Balance The Equation. C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
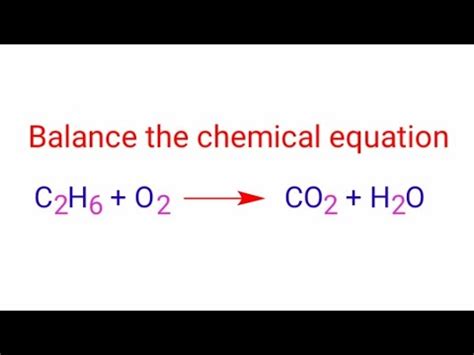
Table of Contents
Balancing the Equation: C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
Balancing chemical equations is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for understanding stoichiometry and performing accurate chemical calculations. This article will delve deep into balancing the combustion equation of ethane (C₂H₆) with oxygen (O₂), producing carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O). We'll explore various methods, explain the underlying principles, and provide practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding the Combustion of Ethane
Before we jump into balancing the equation, let's briefly understand the chemical process involved. The combustion of ethane is a reaction where ethane reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing a significant amount of energy in the form of heat. This is an exothermic reaction, commonly used in various applications, from heating homes to powering industrial processes. The unbalanced equation representing this reaction is:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O
Methods for Balancing Chemical Equations
Several methods exist for balancing chemical equations, each with its advantages and disadvantages. We'll focus on two common and effective approaches:
1. The Inspection Method (Trial and Error)
This method involves systematically adjusting the coefficients (the numbers in front of the chemical formulas) until the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. It's a trial-and-error process, but with practice, it becomes quite efficient. Let's apply this to our ethane combustion equation:
-
Balance Carbon (C): We have 2 carbon atoms on the left (in C₂H₆) and 1 on the right (in CO₂). To balance carbon, we place a coefficient of 2 in front of CO₂:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + H₂O
-
Balance Hydrogen (H): We have 6 hydrogen atoms on the left (in C₂H₆) and 2 on the right (in H₂O). To balance hydrogen, we place a coefficient of 3 in front of H₂O:
C₂H₆ + O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
-
Balance Oxygen (O): Now, let's count the oxygen atoms. On the right side, we have 4 oxygen atoms from 2CO₂ (2 x 2 = 4) and 3 oxygen atoms from 3H₂O (3 x 1 = 3), totaling 7 oxygen atoms. On the left side, we have only 2 oxygen atoms in O₂. To balance oxygen, we need a coefficient of 7/2 in front of O₂:
C₂H₆ + (7/2)O₂ → 2CO₂ + 3H₂O
While this balances the equation, using fractions in chemical equations is generally avoided. To eliminate the fraction, we multiply the entire equation by 2:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
This is the balanced equation for the complete combustion of ethane. Now, the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation:
- Carbon (C): 4 atoms on each side
- Hydrogen (H): 12 atoms on each side
- Oxygen (O): 14 atoms on each side
2. The Algebraic Method
This method is more systematic and avoids the guesswork involved in the inspection method. It involves assigning variables to the coefficients and setting up a system of algebraic equations based on the conservation of atoms.
Let's use this method for the ethane combustion equation:
aC₂H₆ + bO₂ → cCO₂ + dH₂O
Now, we can set up equations for each element:
- Carbon (C): 2a = c
- Hydrogen (H): 6a = 2d
- Oxygen (O): 2b = 2c + d
We can solve this system of equations. Let's choose a value for one of the variables, say a = 1 (this is a common starting point). Then:
- c = 2a = 2
- d = 3a = 3
- 2b = 2(2) + 3 = 7 => b = 7/2
Again, we get a fraction. To eliminate it, we multiply all coefficients by 2:
a = 2, b = 7, c = 4, d = 6
This leads us to the same balanced equation as before:
2C₂H₆ + 7O₂ → 4CO₂ + 6H₂O
Importance of Balanced Chemical Equations
Balanced chemical equations are essential for several reasons:
-
Stoichiometric Calculations: They provide the molar ratios of reactants and products, allowing us to calculate the amounts of reactants needed or products formed in a chemical reaction. This is crucial in industrial chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and many other fields.
-
Understanding Reaction Mechanisms: Balanced equations help us visualize the overall changes occurring in a reaction. They don't show the steps involved, but they show the starting materials and end results.
-
Predicting Reaction Outcomes: By knowing the balanced equation, we can predict the products and their amounts, given the amount of reactants.
-
Environmental Considerations: In combustion reactions, balancing the equation helps determine the amount of pollutants (such as carbon monoxide) that may be formed if the combustion is incomplete.
Incomplete Combustion of Ethane
It's important to note that the equation we've balanced represents complete combustion of ethane. In reality, incomplete combustion can occur, particularly when there is insufficient oxygen. This produces carbon monoxide (CO) and/or soot (carbon particles) along with carbon dioxide and water. The equation for incomplete combustion would be different and more complex to balance, often requiring multiple equations to represent different possible incomplete combustion products. For example, one possible incomplete combustion equation could be:
2C₂H₆ + 5O₂ → 4CO + 6H₂O
Practical Applications of Ethane Combustion
Ethane combustion plays a vital role in various applications:
-
Power Generation: Ethane is a significant fuel source in power plants, providing electricity to homes and industries.
-
Heating: Ethane is used in domestic and industrial heating systems.
-
Chemical Industry: Ethane is a feedstock for the production of various chemicals, including ethylene, a crucial building block for plastics.
-
Refrigeration: Although less common now, ethane was historically used in some refrigeration applications.
Conclusion
Balancing the chemical equation for the combustion of ethane, C₂H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O, demonstrates the fundamental principles of stoichiometry. Both the inspection and algebraic methods are effective approaches to achieve a balanced equation, which is crucial for quantitative analysis and understanding the reaction's implications. Remember that complete combustion produces CO₂ and H₂O, while incomplete combustion can result in the formation of CO or soot, depending on the oxygen supply. The balanced equation provides the foundation for understanding and predicting the outcomes of this vital chemical reaction. This comprehensive understanding is critical across numerous scientific and industrial applications. Further exploration into different types of combustion reactions and their specific balancing requirements will deepen your comprehension of chemical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Two Elements Have Similar Characteristics
Mar 25, 2025
-
5r 2 44r 120 30 11r
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is 87 A Prime Or Composite
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Band Of Stability
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 4 To The 2 Power
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Balance The Equation. C2h6 O2 Co2 H2o . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
