What Are The Factors For 43
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
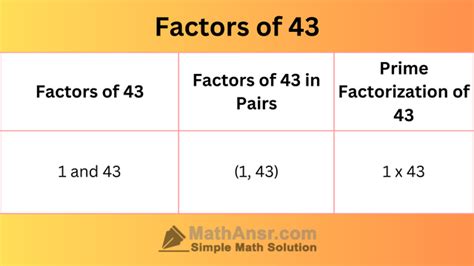
Table of Contents
Decoding the Factors of 43: A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 43?", opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the answer itself is straightforward, understanding why the answer is what it is provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between numbers.
This article will delve into the factors of 43, exploring the concepts of prime numbers, divisibility rules, and the significance of prime factorization. We'll also touch upon related mathematical concepts and demonstrate practical applications of understanding factors.
What are Factors?
Before we tackle the factors of 43, let's define what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any whole number that divides the given number evenly, leaving no remainder. In other words, if you divide the number by its factor, the result is a whole number.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Identifying the Factors of 43
Now, let's focus on 43. To find the factors, we need to systematically check which whole numbers divide 43 without leaving a remainder.
- 1: 43 divided by 1 is 43 (a whole number).
- 43: 43 divided by 43 is 1 (a whole number).
That's it! The only whole numbers that divide 43 evenly are 1 and 43 itself. Therefore, the factors of 43 are 1 and 43.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
The fact that 43 only has two factors—1 and itself—makes it a prime number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and the number itself. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers, as they cannot be broken down into smaller whole number factors.
Prime numbers hold a special place in mathematics. They are crucial in cryptography, ensuring the security of online transactions and data. Their distribution and properties are subjects of ongoing mathematical research.
Divisibility Rules and 43
Understanding divisibility rules can help us quickly determine whether a number is divisible by certain factors. While there isn't a specific divisibility rule for 43 (as it's a prime number), knowing the divisibility rules for smaller numbers can aid in determining if a number is divisible by their product. For instance, if a number is divisible by both 3 and 14, then it's also divisible by 42 (3 x 14).
However, since 43 is a prime number, this approach simplifies significantly because there aren't any smaller whole numbers that divide it except 1.
Prime Factorization and 43
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 (2² x 3).
Since 43 is a prime number, its prime factorization is simply 43. It's already expressed as a product of its prime factors (itself).
The Importance of Understanding Factors
Understanding factors has wide-ranging applications in various fields, including:
- Algebra: Factoring expressions is a fundamental skill in algebra, allowing simplification and solving equations.
- Number Theory: Factors form the basis of many number theory concepts, such as prime factorization, greatest common divisor (GCD), and least common multiple (LCM).
- Computer Science: Factors are crucial in algorithms for cryptography, data compression, and optimization.
- Real-World Applications: Factors are used in everyday scenarios, such as dividing items equally among people or calculating ratios and proportions.
Exploring Further: Related Number Theory Concepts
Several related mathematical concepts build upon the understanding of factors:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them evenly. For example, the GCD of 12 and 18 is 6.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. For example, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
- Euclidean Algorithm: This efficient algorithm is used to find the GCD of two integers.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: This algorithm is used to find all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
Practical Applications: Working with Factors
Let's look at some practical examples of how understanding factors can be helpful:
Scenario 1: Equally Distributing Items
You have 43 cookies, and you want to divide them equally among your friends. Since 43 is a prime number, you can only divide them equally among 1 friend (giving them all 43 cookies) or among 43 friends (giving each 1 cookie).
Scenario 2: Simplifying Fractions
To simplify the fraction 43/86, you need to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 43 and 86. Since 43 is a prime number and 86 = 2 x 43, the GCD is 43. Therefore, the simplified fraction is 1/2 (43/86 ÷ 43/43 = 1/2).
Scenario 3: Solving Equations
In algebra, factoring is often used to solve equations. For example, the equation x² - 43x = 0 can be factored as x(x - 43) = 0, leading to solutions x = 0 and x = 43.
Conclusion: The Undeniable Importance of 43 and its Factors
While at first glance, the factors of 43 seem simple (1 and 43), this seemingly straightforward answer unlocks a world of mathematical concepts. Understanding prime numbers, divisibility rules, prime factorization, and related concepts like GCD and LCM allows us to appreciate the fundamental nature of numbers and their diverse applications across various fields. The number 43, as a prime number, serves as a perfect example to illustrate these foundational principles in number theory and their practical significance in problem-solving and advanced mathematical applications. Its simplicity belies its crucial role in the broader landscape of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 28 And 42
Mar 26, 2025
-
Does Nitrogen Follow The Octet Rule
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is 37 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
21 Out Of 30 Is What Percent
Mar 26, 2025
-
Cos 4x Sin 4x Cos 2x
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 43 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
