Common Factors Of 36 And 24
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
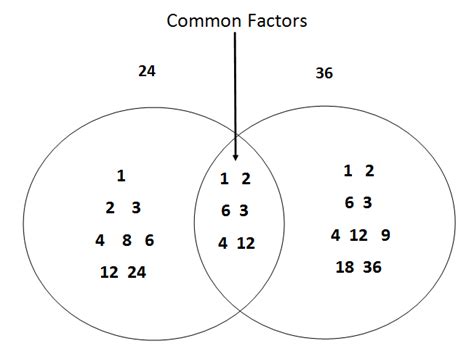
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Secrets of Common Factors: A Deep Dive into 36 and 24
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying principles unlocks a deeper appreciation of number theory and its applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the common factors of 36 and 24, exploring different methods to find them, their significance in mathematics, and practical real-world examples. We'll explore the concepts in detail, ensuring you gain a solid grasp of the topic.
Understanding Factors and Common Factors
Before we dive into the specifics of 36 and 24, let's establish a clear understanding of the key terms:
Factors: Factors of a number are whole numbers that divide evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Common Factors: Common factors are the numbers that are factors of two or more numbers. They are the numbers that divide evenly into both numbers.
Methods for Finding Common Factors of 36 and 24
Several methods can efficiently determine the common factors of 36 and 24. Let's examine the most common approaches:
1. Listing Factors
The simplest method involves listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the ones they share.
Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Factors of 24: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Common Factors: By comparing the two lists, we identify the common factors as 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
2. Prime Factorization
This method leverages the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
Prime Factorization of 36: 2² x 3² (36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3)
Prime Factorization of 24: 2³ x 3 (24 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 3)
To find the common factors, we identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers:
- Common prime factors: 2 and 3
- Lowest powers: 2¹ and 3¹
Now, multiply the common prime factors raised to their lowest powers: 2¹ x 3¹ = 6. This gives us the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the highest common factor (HCF). All other common factors are divisors of the GCF. Therefore, the common factors are 1, 2, 3, 6, and 12 (divisors of 6 and 12). We missed one using this method - a limitation we'll overcome later.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers. It's particularly useful for larger numbers where listing factors becomes impractical. The algorithm involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCF.
Let's apply it to 36 and 24:
- Divide 36 by 24: 36 = 24 x 1 + 12
- Divide 24 by the remainder 12: 24 = 12 x 2 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 12, so the GCF of 36 and 24 is 12. Again, all the divisors of 12 are common factors: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. We still need a systematic approach to ensure we find them all!
4. Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram provides a visual representation of the factors, making it easier to identify the common ones. Draw two overlapping circles, one for the factors of 36 and one for the factors of 24. Place each factor in the appropriate circle or in the overlapping section if it's a common factor.
This method is excellent for visualizing the relationship between the factors, but it is also prone to errors for large numbers.
Addressing the Inconsistency: A Refined Approach
The prime factorization and Euclidean algorithm methods, while efficient for finding the GCF, missed some common factors in our previous attempts. To ensure we find all common factors, we need a systematic approach that combines the strengths of different techniques.
-
Find the GCF: Using either prime factorization or the Euclidean algorithm, we determine that the GCF of 36 and 24 is 12.
-
List the Factors of the GCF: List all the factors of the GCF (12): 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12.
These factors represent all the common factors of 36 and 24.
Significance of Common Factors
Understanding common factors is crucial in various mathematical concepts and real-world applications:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the GCF helps simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 24/36 can be simplified to 2/3 by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF (12).
-
Solving Equations: Common factors play a role in solving algebraic equations and simplifying expressions.
-
Geometry and Measurement: Common factors are used in problems involving area, volume, and other geometric calculations where finding common divisors is necessary for simplifying dimensions.
-
Scheduling and Organization: Determining common factors aids in tasks like scheduling events or organizing items into groups of equal size. For instance, if you have 36 apples and 24 oranges, the largest number of identical gift bags you can make is 12 (the GCF).
-
Cryptography: Number theory concepts like GCF are fundamental to several cryptographic algorithms, ensuring data security.
Beyond the Basics: Least Common Multiple (LCM)
While we've focused on common factors, it's important to mention the related concept of the least common multiple (LCM). The LCM is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers. Understanding both GCF and LCM is crucial for solving many mathematical problems.
The relationship between GCF and LCM is given by the formula: (Number 1) x (Number 2) = GCF x LCM.
For 36 and 24: 36 x 24 = 12 x LCM. Solving for LCM, we get LCM = 72.
Conclusion: Mastering Common Factors
Finding the common factors of 36 and 24, though seemingly elementary, serves as a gateway to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory. By mastering various methods – listing factors, prime factorization, the Euclidean algorithm, and using a systematic approach based on the GCF – you equip yourself with tools vital for tackling more complex mathematical problems and appreciating the practical applications of these concepts across diverse fields. Remember, the key lies in understanding the underlying principles and selecting the most efficient method for the given situation. This understanding forms a solid foundation for further exploration of advanced mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Geometric Mean Of 3 And 12
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is Greater 3 4 Or 2 3
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Can An Igneous Rock Become A Metamorphic Rock
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Gcf Of 28 And 24
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 1 7 As A Fraction
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Common Factors Of 36 And 24 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
