Derivative Of Square Root X 2
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
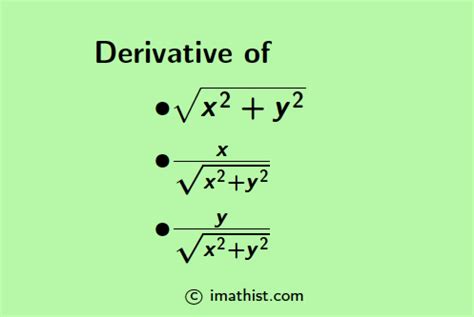
Table of Contents
Understanding the Derivative of √(x²): A Comprehensive Guide
The derivative of √(x²) is a fundamental concept in calculus, crucial for understanding rates of change and optimization problems. While seemingly simple, a complete understanding requires careful consideration of the absolute value function and its implications. This article will provide a comprehensive exploration of this derivative, addressing different approaches and nuances. We'll delve into the process, explore the significance of the absolute value, and examine practical applications.
Defining the Function and its Domain
Before diving into the derivative, let's clearly define the function: f(x) = √(x²). This represents the principal square root of x², which is always non-negative. Crucially, this is not simply x.
The domain of f(x) = √(x²) is all real numbers, (-∞, ∞). This is because the square of any real number is non-negative, and the square root of a non-negative number is always defined (in the real number system).
Method 1: Using the Chain Rule
One way to find the derivative is by employing the chain rule. Remember that the chain rule states that the derivative of a composite function is the derivative of the outer function (with the inside function left alone) times the derivative of the inner function.
Let's rewrite the function as:
f(x) = (x²)^(1/2)
Now, applying the chain rule:
-
Outer function: u^(1/2) The derivative is (1/2)u^(-1/2)
-
Inner function: x² The derivative is 2x
Therefore, using the chain rule:
f'(x) = (1/2)(x²)^(-1/2) * 2x = x / √(x²)
The Crucial Role of the Absolute Value
Notice that we have x / √(x²). While this might seem like it simplifies to 1, it's crucial to remember that √(x²) = |x|, the absolute value of x. This is because the square root function always returns a non-negative value.
Therefore, the derivative is actually:
f'(x) = x / |x|
This function is defined for all x ≠ 0. For positive x, x/|x| = 1. For negative x, x/|x| = -1.
Consequently, the derivative of √(x²) is a piecewise function:
f'(x) = { 1, if x > 0 { -1, if x < 0 { Undefined, if x = 0
Method 2: Considering the Piecewise Nature of the Function
We can also approach the problem by considering the piecewise nature of √(x²) directly.
For x ≥ 0, √(x²) = x. The derivative of x is simply 1.
For x < 0, √(x²) = -x. The derivative of -x is -1.
This again leads us to the same piecewise derivative:
f'(x) = { 1, if x > 0 { -1, if x < 0 { Undefined, if x = 0
Graphical Interpretation
The graph of f(x) = √(x²) is a V-shaped graph with its vertex at the origin (0,0). The slope of the graph is 1 for positive x values and -1 for negative x values. At x = 0, the graph has a sharp corner, which explains why the derivative is undefined at this point. The derivative represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function, and the abrupt change in slope at the origin results in the discontinuity of the derivative.
Applications and Implications
Understanding the derivative of √(x²) has significant applications in various areas, including:
1. Optimization Problems
In optimization problems, finding the critical points (where the derivative is zero or undefined) is essential for identifying potential maxima or minima. The derivative of √(x²) highlights the importance of considering the absolute value when dealing with square roots.
2. Physics and Engineering
Many physical phenomena involve functions with similar characteristics to √(x²). Analyzing the rate of change of these functions often requires understanding the derivative and its piecewise nature. For example, consider situations where displacement is related to time in a non-linear manner.
3. Advanced Calculus
The concept of the derivative of √(x²) lays a foundation for understanding more complex functions and their derivatives. It demonstrates the importance of carefully considering the domain and range of functions and how they impact their derivatives. The non-differentiability at x = 0 underscores the limitations of basic differentiation rules and highlights the need for a more nuanced approach.
4. Numerical Analysis
When dealing with numerical approximations of derivatives, the piecewise nature of the derivative of √(x²) necessitates careful consideration of the point at which the derivative is being approximated. The discontinuity at x=0 requires special handling in numerical methods.
Comparison with the Derivative of x
It's essential to contrast the derivative of √(x²) with the derivative of simply x. The derivative of x is a constant function, f'(x) = 1, defined for all real numbers. This contrasts sharply with the derivative of √(x²), which is piecewise and undefined at x = 0. This comparison highlights the significant difference between the two functions, particularly around x = 0.
Addressing Common Mistakes
A common mistake is assuming that √(x²) simplifies to x, leading to an incorrect derivative of 1. This ignores the crucial role of the absolute value and the piecewise nature of the function.
Another mistake is neglecting the discontinuity at x = 0. The derivative is not defined at this point, a fact often overlooked in simpler analyses. Understanding this discontinuity is crucial for accurate analysis and avoids erroneous conclusions in applications.
Conclusion
The derivative of √(x²), while seemingly simple at first glance, unveils a rich understanding of functions, derivatives, and absolute values. The piecewise nature of the derivative, f'(x) = x/|x|, emphasizes the importance of careful mathematical reasoning and highlights the limitations of straightforward applications of differentiation rules. Understanding this derivative is not just an exercise in calculus; it provides insights into the complexities of functions and their applications in diverse fields, emphasizing the significance of a thorough grasp of mathematical concepts for accurate and meaningful analysis. The absolute value function cannot be ignored; its inclusion ensures the accuracy of the derivative and prevents misconceptions that can lead to inaccurate conclusions in problem-solving and application scenarios. Mastering this concept builds a strong foundation for more advanced studies in calculus and related fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Square Root Of 87
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Percent Of 36 Is 18
Mar 28, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 18
Mar 28, 2025
-
Do You Have To Add Water To Acid
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Fraction Of 70
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Derivative Of Square Root X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
