Consider The Trinomial 9x2 21x 10
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
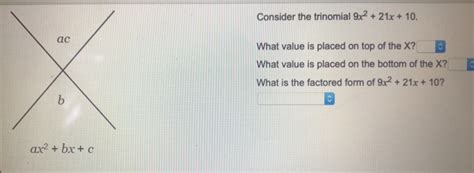
Table of Contents
Consider the Trinomial 9x² + 21x + 10: A Comprehensive Exploration
The trinomial 9x² + 21x + 10 presents a valuable opportunity to explore various algebraic concepts, from factoring and solving quadratic equations to understanding the relationship between roots and coefficients. This comprehensive exploration will delve into multiple methods for tackling this trinomial, analyzing its properties, and highlighting its significance in the broader context of algebra.
Factoring the Trinomial: Unveiling the Roots
The most fundamental approach to understanding a quadratic trinomial lies in factoring it. Factoring breaks down the expression into a product of simpler expressions, revealing the roots (or zeros) of the corresponding quadratic equation. Several methods exist for factoring trinomials, and we'll explore two common techniques for 9x² + 21x + 10.
Method 1: AC Method
The AC method, also known as the grouping method, involves finding two numbers that multiply to the product of the leading coefficient (A) and the constant term (C), and add up to the coefficient of the linear term (B). In our trinomial, A = 9, B = 21, and C = 10.
- Find AC: 9 * 10 = 90
- Find two numbers: We need two numbers that multiply to 90 and add up to 21. These numbers are 6 and 15.
- Rewrite the middle term: We rewrite the middle term (21x) as the sum of 6x and 15x: 9x² + 6x + 15x + 10
- Factor by grouping: Group the terms in pairs and factor out the greatest common factor (GCF) from each pair: 3x(3x + 2) + 5(3x + 2)
- Factor out the common binomial: (3x + 2)(3x + 5)
Therefore, the factored form of 9x² + 21x + 10 is (3x + 2)(3x + 5).
Method 2: Trial and Error
This method involves directly testing different factor pairs of the leading coefficient and the constant term until we find a combination that produces the correct middle term. While less systematic than the AC method, it can be faster with practice.
For 9x² + 21x + 10, we consider the factors of 9 (1, 9; 3, 3) and the factors of 10 (1, 10; 2, 5). By trial and error, we quickly discover that (3x + 2)(3x + 5) expands to give the original trinomial.
Solving the Quadratic Equation: Finding the Roots
Once we have factored the trinomial, we can easily solve the corresponding quadratic equation, 9x² + 21x + 10 = 0. The roots of the equation are the values of x that make the equation true.
Since the factored form is (3x + 2)(3x + 5) = 0, we can use the zero-product property: if the product of two factors is zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero. This leads to two separate equations:
- 3x + 2 = 0 => 3x = -2 => x = -2/3
- 3x + 5 = 0 => 3x = -5 => x = -5/3
Therefore, the roots of the quadratic equation 9x² + 21x + 10 = 0 are x = -2/3 and x = -5/3. These are also the x-intercepts of the parabola represented by the quadratic function y = 9x² + 21x + 10.
Analyzing the Parabola: Vertex, Axis of Symmetry, and Graph
The quadratic equation y = 9x² + 21x + 10 represents a parabola. Understanding its key features provides further insight into the trinomial's behavior.
Finding the Vertex
The x-coordinate of the vertex of a parabola given by the equation y = ax² + bx + c is found using the formula x = -b/(2a). In our case, a = 9 and b = 21, so:
x = -21/(2 * 9) = -21/18 = -7/6
To find the y-coordinate, substitute this x-value back into the equation:
y = 9(-7/6)² + 21(-7/6) + 10 = 9(49/36) - 147/6 + 10 = 49/4 - 147/6 + 10 = (147 - 294 + 120)/12 = -27/12 = -9/4
Therefore, the vertex of the parabola is (-7/6, -9/4). This point represents the minimum value of the quadratic function since the parabola opens upwards (because a = 9 > 0).
Determining the Axis of Symmetry
The axis of symmetry is a vertical line that passes through the vertex. Its equation is simply x = the x-coordinate of the vertex. Therefore, the axis of symmetry is x = -7/6.
Sketching the Parabola
Knowing the vertex, axis of symmetry, and x-intercepts (-2/3 and -5/3), we can accurately sketch the parabola. The parabola opens upwards, intersects the x-axis at -2/3 and -5/3, and has its minimum point at (-7/6, -9/4).
Relationship between Roots and Coefficients: Vieta's Formulas
Vieta's formulas establish a powerful connection between the roots of a quadratic equation and its coefficients. For a quadratic equation of the form ax² + bx + c = 0 with roots α and β, Vieta's formulas state:
- α + β = -b/a
- αβ = c/a
Let's verify these formulas for our trinomial:
- Sum of roots: (-2/3) + (-5/3) = -7/3. -b/a = -21/9 = -7/3. The formula holds true.
- Product of roots: (-2/3) * (-5/3) = 10/9. c/a = 10/9. The formula holds true.
Vieta's formulas demonstrate a fundamental relationship between the coefficients and the roots, highlighting the inherent interconnectedness within quadratic equations.
Applications and Extensions
The trinomial 9x² + 21x + 10, while seemingly simple, serves as a foundational example applicable to numerous areas:
- Physics: Quadratic equations frequently model projectile motion, where the trinomial could represent the height of an object over time.
- Engineering: Many engineering problems involve solving quadratic equations to design structures or analyze systems.
- Economics: Quadratic functions can model cost, revenue, and profit functions, where finding the roots might indicate break-even points.
- Calculus: Understanding quadratic functions is crucial for grasping concepts such as derivatives and integrals.
Furthermore, exploring more complex trinomials and higher-degree polynomials builds upon the fundamental principles learned from analyzing 9x² + 21x + 10. The techniques of factoring, solving, and analyzing the properties of the resulting functions remain central to advanced algebraic concepts.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple trinomial 9x² + 21x + 10 offers a rich landscape for exploring core algebraic concepts. Through factoring, solving the quadratic equation, analyzing the parabola's properties, and understanding Vieta's formulas, we've gained a deep appreciation for its significance. This exploration lays a solid foundation for tackling more complex algebraic problems and understanding the applications of quadratic functions in various fields. The meticulous analysis demonstrates the importance of mastering fundamental algebraic techniques, underscoring the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and their practical relevance. This thorough examination highlights the beauty and utility of even the simplest algebraic expressions, providing a comprehensive understanding that extends far beyond the initial problem.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Muscle Subdivides The Ventral Body Cavity
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Are Three Main Ideas Of The Cell Theory
Mar 28, 2025
-
Hcl Ba Oh 2 Balanced Equation
Mar 28, 2025
-
7x 2y 13 X 2y 11
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is Digesting Food A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Consider The Trinomial 9x2 21x 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
