Differences Between The Federalist And Anti Federalist
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 7 min read
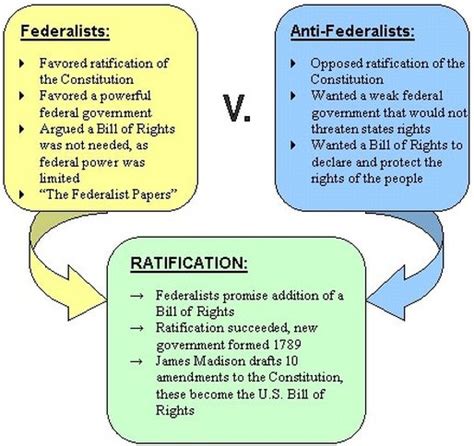
Table of Contents
The Great Divide: Understanding the Key Differences Between Federalists and Anti-Federalists
The birth of the United States was not a smooth transition. Following the Revolutionary War and the drafting of the Articles of Confederation, a fierce debate erupted over the structure of the new nation. This debate pitted two powerful factions against each other: the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists. Their disagreement wasn't merely about the details of governance; it was a fundamental clash of visions for the future of America, a battle over the very essence of liberty and the balance of power. Understanding these differences is crucial to grasping the foundations of American government and its ongoing evolution.
Core Beliefs and Ideologies: A Fundamental Clash
At the heart of the Federalist-Anti-Federalist divide lay vastly different interpretations of human nature, the ideal form of government, and the role of the central authority.
Federalist Beliefs:
- Strong Central Government: Federalists championed a strong, centralized federal government capable of effectively governing the newly formed nation. They believed a powerful national government was essential to maintain order, promote economic stability, and defend the country against external threats. This stemmed from their belief in a more structured and regulated society.
- Checks and Balances: A key element of the Federalist vision was the system of checks and balances, meticulously designed to prevent any single branch of government from becoming too powerful. This intricate system, enshrined in the Constitution, aimed to distribute power and limit the potential for tyranny.
- Representation and Republicanism: While advocating for a strong central government, Federalists also believed in representative government. They argued that elected representatives, chosen by the people, would best serve the interests of the nation as a whole. Their republican ideals emphasized civic virtue and the importance of public service.
- Emphasis on National Unity: Federalists placed a strong emphasis on national unity and the need for a cohesive nation. They saw a powerful central government as crucial for binding together the diverse states and preventing the fracturing of the newly independent nation. They feared a weak central government would lead to chaos and instability.
- Loose Interpretation of the Constitution: Federalists generally favored a loose interpretation of the Constitution, arguing that the government had implied powers beyond those explicitly stated in the document. This approach allowed for greater flexibility and adaptation to changing circumstances.
Anti-Federalist Beliefs:
- Limited Central Government: Anti-Federalists, conversely, feared a strong central government. They believed that concentrated power inevitably leads to tyranny and the suppression of individual liberty. Their vision favored a more decentralized system, with greater power vested in the individual states.
- Protection of Individual Rights: The primary concern of the Anti-Federalists was the protection of individual liberties. They worried that a powerful federal government could easily trample upon these rights, leaving citizens vulnerable to oppression. This fear was deeply rooted in their experience under British rule.
- Emphasis on States' Rights: Anti-Federalists strongly championed states' rights, advocating for a system where states retained significant autonomy and control over their own affairs. They believed this decentralization would better reflect the diverse interests and needs of different regions.
- Fear of Elite Rule: Many Anti-Federalists feared that a powerful central government would inevitably fall under the control of a wealthy elite, leaving the common man with little voice or influence. This fear fueled their resistance to ratification of the Constitution.
- Strict Interpretation of the Constitution: Anti-Federalists favored a strict interpretation of the Constitution, arguing that the government's powers should be limited to those explicitly stated in the document. This approach aimed to constrain the power of the federal government and prevent overreach.
Key Figures: The Faces of the Debate
The Federalist-Anti-Federalist debate was shaped by numerous influential figures, each contributing significantly to the discourse.
