Do Acids And Bases Conduct Electricity
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
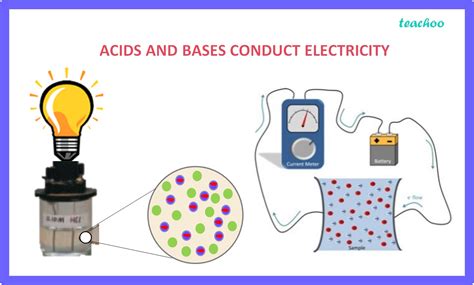
Table of Contents
Do Acids and Bases Conduct Electricity? Exploring the Role of Ions
Acids and bases are fundamental concepts in chemistry, playing crucial roles in numerous natural processes and industrial applications. One of their fascinating properties is their ability to conduct electricity, a characteristic directly linked to their chemical nature. This article delves into the reasons behind this conductivity, exploring the differences between strong and weak acids and bases, and examining the crucial role of ions in facilitating electrical current. We’ll also touch upon practical applications and safety considerations related to the electrical conductivity of these substances.
The Crucial Role of Ions in Electrical Conductivity
The ability of a substance to conduct electricity depends on the presence of free-moving charged particles, known as ions. These ions, which are atoms or molecules carrying a net electrical charge (positive or negative), can readily move under the influence of an electric field, thus carrying an electric current. Pure water, for instance, is a poor conductor because it contains very few ions.
Acids and bases, however, are unique in their ability to generate significant numbers of ions when dissolved in water. This ionization process is what makes them effective electrolytes, meaning substances that increase the conductivity of water. The more ions produced, the higher the conductivity.
How Acids Conduct Electricity
Acids, by definition, are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) when dissolved in water. This donation process, known as ionization or dissociation, results in the formation of positively charged hydrogen ions (H⁺) and negatively charged anions.
Strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and nitric acid (HNO₃), completely dissociate in water, meaning almost every acid molecule breaks down into ions. This leads to a high concentration of ions, resulting in excellent electrical conductivity.
Weak acids, such as acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), only partially dissociate in water. Only a small fraction of the acid molecules break down into ions, resulting in a lower concentration of ions and hence, lower electrical conductivity compared to strong acids.
Example: When hydrochloric acid (HCl) is dissolved in water, it completely ionizes into hydrogen ions (H⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻):
HCl(aq) → H⁺(aq) + Cl⁻(aq)
These freely moving H⁺ and Cl⁻ ions facilitate the flow of electric current.
How Bases Conduct Electricity
Bases, on the other hand, are substances that accept protons (H⁺ ions) or donate hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water. Similar to acids, the extent of ionization determines their electrical conductivity.
Strong bases, such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH), completely dissociate in water, releasing a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) and positively charged cations (e.g., Na⁺, K⁺). This high concentration of ions results in excellent electrical conductivity.
Weak bases, such as ammonia (NH₃), only partially dissociate in water, generating a lower concentration of ions and thus exhibiting lower electrical conductivity.
Example: When sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is dissolved in water, it completely dissociates into sodium ions (Na⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻):
NaOH(aq) → Na⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
These ions contribute to the solution's electrical conductivity.
Factors Affecting Electrical Conductivity
Several factors influence the electrical conductivity of acid and base solutions:
- Concentration: Higher concentrations of acids and bases lead to higher ion concentrations, resulting in increased conductivity.
- Temperature: Increased temperature generally increases the mobility of ions, leading to improved conductivity.
- Type of acid or base: Strong acids and bases conduct electricity better than weak acids and bases due to their complete or near-complete dissociation.
- Solvent: The solvent used can affect the extent of ionization and thus the conductivity. Water is a common solvent, but other solvents can also be used.
Practical Applications of Electrical Conductivity
The electrical conductivity of acids and bases has several practical applications:
- Electroplating: Electroplating involves using an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a surface. Acidic or basic electrolytes are often used to conduct the current and facilitate the deposition process.
- Batteries: Batteries rely on the flow of ions between electrodes to generate electricity. Acids and bases are commonly used in battery electrolytes.
- Conductivity meters: Conductivity meters measure the electrical conductivity of a solution, which can be used to determine the concentration of ions and hence the concentration of acids or bases. This is particularly useful in various industrial and environmental monitoring applications.
- Sensors: Electrical conductivity is utilized in various sensors for monitoring different chemical processes and determining the concentration of acids or bases in solutions. Such sensors are vital in industries like water treatment and chemical manufacturing.
Safety Precautions when Working with Conductive Solutions
It is crucial to exercise caution when handling solutions of acids and bases due to their electrical conductivity:
- Avoid contact with bare skin: Acid and base solutions can cause burns or irritation upon contact with the skin.
- Avoid contact with eyes: Contact with eyes can cause severe damage. Always wear appropriate eye protection.
- Use insulated equipment: When working with electrical circuits involving conductive solutions, ensure that the equipment is properly insulated to prevent electric shocks.
- Proper disposal: Dispose of acid and base solutions according to safety regulations to prevent environmental damage.
Conclusion
The electrical conductivity of acids and bases is a direct consequence of the presence of ions generated through their ionization or dissociation in water. Strong acids and bases, characterized by complete ionization, exhibit higher conductivity compared to weak acids and bases. This property has significant implications in various applications, from electroplating to battery technology and environmental monitoring. However, it is crucial to handle these conductive solutions with care due to potential safety hazards. Understanding the fundamental principles governing the electrical conductivity of acids and bases is essential for both scientific and practical applications. This knowledge allows for safer and more efficient utilization of these important chemical substances. Further research into new electrolytes and applications of conductivity in diverse fields is constantly progressing, highlighting the continued importance of understanding this fundamental chemical property. The advancements in sensor technology and improved methodologies for monitoring conductivity continue to open up new possibilities across a range of disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 1 2 As An Improper Fraction
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Nitrogen
Mar 21, 2025
-
Integral Of Sin 3x Cos 2x
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 10 Minutes Of An Hour
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 2 10 In Decimal Form
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Do Acids And Bases Conduct Electricity . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
