Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 4
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
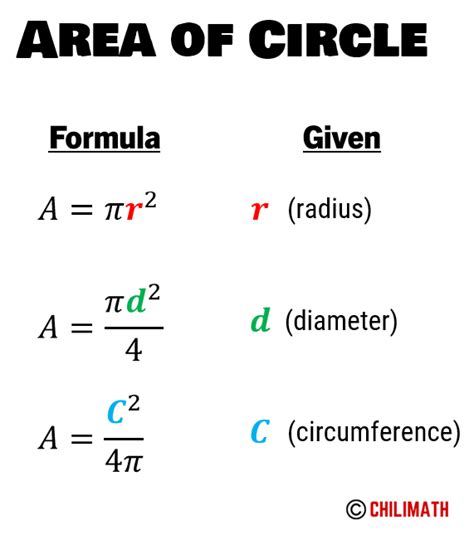
Table of Contents
- Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 4
- Table of Contents
- Calculating the Area of a Circle with a Radius of 4: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Formula: πr²
- Calculating the Area: A Step-by-Step Approach
- The Significance of π (Pi)
- Beyond the Basic Calculation: Exploring Applications
- Engineering and Architecture:
- Science and Technology:
- Everyday Applications:
- Beyond the Radius: Exploring Diameter and Circumference
- Advanced Concepts and Extensions
- Areas of Sectors and Segments:
- Areas of Annuluses:
- Integration and Calculus:
- Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the Area of a Circle
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Calculating the Area of a Circle with a Radius of 4: A Comprehensive Guide
The seemingly simple task of calculating the area of a circle with a radius of 4 units opens up a world of mathematical concepts and real-world applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into the calculation itself, explore the underlying principles, and discuss various applications where understanding this fundamental geometrical concept proves invaluable.
Understanding the Formula: πr²
The area of any circle is determined by a single, crucial measurement: its radius. The radius (denoted by 'r') is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. The formula for calculating the area (A) of a circle is:
A = πr²
Where:
- A represents the area of the circle.
- r represents the radius of the circle.
- π (pi) is a mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159. It represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter.
This formula is fundamental to geometry and is used extensively in various fields. Understanding its derivation and application is key to mastering numerous mathematical and scientific concepts.
Calculating the Area: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's apply the formula to calculate the area of a circle with a radius of 4 units.
Step 1: Identify the radius.
In this case, the radius (r) is given as 4 units. This could be 4 centimeters, 4 meters, 4 inches – the unit of measurement doesn't change the calculation, but it's crucial to remember the units when stating the final answer.
Step 2: Substitute the radius into the formula.
Substitute r = 4 into the area formula:
A = π(4)²
Step 3: Square the radius.
4 squared (4²) is 4 multiplied by itself, resulting in 16. The equation now becomes:
A = π(16)
Step 4: Multiply by π.
Multiply 16 by π. Using the approximation of π ≈ 3.14159, we get:
A ≈ 3.14159 × 16 ≈ 50.26544
Step 5: State the final answer.
Therefore, the area of a circle with a radius of 4 units is approximately 50.27 square units (depending on the level of precision required). Remember to include the appropriate square units (e.g., square centimeters, square meters, square inches).
The Significance of π (Pi)
The constant π is central to understanding circles and their properties. It's an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. The approximation 3.14159 is commonly used, but more precise values are used for high-accuracy calculations. The remarkable properties of π extend far beyond the calculation of a circle's area; it's deeply ingrained in various mathematical fields including trigonometry, calculus, and complex analysis. Its appearance in seemingly unrelated areas of mathematics highlights its fundamental role in describing the nature of circles and related geometrical shapes.
Beyond the Basic Calculation: Exploring Applications
The ability to calculate the area of a circle isn't just an academic exercise; it has numerous real-world applications across diverse fields:
Engineering and Architecture:
- Designing circular structures: Architects and engineers use this formula to determine the amount of material needed for building circular structures such as domes, stadiums, and water tanks. Accurate area calculation is crucial for material estimation and cost control.
- Pipe and conduit sizing: Understanding the cross-sectional area of pipes and conduits is crucial for fluid dynamics calculations, ensuring efficient flow and preventing blockages. This is vital in applications ranging from plumbing to oil pipelines.
- Calculating surface areas: Many mechanical components incorporate circular elements. Accurate area calculation aids in surface treatment processes such as painting, plating, or applying heat treatments.
Science and Technology:
- Calculating the area of a circular lens: In optics, the area of a lens is critical for determining its light-gathering capacity and resolving power. This is especially relevant in telescopes, microscopes, and cameras.
- Analyzing circular motion: In physics, the area of a circle is related to the concepts of angular velocity and angular acceleration, crucial for understanding rotational motion.
- Data analysis and statistics: Circular diagrams, such as pie charts, represent data proportions using circular sectors whose areas directly relate to the data values.
Everyday Applications:
- Gardening and landscaping: Calculating the area of circular flower beds or garden features helps in determining the amount of soil, plants, or mulch required.
- Cooking and baking: Understanding the area of a circular pan is useful for scaling recipes and ensuring even cooking.
- Arts and crafts: Creating circular designs for projects like quilting, pottery, or drawing involves calculating area for material estimation and design planning.
Beyond the Radius: Exploring Diameter and Circumference
While the radius is directly used in the area calculation, the diameter and circumference are closely related. The diameter (d) is twice the radius (d = 2r), and the circumference (C) is the distance around the circle, calculated as C = 2πr or C = πd. These relationships are fundamental in understanding the geometry of circles.
Knowing the diameter, you can easily calculate the radius (r = d/2) and subsequently compute the area. Similarly, if the circumference is known, the radius can be calculated (r = C/2π) followed by the area calculation. The interconnectedness of these measurements highlights the cohesive nature of geometrical principles.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
The formula A = πr² forms the basis for many more complex calculations.
Areas of Sectors and Segments:
A sector is a portion of a circle enclosed by two radii and an arc. A segment is the area enclosed by a chord and an arc. The formulas for calculating their areas are derived from the fundamental circle area formula, requiring additional trigonometric considerations to account for the central angle or the length of the chord.
Areas of Annuluses:
An annulus is the region between two concentric circles (circles with the same center). Its area is calculated by subtracting the area of the smaller circle from the area of the larger circle.
Integration and Calculus:
In calculus, the concept of area is extended to more complex shapes using integration. The formula for the area of a circle can be derived using integration techniques, further solidifying its place within advanced mathematical frameworks.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of the Area of a Circle
The seemingly simple calculation of the area of a circle with a radius of 4, which results in approximately 50.27 square units, represents a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications across numerous fields. From the design of colossal structures to the analysis of microscopic phenomena, understanding this fundamental geometric principle proves essential. This guide has not only provided a step-by-step calculation but has also explored the broader mathematical context, emphasizing the importance of π, and showcasing the wide-ranging applications of this core geometrical concept in diverse areas of science, technology, engineering, and everyday life. The formula A = πr² may appear simple, but its significance extends far beyond its straightforward application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Feet Is 168 Cm
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Medium Do Mechanical Waves Travel Through The Fastest
Mar 21, 2025
-
7 To The Power Of 7
Mar 21, 2025
-
Find The Area Inside The Oval Limacon
Mar 21, 2025
-
Write A Polynomial In Standard Form
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Area Of A Circle With A Radius Of 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