Leading Federalists:
- Alexander Hamilton: A key architect of the Federalist Papers, Hamilton was a forceful advocate for a strong central government and a national bank. His vision of a robust federal system was instrumental in shaping the early years of the United States.
- James Madison: Often considered the "Father of the Constitution," Madison played a crucial role in drafting the Constitution and co-authoring the Federalist Papers. He eloquently argued for the necessity of a balanced government with checks and balances.
- John Jay: A prominent diplomat and co-author of the Federalist Papers, Jay helped to establish the legitimacy of the new government and solidify support for ratification.
Leading Anti-Federalists:
- Patrick Henry: A fiery orator and prominent figure in the American Revolution, Henry vehemently opposed the Constitution, fearing it would lead to tyranny and the erosion of states' rights. His famous quote, "Give me liberty, or give me death," epitomized his unwavering commitment to individual freedom.
- George Mason: A key figure in the drafting of the Virginia Declaration of Rights, Mason played a crucial role in shaping the Anti-Federalist opposition to the Constitution. He refused to sign the Constitution, believing it lacked sufficient protection for individual liberties.
- Samuel Adams: A radical leader of the American Revolution, Adams, initially a skeptic, eventually reluctantly accepted the Constitution after the Bill of Rights was added.
The Federalist Papers: A Powerful Argument for Ratification
The Federalist Papers, a collection of 85 essays written by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay under the pseudonym "Publius," played a pivotal role in swaying public opinion towards the ratification of the Constitution. These essays presented a compelling case for the benefits of a strong central government and addressed many of the concerns raised by the Anti-Federalists. Their sophisticated arguments and persuasive language helped to secure the Constitution's adoption.
The papers are remarkable for their in-depth analysis of the proposed government, its strengths, and its safeguards against tyranny. They brilliantly articulated the principles of separation of powers, checks and balances, and federalism, providing a blueprint for a government that would be both effective and protective of individual liberties.
The Bill of Rights: A Compromise and a Legacy
The Anti-Federalists' insistence on the protection of individual liberties proved instrumental in the addition of the Bill of Rights to the Constitution. The Bill of Rights, comprising the first ten amendments, guarantees fundamental rights such as freedom of speech, religion, and the press, as well as the right to bear arms, protection against unreasonable searches and seizures, and the right to due process and a fair trial. This compromise, a crucial concession to the Anti-Federalists, helped secure the ratification of the Constitution and cemented the protection of individual rights as a cornerstone of American democracy.
Lasting Impacts: A Continuing Dialogue
The Federalist-Anti-Federalist debate left an enduring legacy on American political thought and governance. The tension between a strong central government and the protection of individual liberties continues to shape American political discourse.
Ongoing Relevance:
- States' Rights vs. Federal Power: The debate over the balance of power between the federal government and individual states remains a central theme in American politics. Issues such as healthcare, education, and environmental regulation regularly spark clashes between those who advocate for stronger federal action and those who champion greater state autonomy.
- Individual Liberties vs. National Security: The tension between individual liberties and national security is another enduring legacy of this historical debate. Issues such as surveillance, counter-terrorism measures, and the balance between individual rights and collective safety continue to engage in ongoing conversations.
- Interpretations of the Constitution: The debate over the proper interpretation of the Constitution continues to shape legal and political discussions. The ongoing tension between loose and strict constructionism reflects the fundamental differences between the Federalists and Anti-Federalists.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Debate and Compromise
The Federalist-Anti-Federalist debate was a defining moment in American history. It shaped the structure of the American government, influencing the balance between national unity and states' rights, and ultimately establishing a system that seeks to balance the power of the state with the protection of individual liberties. While the specific arguments may have shifted, the fundamental questions raised by this historic debate continue to shape the political landscape and ongoing dialogue of the United States. Understanding the differences between these two factions provides critical insight into the complexities and enduring challenges of American democracy. The legacy of this great divide continues to resonate today, reminding us of the ongoing necessity of balancing competing values in the pursuit of a just and equitable society.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 5
Mar 26, 2025
-
Derivative Of Square Root Of Xy
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 10 5 As A Decimal
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are The Factors For 43
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Convert Polar Equations To Rectangular Form
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Differences Between The Federalist And Anti Federalist . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
