Common Factors Of 45 And 75
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
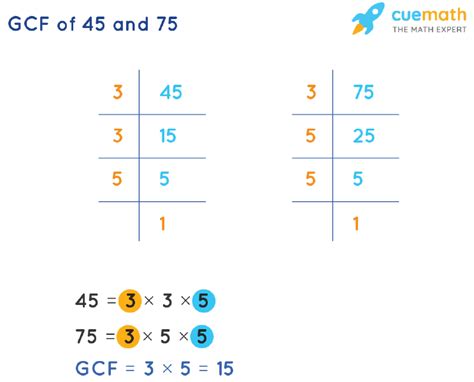
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Secrets of Numbers: Finding the Common Factors of 45 and 75
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple mathematical task, but understanding the underlying principles can unlock a deeper appreciation for number theory and its applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the process of determining the common factors of 45 and 75, exploring various methods and illuminating the concepts behind them. We'll move beyond simply finding the answer to understanding why those factors are common and how this knowledge can be applied in more complex scenarios.
What are Factors?
Before we dive into finding the common factors of 45 and 75, let's clarify what a factor is. A factor of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding the Factors of 45
To find the common factors of 45 and 75, we first need to determine the factors of each number individually. Let's start with 45:
- 1: 45 divided by 1 equals 45.
- 3: 45 divided by 3 equals 15.
- 5: 45 divided by 5 equals 9.
- 9: 45 divided by 9 equals 5.
- 15: 45 divided by 15 equals 3.
- 45: 45 divided by 45 equals 1.
Therefore, the factors of 45 are 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, and 45.
Finding the Factors of 75
Now let's find the factors of 75:
- 1: 75 divided by 1 equals 75.
- 3: 75 divided by 3 equals 25.
- 5: 75 divided by 5 equals 15.
- 15: 75 divided by 15 equals 5.
- 25: 75 divided by 25 equals 3.
- 75: 75 divided by 75 equals 1.
Thus, the factors of 75 are 1, 3, 5, 15, 25, and 75.
Identifying Common Factors: The Intersection Method
Now that we have the factors of both 45 and 75, we can identify the common factors. These are the numbers that appear in both lists. A simple way to visualize this is using an intersection:
Factors of 45: {1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 45} Factors of 75: {1, 3, 5, 15, 25, 75}
Common Factors: {1, 3, 5, 15}
Therefore, the common factors of 45 and 75 are 1, 3, 5, and 15.
Understanding Prime Factorization: A Deeper Dive
Prime factorization provides a more systematic and efficient method for finding common factors, especially when dealing with larger numbers. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.).
Let's find the prime factorization of 45 and 75:
- 45: 45 = 3 x 3 x 5 = 3² x 5
- 75: 75 = 3 x 5 x 5 = 3 x 5²
Now, to find the common factors, we look for the prime factors that both numbers share. Both 45 and 75 share one 3 and one 5. Therefore:
- Common Prime Factors: 3 and 5
We can then generate the common factors by combining these prime factors in all possible ways:
- 3 x 1 = 3
- 5 x 1 = 5
- 3 x 5 = 15
- 1 =1 (always a common factor)
This confirms our previous finding that the common factors are 1, 3, 5, and 15.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The Highest Common Factor
Among the common factors, there's always a greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the highest common factor (HCF). This is simply the largest number that divides both numbers evenly. In the case of 45 and 75, the GCF is 15.
The GCF is crucial in various mathematical applications, including simplifying fractions and solving algebraic equations.
Applications of Common Factors and GCF
The concept of common factors and the GCF extends beyond simple number theory and finds practical applications in various fields:
1. Simplifying Fractions:
When simplifying fractions, we divide both the numerator and denominator by their GCF. For example, if we have the fraction 45/75, we can simplify it by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF, which is 15:
45/75 = (45 ÷ 15) / (75 ÷ 15) = 3/5
2. Geometry and Measurement:
Finding the GCF is essential when dealing with geometric problems involving area and volume calculations. For example, if you need to divide a rectangular area with dimensions 45 units by 75 units into smaller squares of equal size, the side length of the largest possible square would be the GCF (15 units).
3. Data Analysis and Organization:
In data analysis, understanding common factors can help organize data into groups or sets with shared characteristics. This is particularly relevant in fields like statistics and database management.
4. Cryptography:
Prime factorization, a closely related concept, plays a vital role in modern cryptography. The security of many encryption algorithms relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Least Common Multiple (LCM)
While this article focuses on common factors, it's important to mention the closely related concept of the least common multiple (LCM). The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers. Understanding both GCF and LCM provides a complete picture of the relationship between two numbers. You can find the LCM using various methods, including the prime factorization method.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of Number Theory
Finding the common factors of 45 and 75, while seemingly a basic mathematical exercise, reveals fundamental concepts in number theory with far-reaching applications. From simplifying fractions to understanding the underlying principles of cryptography, the ability to identify common factors and the GCF is a valuable skill with relevance across numerous disciplines. By understanding the process, whether through direct factorization or prime factorization, one gains a stronger grasp of number relationships and their practical implications in various fields. The journey from finding simple factors to understanding the significance of the GCF is a step towards mastering fundamental number theory.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Rectangle
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In 15 Miles
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Calculate The Number Of Electrons
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 14 And 21
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 10 Minutes In Hours
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 45 And 75 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
