Creatine Phosphate Functions Within The Muscle Cells By
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
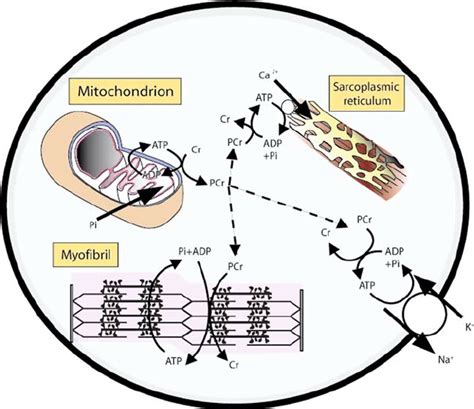
Table of Contents
Creatine Phosphate: The Muscle Cell's Energy Powerhouse
Creatine phosphate (CrP), also known as phosphocreatine, is a crucial high-energy phosphate compound primarily found in skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and the brain. Its primary function within these cells is to act as a rapid energy buffer, providing a readily available source of phosphate to regenerate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the body's main energy currency. Understanding its role is vital for comprehending muscle function, athletic performance, and even neurological health. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of creatine phosphate's functions within muscle cells.
The ATP-Creatine Phosphate System: A Quick Energy Burst
The human body requires a constant supply of ATP to power various cellular processes, including muscle contraction. While cellular respiration (both aerobic and anaerobic) generates ATP, these processes are not instantaneous. This is where the creatine phosphate system steps in, providing a rapid, readily available source of energy for short, high-intensity activities.
How Creatine Phosphate Replenishes ATP
The key to CrP's function lies in its high-energy phosphate bond. When ATP is hydrolyzed (broken down) to ADP (adenosine diphosphate) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) to release energy for muscle contraction, CrP steps in. The enzyme creatine kinase (CK) catalyzes the transfer of the phosphate group from CrP to ADP, quickly regenerating ATP. This reaction is remarkably fast, allowing for immediate replenishment of ATP stores.
The reaction can be summarized as:
Creatine phosphate + ADP <=> Creatine + ATP
This rapid regeneration of ATP is crucial for activities requiring short bursts of intense energy, such as sprinting, weightlifting, and other high-intensity exercises. Without the CrP system, muscle contraction would be significantly impaired during these high-demand situations.
The Role of Creatine Kinase (CK)
Creatine kinase (CK) is the enzyme responsible for catalyzing the reversible reaction between CrP and ATP. It plays a pivotal role in regulating the energy balance within the muscle cell. CK exists in various isoforms, with MM-CK being the predominant form found in skeletal muscle. This isoform's location within the muscle fiber is also strategic, often found in close proximity to both the myofibrils (the contractile units of muscle) and the mitochondria (the powerhouses of the cell). This strategic placement ensures efficient and rapid ATP regeneration wherever it is needed most.
CK Isoenzymes and Their Significance
The presence of different CK isoenzymes in various tissues provides a valuable diagnostic tool. For example, elevated levels of CK in the blood can indicate muscle damage, such as a heart attack (elevated CK-MB) or muscle injury (elevated CK-MM). This highlights the clinical importance of understanding CK's role in energy metabolism and its implications for muscle health.
Beyond Muscle Contraction: Other Functions of Creatine Phosphate
While its primary function is linked to energy production for muscle contraction, CrP's role extends beyond this crucial aspect. Emerging research suggests other important functions, including:
1. Brain Function and Neurological Health:
CrP is found in the brain, where it likely plays a role in maintaining energy homeostasis and supporting neuronal function. Research suggests potential links between CrP levels and cognitive function, particularly in situations of stress or injury. However, more research is needed to fully elucidate its roles in brain function and neurological health.
2. Cellular Signaling and Protection:
Some studies propose that CrP may act as a signaling molecule, influencing various cellular processes beyond energy metabolism. Furthermore, its high-energy phosphate bond may contribute to cellular protection against oxidative stress, a contributor to various diseases.
3. Cardiac Muscle Function:
In the heart, CrP contributes significantly to maintaining the rapid energy demands of cardiac muscle contraction. Its role in supporting efficient heart function is equally critical, ensuring the continuous pumping of blood throughout the body. Disruptions in CrP levels can have significant implications for cardiac health.
Factors Affecting Creatine Phosphate Levels
Several factors can influence the levels of CrP within muscle cells:
-
Training Status: Highly trained athletes generally have higher CrP stores in their muscles compared to sedentary individuals. This reflects the body's adaptation to increased energy demands of regular exercise.
-
Diet: Dietary intake of creatine, either through meat consumption or supplementation, can significantly increase muscle CrP levels. Supplementation is a common practice among athletes to enhance performance and muscle growth.
-
Genetics: Genetic factors also influence CrP levels, with some individuals naturally possessing higher stores than others.
-
Age: CrP levels tend to decline with age, potentially contributing to decreased muscle function and strength in older adults.
-
Health Conditions: Certain health conditions can also affect CrP levels, including muscle diseases and metabolic disorders.
Creatine Supplementation: Enhancing Performance and Muscle Growth
Creatine supplementation is a widely used ergogenic aid (performance-enhancing substance) among athletes and fitness enthusiasts. By increasing muscle CrP stores, supplementation can:
-
Enhance short-term power output: By providing a readily available phosphate source, creatine supplementation improves the ability to perform short, high-intensity bursts of activity.
-
Increase muscle mass and strength: While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, creatine supplementation is associated with increased muscle protein synthesis and muscle growth.
-
Improve muscle recovery: Supplementation may aid in muscle recovery after intense exercise by helping to replenish ATP stores and reducing muscle damage.
It is crucial to note that creatine supplementation is generally considered safe when used appropriately. However, individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult with their healthcare provider before using creatine supplements.
Conclusion: Creatine Phosphate – A Crucial Component of Cellular Energy
Creatine phosphate plays a vital role in maintaining energy homeostasis within muscle cells, particularly during short bursts of high-intensity activity. Its function as a rapid ATP regenerator is crucial for muscle contraction, and its role extends beyond muscle function to other areas like brain function and cardiac health. While the research continues to uncover its complete array of functionalities, the importance of CrP in maintaining cellular energy is undeniable. Understanding its function is essential for comprehending both athletic performance and overall health. Further research is continuously expanding our understanding of this critical compound, promising further insights into its implications for human health and performance. The interplay between CrP, ATP, and CK exemplifies the intricate and elegant mechanisms that maintain life's essential processes. Its significance underscores the body's remarkable capacity for efficient energy management, making it a fascinating subject of ongoing scientific investigation.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Graph The Inequality Y 2x 1
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Charge Of Iron
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is A Fraction That Is Equivalent To 3 4
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Are The Factors Of 44
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is Another Name For The First Law Of Motion
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Creatine Phosphate Functions Within The Muscle Cells By . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
