Area Of A Cross Section Of A Sphere
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
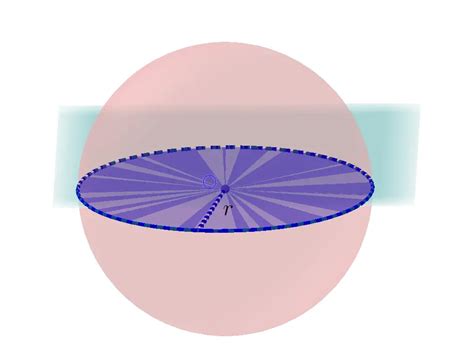
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of a Sphere's Cross-Sectional Area: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the area of a cross-section of a sphere is crucial in various fields, from engineering and architecture to physics and mathematics. Whether you're calculating the volume of a partially filled spherical tank, designing a lens, or simply exploring the geometry of three-dimensional shapes, mastering this concept is key. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of calculating the cross-sectional area of a sphere, exploring different approaches and providing practical examples.
What is a Cross-Section?
Before we delve into the calculations, let's clarify what a cross-section is. A cross-section is the shape you get when you slice through a three-dimensional object. Imagine slicing a loaf of bread—each slice represents a cross-section. In the case of a sphere, the cross-section is always a circle. However, the size of this circle depends on where the slice is taken.
The Radius and its Significance
The key to determining the cross-sectional area of a sphere lies in understanding the relationship between the sphere's radius (r) and the radius of the circular cross-section (r<sub>c</sub>). The sphere's radius is the distance from its center to any point on its surface. The cross-section's radius, on the other hand, depends on the distance of the cutting plane from the sphere's center.
Understanding the Relationship
Imagine a sphere with radius r. Now, consider a plane that cuts through the sphere at a distance d from the center. The radius of the circular cross-section (r<sub>c</sub>) can be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
r<sub>c</sub>² + d² = r²
This equation highlights the crucial relationship: the radius of the cross-section is dependent on both the sphere's radius and the distance of the plane from the sphere's center. The farther the cutting plane is from the center, the smaller the cross-sectional radius. Conversely, the closer the plane is to the center, the larger the radius of the cross-section, reaching its maximum (equal to the sphere's radius) when the plane passes through the center.
Calculating the Cross-Sectional Area
Once we have the radius of the cross-section (r<sub>c</sub>), calculating the area is straightforward. The area of a circle is given by the formula:
A = πr<sub>c</sub>²
Therefore, combining the two equations, we can express the area of a sphere's cross-section as a function of the sphere's radius (r) and the distance (d) of the cutting plane from the center:
A = π(r² - d²)
This formula allows us to calculate the area of any cross-section of a sphere, given its radius and the distance of the plane from the center.
Illustrative Examples
Let's solidify our understanding with a few examples:
Example 1: Cross-section through the center
Imagine a sphere with a radius of 5 cm. If the cross-section is taken directly through the center (d = 0), then:
- r<sub>c</sub> = r = 5 cm
- A = π(5 cm)² = 25π cm² ≈ 78.54 cm²
This represents the largest possible cross-sectional area for this sphere.
Example 2: Cross-section away from the center
Consider the same sphere (radius = 5 cm), but this time the cutting plane is 3 cm away from the center (d = 3 cm). Then:
- r<sub>c</sub>² = r² - d² = (5 cm)² - (3 cm)² = 16 cm²
- r<sub>c</sub> = 4 cm
- A = π(4 cm)² = 16π cm² ≈ 50.27 cm²
Notice that the cross-sectional area is smaller than in the previous example, as expected.
Example 3: A more complex scenario
Let's say we have a sphere with a radius of 10 meters. A plane cuts the sphere such that the resulting circular cross-section has a diameter of 12 meters. This seems impossible, right? Let's explore why. The diameter of 12 meters implies that the cross-sectional radius is 6 meters. The relationship r<sub>c</sub>² + d² = r² becomes:
6² + d² = 10²
Solving for d, we get d² = 64, meaning d = 8 meters. Therefore, a plane located 8 meters from the center of the sphere will produce a circular cross-section of radius 6 meters. The area is then calculated as:
A = π * 6² = 36π square meters.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The ability to calculate the cross-sectional area of a sphere has wide-ranging applications:
- Engineering: Designing spherical tanks, pressure vessels, and other components requires accurate calculations of cross-sectional areas to determine volume, strength, and stability.
- Architecture: Spherical domes and other architectural features necessitate precise calculations for structural integrity and material estimations.
- Physics: Understanding the cross-sectional area is crucial in various physics problems involving spheres, such as calculating the interaction of light with lenses or determining the rate of fluid flow through spherical pipes.
- Medicine: In medical imaging and radiation therapy, understanding cross-sectional areas helps in precise targeting and dosage calculations.
Beyond the Basics: Spherical Segments and Caps
The calculations presented so far pertain to a plane cutting through the sphere, creating a single circular cross-section. However, more complex scenarios involve spherical segments and caps.
A spherical segment is the portion of a sphere that lies between two parallel planes. A spherical cap is a special case of a spherical segment where one of the planes is tangent to the sphere. Calculating the areas of these more intricate shapes involves slightly more complex formulas that often incorporate calculus techniques. However, the fundamental principles of understanding the relationship between the sphere's radius and the distance of the cutting planes remain crucial.
Conclusion
Mastering the calculation of a sphere's cross-sectional area is a valuable skill with broad applicability. From simple calculations involving a single plane to the more complex scenarios involving segments and caps, understanding the underlying principles ensures accurate estimations in various fields. By understanding the relationship between the sphere's radius, the distance of the cutting plane, and the resulting cross-sectional radius, you're equipped to tackle numerous problems and successfully apply this geometric knowledge to real-world situations. Remember to always double-check your units and pay close attention to the details of the problem to avoid errors. The power lies in your understanding of the fundamental principles and the ability to apply them correctly.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does Ni Have
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 375 As A Percentage
Mar 23, 2025
-
5 To The Negative 1 Power
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Are In Neon
Mar 23, 2025
-
You Need To Prepare An Acetate Buffer Of Ph
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of A Cross Section Of A Sphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
