between a circle's diameter and its circumference. The circumference is the distance around the circle, while the diameter is the distance across the circle passing through the center. These two measurements are intrinsically linked through a fundamental mathematical constant: π (pi).
Pi (π) is an irrational number, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as:
Circumference (C) = π * Diameter (d)
This simple equation forms the basis for all our calculations. By rearranging this equation, we can easily derive formulas to calculate the diameter if the circumference is known.
Calculating Diameter from Circumference: Methods and Examples
Several methods can be employed to calculate the diameter from the known circumference. Let's explore the most common approaches:
Method 1: Direct Application of the Formula
The most straightforward method involves directly manipulating the fundamental formula: C = πd. To solve for 'd' (diameter), we simply divide both sides of the equation by π:
Diameter (d) = Circumference (C) / π
Example:
Let's say you have a circle with a circumference of 25 centimeters. To find its diameter, you would perform the following calculation:
d = 25 cm / π ≈ 25 cm / 3.14159 ≈ 7.9577 cm
Therefore, the diameter of the circle is approximately 7.96 centimeters. Remember to always specify the units (cm, inches, meters, etc.) in your answer.
Method 2: Using an Approximate Value of Pi
For quick estimations, you can use a simplified approximation of pi, such as 3.14 or 22/7. While this method introduces a small margin of error, it's perfectly acceptable for many practical applications where high precision isn't required.
Example:
Using the same circumference of 25 cm, and approximating π as 3.14:
d = 25 cm / 3.14 ≈ 7.96 cm
As you can see, the result is very close to the more precise calculation using a more accurate value of π.
Method 3: Using a Calculator or Software
Most scientific calculators and mathematical software packages have a built-in π constant, allowing for precise calculations. Using these tools ensures accuracy and saves time, especially when dealing with larger numbers or complex calculations involving multiple circles.
Practical Applications: Where This Calculation Matters
The ability to calculate diameter from circumference is indispensable across numerous fields:
Engineering and Design
- Pipe Sizing: In plumbing and engineering projects, determining the internal diameter of pipes is crucial for flow rate calculations and material selection. The circumference can often be easily measured, providing a convenient way to determine the diameter.
- Wheel Design: Designing wheels for vehicles or machinery requires precise calculations of diameter and circumference to ensure proper functionality and performance.
- Construction: In construction, calculating diameters of circular structures like columns, pillars, or domes is essential for accurate measurements and material estimations.
Manufacturing and Production
- Quality Control: In manufacturing, measuring the diameter of circular components is a critical aspect of quality control to ensure they meet specified tolerances. Circumference measurement can be a quicker and sometimes more practical approach.
- Machining: Machinists frequently need to determine the diameter of cylindrical parts based on measured circumferences to set up machining processes accurately.
Science and Research
- Astronomy: In astronomy, the apparent size of celestial bodies can be expressed in terms of angular diameter or circumference. Calculating the actual diameter necessitates knowing the distance and using the measured circumference.
- Biology: In biology, measuring the diameter of cells or microorganisms frequently relies on indirect methods involving circumference measurements.
- Physics: Various physics experiments involve circles and require accurate diameter calculations from measured circumferences.
Everyday Life
- Baking: Determining the diameter of a cake pan or pizza based on its circumference is useful for recipe scaling and portioning.
- Gardening: Calculating the diameter of a circular garden bed based on its circumference assists in planning and material estimations.
- DIY Projects: Numerous DIY projects involve circular shapes where determining the diameter from circumference can be crucial for accurate construction.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While the calculation itself is relatively straightforward, several factors can introduce challenges:
Measurement Accuracy
The accuracy of the diameter calculation is directly dependent on the accuracy of the circumference measurement. Inaccurate measurements will inevitably lead to inaccurate diameter calculations. Employing precise measuring instruments and careful measurement techniques is crucial.
Irregular Shapes
The formulas discussed above apply only to perfect circles. If the shape is slightly elliptical or irregular, the calculated diameter will be an approximation. More advanced techniques may be needed for highly irregular shapes.
Units of Measurement
Consistency in units is paramount. Ensure that both the circumference and the value of π used in the calculation are expressed in the same units. Converting between units (e.g., centimeters to meters) is necessary if they are not initially consistent.
Understanding Error Propagation
Errors in the measurement of the circumference will propagate to the calculated diameter. Understanding this error propagation is essential for evaluating the reliability of the result. Larger measurement errors will result in larger errors in the calculated diameter.
Conclusion
Calculating the diameter of a circle from its circumference is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications. Understanding the relationship between diameter, circumference, and π allows for efficient and accurate calculations in various fields. By mastering the methods outlined in this guide and considering the potential challenges, you can confidently tackle diameter calculations in any context. Remember to always prioritize accuracy in measurement and apply the appropriate value of π for the desired level of precision. This knowledge will empower you to solve problems and complete tasks more effectively in numerous professional and personal situations.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between A Biome And An Ecosystem
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Balanced Equation Represents A Redox Reaction
Mar 28, 2025
-
Solve This Equation 2s S 12 132
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 10
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is Water Condensing Endothermic Or Exothermic
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Figure Diameter With Circumference . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
